| Ricinodendron Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Ricinodendron |
| Scientific Name: | Ricinodendron heudelotii |
| Origin | Senegal in West Africa to Sudan, Uganda, and Tanzania, and from Sudan down to the western coast of Sub-Saharan Africa to Angola |
| Colors | Green when young, black when ripe |
| Shapes | Two to three lobed drupe 2.5–3.5 cm long and 4–5 cm wide |
| Health benefits | Edema, Cures Anemia, Blennorrhoea, Cures Diarrhea, Strengthens Premature Babies, Treats Cough, Treatment of Sexual Problems, Destruction of Worms, Treats Babies Fever, Relieves Labor Pain |
| Name | Ricinodendron |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Ricinodendron heudelotii |
| Native | Tropical Africa. The native geographic location of njangsa reaches from Senegal in West Africa to Sudan, Uganda, and Tanzania, and from Sudan down to the western coast of Sub-Saharan Africa to Angola. The tree is also found on Madagascar |
| Common Names | Groundnut tree, Zambezi almond, cork wood, African nut tree, corkwood tree, African oil-nut tree, African wood, Manketti nut |
| Name in Other Languages | Angola: Minguella, Munguella Cameroon: Andjejang , Djansang, Essessang, Ezang, Ezezang, N’jansan Chinese: Bì má tong (蓖麻桐), Nǐ bì má (拟蓖麻) Congo: Sa sanga, Sanga sanga East Africa: Mungomo English: African nut tree, African wood oil nut tree, Cork wood, Essang nuts, , Ojok nuts, Sanga nuts, African oil-nut-tree, Ezang, Njangsa, Okhuen Equatorial Guinea: Ekok French: Bois jasanga, Essang, essessang Gabon: Engessam German: Afrikanisches Mahagoni Ghana: Anwama, Wama Hausa: Wawan kurmi Ivory Coast: Agqui Japanese: Essuessusando (エッスエッスサンド), Essessando Kenya: Muawa Liberia: Karro tu, Koor Nigeria: Eke, Erimado, Okhuen, Okwe Portuguese: Menguela, Munguella Sierra Leone: Gbolei Swahili: Muawa Swedish: Muawa Uganda: Kishongo, Kisogo, Musodo Yoruba: Erinmado, Putu Zaire: Bofeko, Kisongo, Kitililundo |
| Plant Growth Habit | Fast-growing, deciduous, medium-sized tree |
| Growing Climates | Occurs in humid secondary forest, clearings in rainforest, fringing, secondary and deciduous forests, semi-dry wooded-savannah zone, rain forests and on abandoned farmland |
| Soil | Prefers medium textured, freely draining/acidic soils |
| Plant Size | Grow between 20 to 50 m height with straight trunk that has a diameter of approximately 2.7 m |
| Bark | Bark grey, smooth at first, becoming scaly with ageing; slash dark red, densely mottled with scattered pits and orange stone-cell granules |
| Leaf | Young leaves are pale green in color while the mature leaves are dark green in color |
| Flowering season | April and May |
| Flower | Yellowish-white in colour. The flowers measure approximately 5 mm long with some long terminal loose branching cluster of flowers (panicles) that measure between 15 to 40 cm |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Two to three lobed drupe 2.5–3.5 cm long and 4–5 cm wide, and contain two cells where the seeds lie. |
| Fruit Color | Green when young, black when ripe |
| Seed | Rounded in appearance and can be black or red-brown in colour |
| Plant Parts Used | Roots, trunk, stem, bark, seeds, leaves and the latex |
| Propagation | By seeds, stem cutting, layering or by side grafting |
| Health benefits |
|
| Season | September and October |
Plant Description
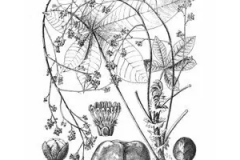
Ricinodendron is a fast-growing, deciduous, medium-sized tree with an open and spreading rounded crown, and a cylindrical and straight short-buttressed bole. The plant normally grows between 20 to 50 m tall with straight trunk which has a diameter of about 2.7 m. The plant is found growing in humid secondary forest, clearings in rainforest, fringing, secondary and deciduous forests, semi-dry wooded-savannah zone, and rain forests and on abandoned farmland. The plant prefers well drained, medium textured acidic soils. Bark is initially grey and smooth, turning to flaking when matured.
Leaves
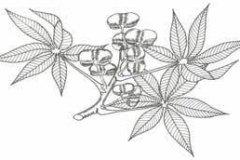
Young leaves are pale green, somewhat shining, and mature leaves are smooth, somewhat shiny, sub-coriaceous, dark green and slightly paler below, or medium green. There are about 10-16 lateral nerves in each pairs. Midrib is dark green towards the base and pale green at the apex below, while the main nerves are pale green below. Branch nerves are elevated on two sides, with reticulation of the veins somewhat different and dark green below. Leaf margins got some smaller glandular teeth. Petiole is about 20 cm long, and sometimes up to 40 cm in length, glandular at the base. Petiole is very dark green along with medium green spots, blackish at the base, and glands are dark grey green colored.
Flowers
Ricinodendron is monoecious (mistakenly called in Shiembo as dioecious) with the tomentose inflorescence within panicles. Male blossoms are gathered in roughly separated terminal panicles about 15-40 cm long of small white flowers (0.7 cm diameter) on short flower stalks. They consist of 5 sepals, 5-lobed corolla tube and about 10-14 stamens. Female flowers are gathered in stouter and shorter panicles. They are white and the same size as male flowers, with a stellate tomentose ovary and 2 styles that are bipartite and slender. The ovary is larger. Flowering normally takes place in between April and May.
Fruits
Fertile flowers are followed by an indehiscent drupe which weight nearly 20 g, compacted at the apex and the base. Fruits are initially yellow green turning to black as they mature, with 2 or 3 lobes, with a fleshy exocarp and a woody endocarp that consists of 2-3 seeds. Seeds are compressed sub-globose about 1.3-1.7 cm in diameter. They are reddish-brown or black colored. Fruit has an aroma of overripe apples.
Health Benefits of Ricinodendron (Njangsa)
Listed below are some of the popular health benefits of using Ricinodendron (Njangsa)
1. Edema
Decocted bark can be used for treating edema. Decoction is applied as lotion or may be used for bathing to reduce inflammation of the ankles and lower legs. Similarly bark can be ground, warmed and used for handling elephantiasis.
2. Cures Anemia
Decocted bark can be used for treating anemia. It is a health condition considered by the shortage of hemoglobin in the blood. To deal with anemia, bark can be boiled with Eremomastax.
3. Blennorrhoea
Research has revealed that bark of the Ricinodendron can be decocted and used for curing blennorrhoea. It is a medical disorder described by extreme release of watery mucus from vagina or urethra.
4. Cures Diarrhea
Bark or a mixture of the root and bark can be infused and used for treating diarrhea. Dysentery can also be treated with this infusion.
5. Strengthens Premature Babies
Certain nations use a bark decoction as a lotion and bathing tonic for strengthening early babies and children pretentious by rickets.
6. Treats Cough
Bark extracts are used for formulating herbal medications for treating catarrh, cold and coughs.
7. Treatment of Sexual Problems
Bark of Ricinodendron can be decocted and used for dealing with menstrual pain, child birth pain as well as other sexual complications.
8. Destruction of Worms
Bark-liquor of Ricinodendron is used for destroying and ejecting worms that may avoid females from conceiving. Latex and leaves can be used for removing guinea-worm.
9. Treats Babies Fever
Seeds are ground and mixed with palm kernel oil to make a cream that are wiped on baby’s’ soft spot affected by fever.
10. Relieves Labor Pain
Bark are infused and used by pregnant ladies to reduce labor pains. Similarly bark can be decocted and used by new moms to reduce tummy ache right after delivery.
Traditional uses and benefits of Ricinodendron
- Lotion or decoction prepared from bark of stem and root is used to treat elephantiasis, constipation, blennorrhoea, cough, edema, cure infertility, dysentery, and painful menstruation, relieve pain in pregnant women, fungal infection, rheumatism, rickets in children, prevent miscarriage and give strength to premature babies.
- Sap is implanted into the eye against ophthalmia and filaria.
- Leaves are also used to treat stomach pain, dysentery and female infertility.
- Latex and fruits are used to cure diarrhea and gonorrhea in West Africa.
- Root are ground up and combined with salt bark and pepper to deal with constipation in Nigeria.
- Liberian females use bark liquor to reduce pains and avoid miscarriage.
- Root-bark decoction taken by mouth is supposed to be a powerful anti-dysentery medicine in Cote d’Ivoire.
- Seed husk and leaf decoction are used to treat various ailments.
- Stem bark decoction is used outwardly to cicatrize and wash sores.
- It is also taken by females ‘to kill a worm of bowels and prevents them from breeding’.
- Externally bark is used to fortify rachitic children and premature babies, and reduces rheumatism and edemas.
- Pulped bark is applied externally to maturate buboes, furuncles and abscesses.
- Bark is crushed and heated and knotted to the body for the cure of elephantiasis.
Culinary Uses
- Seeds are ground and used as condiment for making njangsa stew, njangsa soup, and meat and fish dishes.
- It is also used as a thickening agent.
- Seeds are roasted and made into paste for making akpi sauce or njangsa sauce that is comparable to peanut sauce.
- Seeds are also used for making njangsa oil that can be used as cooking oil.
- Paste from the dried and pounded kernels are stored for making porridge during food deficiency.
- The protein-rich leaves are consumed as a cooked vegetable along with dried fish.
Other Facts
- Bark can be cut and used as stakes for backup other plants.
- It can be used as a natural compost to improve the soil since the roots are occupied by mycorrhizae.
- Bark, stems, woods, leaves and fruits can aid as natural manure.
- Wood is used for making toys, electrical insulation, cutleries etc.
- Wood can also be imprinted into plates, bowls, ladles, spoons, stools, platters, pestles and mortars.
- Seeds are used as rattles for producing musical sounds.
- Seeds, normally mentioned to as okwe are used by inhabitants for playing native games.
- Bark is dried and used for fermenting palm wine.
- Woods are chopped, dried and then used as firewood for cooking food.
- Seeds and husks are processed into oil.
- Wood ash is used as a cooking salt.
- Wood ash is used for manufacturing indigo dye.
- Oil from the dried kernels is used for varnish production.
- Leaves are used as forage for ships and goats.
- Wood is appropriate for plywood, boat building, toys and novelties, sporting goods, hardboard, particle board, wood-pulp and wood-wool.
- Leaves are used as packaging material and for mulching.
- Ricinodendron is planted as amenity tree, as live fence and for erosion control in DR Congo.
- Sawdust is extremely light and is appropriate for making life-saving belts.
- It is a widespread avenue tree in Uganda.
- Normally trees fruit one time in a 2–3 year period, but certain fruit annually.
- Fruit yield per tree might be up to 900 fruits each year.
- Plant yields fruits after 7 years of age in woodlands and 4 years of age in farms.
References:
https://uses.plantnet-project.org/en/Ricinodendron_heudelotii_(PROTA)#Synonyms
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/RIDHE
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Ricinodendron+heudelotii
https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/10.1079/cabicompendium.47583
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-178842