| Bonduc Nut Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
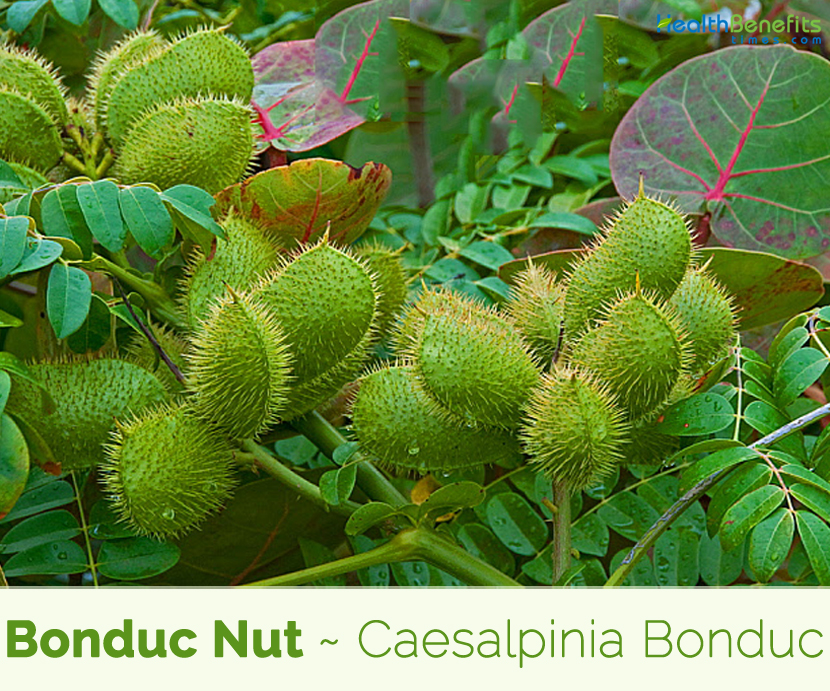
| Name: | Bonduc Nut |
| Scientific Name: | Caesalpinia Bonducella |
| Origin | Hotter places in India, Sri lanks and Burma |
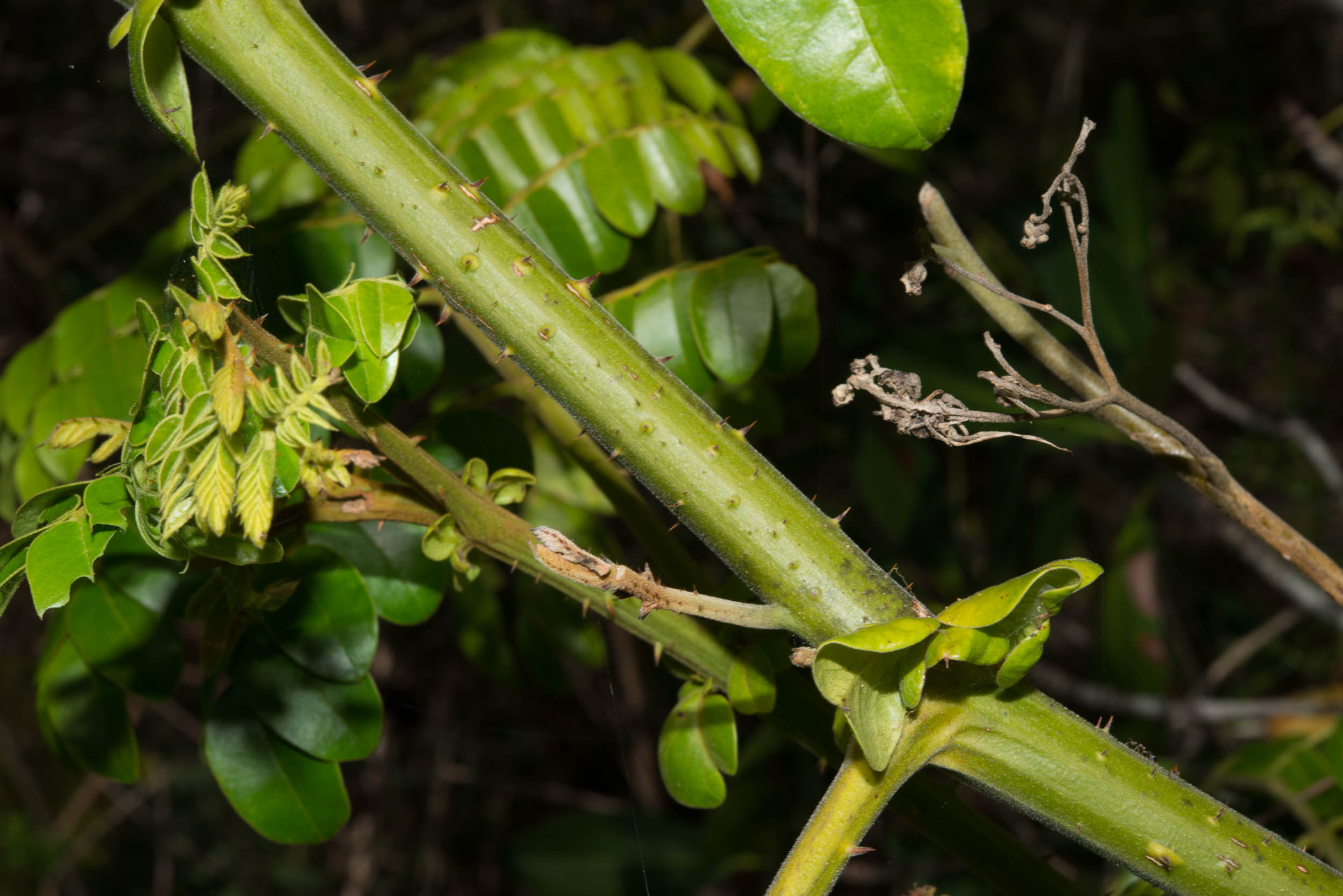
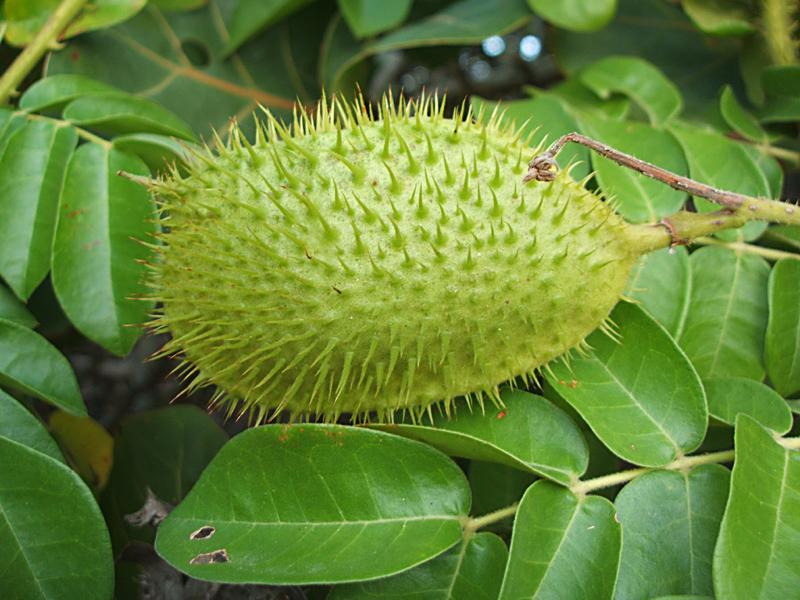
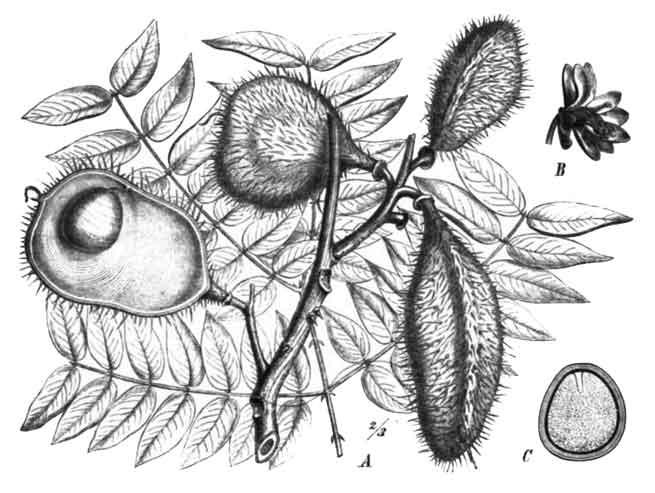
| Shapes | Inflated Pods that are shortly stalked, oblong, 5-7.5 long and 4.5 cm wide densely armed with wiry prickles. |
| Taste | Bitter, astringent, pungent |
| Health benefits | Beneficial for fever, intestinal worms, tumors, amenorrhea, cough, urinary disorders, leucorrhoea, piles and wounds |
| Plant parts | Characteristics |
| Foliage | Evergreen |
| Roots | Deep roots, tap roots |
| Type of stem | Hard and woody |
| Leaf type | Bi-pinnately compound, elliptical, ovate shaped |
| Leaf arrangement | Alternate |
| Leaf color | Green |
| Leaf surface | Glossy |
| Seed type | Dicot |
| Odor | Characteristic |
| Taste | Bitter |
Traditional uses and benefits of Fever Nut
- It is useful in countering Fever, Malarial Fever, and Intermittent Fever.
- Paste made from the leaves and twigs is useful in reducing toothache.
- Boiled leaves are used for gargling to relieve sore throat.
- It cures Sweating Deficiency and curbs Body Odor.
- Its juice is efficient in easing Elephantiasis.
- It is advantageous in combating Smallpox.
- It is fruitful in controlling Diabetes.
- It stops the growth of Tumors.
- It is a good herbal remedy for Liver Problems.
- It keeps a check on the Spleen disorders.
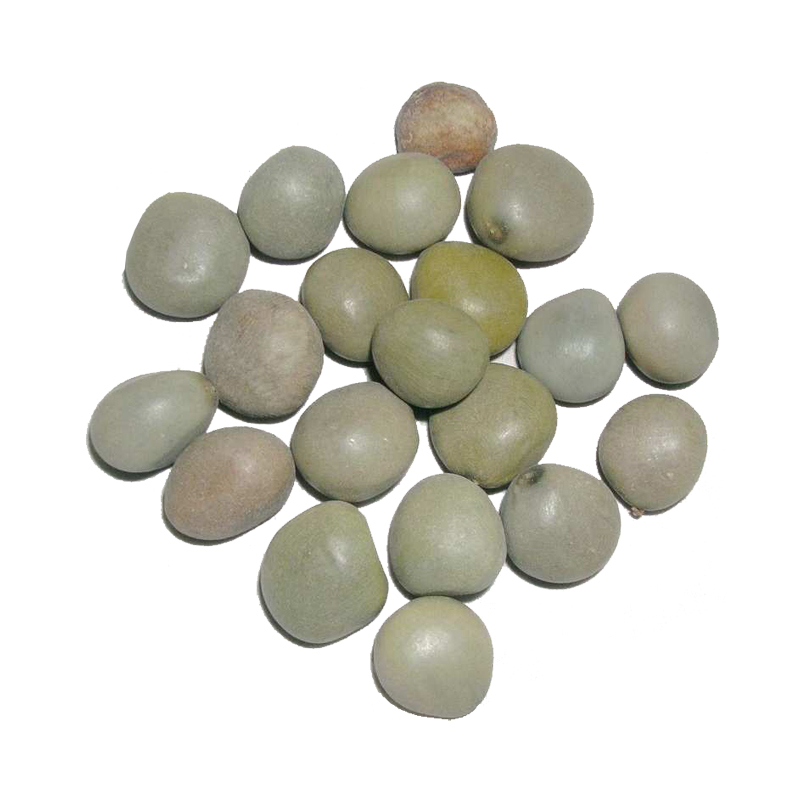
- Seeds of this herb have astringent properties.
- It is used to relieve inflammation, skin diseases, hydrocele, colic, and leprosy.
- Fruit of this tree is useful for eliminating Piles, Wounds, leucorrhoea and Urinary disorders.
- Caesalpinia Bonduc counters the Intestinal worms. It relieves Colitis i.e. inflammation of the Large Intestine. It eases the condition in Colic pain.
- Antidiarrheal activity of Caesalpinia Bonduc cures Diarrhea and Loose Motions.
- It is helpful in treating Menopause troubles namely, intermittent menses or no menses. It calms the abdominal pain during the Menopause.
- It is a good herbal cure for skin troubles namely leprosy, leucoderma, boils, blisters, and wounds.
- It is beneficial in mitigating arthritis and arthralgia i.e. Joint Pain.
- Root bark is used to treat fever, intestinal worms, tumors, amenorrhea, cough and for removing the placenta after childbirth.
- Leaves and their juice are used similarly and also traditionally for elephantiasis and smallpox, disorders of the liver and to destroy perspiration odor.
- In Sri Lanka, they are applied for toothache.
- Seeds are astringent and have been used to control contagious diseases, treat inflammation, colic, hydrocoele, skin diseases and leprosy.
- An ointment is made from the powdered seeds with castor oil and applied externally in Madras.
- Seed sprouts have been used for tumors.
- Fruit is also used to treat urinary disorders, leucorrhoea, piles and wounds.
- Oil from the fruit is applied to indolent ulcers and the oil from the seeds is used in convulsions and paralysis.
- Crushed seeds are considered vesicant and the boiled leaves used as a gargle for sore throat in Guinea.
- Leaves and seeds, after roasting with castor oil, are applied externally to inflammatory swellings, especially to inflamed piles, hydrocele, and orchitis.
- Seeds, leaves and roots are used for the treatment of tachycardia, bradycardia, tuberculosis, tympanitis, pain in the abdomen, fever, cold and cough and liver fluke in ruminants.
- Tender leaves (fresh juice) are given along with the honey to ward off the mucous secretions.
- Skin of the seed is extremely beneficial in the treatment of leucorrhea.
- Juice extract of the leaves are used in controlling elephantiasis and smallpox.
- Oil from the seeds is used to treat rheumatism in Somalia.
- Seeds are also useful for swellings and restraining hemorrhage.
- Oil from the seeds is used in convulsions and paralysis.
- Seeds are ground in water and given internally in snakebite.
- Decoction of roasted kernels is used in asthma.
- Children who are unable to digest mother’s milk are given the extract of the kernel or its powder along with ginger, salt and honey to get good stomachic effect.
- Paste prepared from kernel gives relief from boils and other swellings.
- Cake made of 30 grains of powdered kernels, fried in ghee taken twice a day is a valuable remedy in cases of acute orchitis, ovaritis and scrofula.
- Root-bark is good for tumors and for removing the placenta after child birth.
- Flowers are used in treating ascites and fruits in treating urinary disorders, leucorrhoea, piles and wounds.
- Leaf and twigs are traditionally used in the treatment of tumors, inflammation and liver disorders.
- Leaf juice has been used traditionally in elephantiasis and smallpox.
- Kernel powder with sugar and goat milk is useful in liver disorder.
- Young leaves are used in intermittent fevers, and for expelling intestinal worms in Malaysia.
- They are applied for toothache, and they are also given for worms in children in Ceylon.
- Finely powdered leaves are prescribed as a uterine tonic after child birth.
- Burnt seeds with alum and burnt arecan not are a good dentifrice useful in spongy gums, gum boils, etc.
- Roasted fruits are used in eye diseases, hyper-acidity and as fish poison.
- Pulp of the pod is used for purifying the blood, in congestion and as a laxative in Hawaii Islands.
- Fresh fruit powder with garlic and mixed with lukewarm water is rubbed on the body to mitigate fever in Philippines.
- Seeds, leaves and roots are used for the treatment of tachycardia, bradycardia, tuberculosis, and tympanitis, pain in the abdomen, fever, cold and cough and liver fluke in ruminants.
Ayurvedic Health benefits of Fever Nut
- Diabetes: Crack a Caesalpinia Bonduc seed. Extract the kernel. Soak the Bonduc nut at night. Eat it in the morning. Drink the water also. Repeat for 15 days. Get your blood sugar checked.
- Ascites: Prepare decoction of Caesalpinia Bonduc Flower. Have a glass when needed.
- Ulcers: Take Caesalpinia Bonduc Root bark. Grind. Add water to make paste. Apply over ulcers.
- Scrofula: Dry Caesalpinia Bonduc Kernel. Grind. Fry in Clarified Butter. Apply it over affected area.
- Abscess: Grind Caesalpinia Bonduc kernel. Add water to make paste. Apply it over affected part. Do it twice a day.
- Asthma: Roast Caesalpinia Bonduc kernel. Prepare decoction with roasted kernel. Have half a cup once a day.
- Liver Diseases: Powder Caesalpinia Bonduc seeds. Have 2 pinches with a glass of Goat milk.
- Paralysis: Extract or purchase Caesalpinia Bonduc seed oil. Massage with this lukewarm oil for 10 minutes at night.
- Leprosy: Crush Caesalpinia Bonduc seeds. Add water to make paste. Apply it over affected area daily. It cures the problem.
- Skin Diseases: Dry Caesalpinia Bonduc seeds. Crush them. Add any carrier oil. Apply it over affected area twice a day.
- Styptic: Make a paste of ground Caesalpinia Bonduc seeds by adding water. Apply it over affected area. It prevents the styptic.
- Purgative: Grind dried Caesalpinia Bonduc seeds. Have 2 pinches with water. It is a good purgative.
- Constipation: Fry leaves of Caesalpinia Bonduc in Clarified Butter. Consume 3 g of it thrice a day.
- Diarrhea: Take quarter tsp seed powder of Caesalpinia Bonduc with a cup of lukewarm Milk. Have it twice a day.
- Joint pain: Use Caesalpinia Bonduc seed oil for massage over painful joints.
- Inflammation: Bandage leaves of Caesalpinia Bonduc over inflamed areas.
- Fever: Take 100 g Caesalpinia Bonduc seeds with 15 g Aconitum Heterophyllum seeds. Powder them. Take quarter teaspoon of the powder with same quantity of Sugar. Have it twice a day.
- Fever: If Fever is due to Malaria then try this remedy: Take roasted seeds of Caesalpinia Bonduc with same quantity of Long Pepper. Grind them to make powder. Take quarter teaspoon of it with one teaspoon Honey. Have it twice a day.
- Malaria: Mix seed powder of both Caesalpinia Bonduc and Black Pepper in 2:1 ratio. Take 4 g twice a day.
- Orchitis: Take dry Caesalpinia Bonduc seeds. Grind them. Add Castor oil to make paste. Apply it over affected area and cover. Do it once a day.
- Hydrocele: Grind Caesalpinia Bonduc seeds. Mix Castor oil to make a thick paste. Apply it over affected part. Do it regularly.
- Malaria: Take equal quantity of Caesalpinia Bonduc seeds and Black Pepper. Grind them together. Have 2 pinches with water once a day.
- Expectorant: Grind Caesalpinia Bonduc seeds and Long Pepper in equal quantity. Take 1/4 teaspoon with Honey in morning for 3 days.
- Gum Diseases: Take 2 gm. each of Caesalpinia Bonduc seeds, areca nuts and alum. Burn them. Crush them. Add little water and apply it over affected area.
- Fever: Take Caesalpinia Bonduc kernel and black pepper in equal amount. Grind them together. (Dosage: 5 gram by adults or 2 gm. by children)
- Prostate enlargement: Take half teaspoon each of Tribulus Terrestris, Caesalpinia bonducella, Areca Catechu, Asparagus Recemosus, Crataeva Nurvala and Agate Gemstone. Take them daily after meals for three months. OR Buy capsules containing all the above herbs. Take 1 tablet 2 times a day, daily after meals. OR Buy Mother – Tincture from a Homeopathic Shop of the above herbs. Starts with 3 drops of each herb, if it suits then increase the dosage accordingly.
Other facts
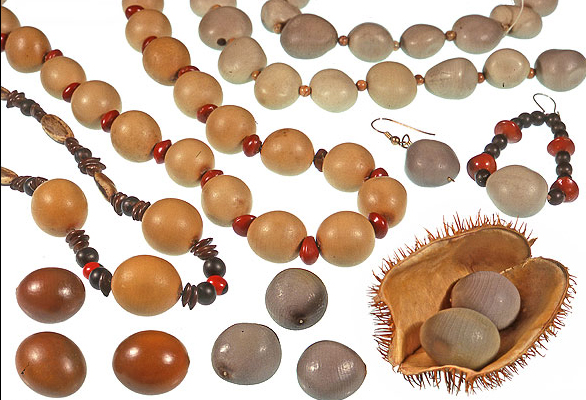
- Seeds of this species are found washed up on beaches throughout the world.
- Seeds are widely used as beads for necklaces, bracelets, rosaries etc. in various places.
- Seeds are sometimes used by Indian children as marbles.
- Oil pressed from the seeds has been used to remove freckles from the face, as a cosmetic, and to stop discharges from ears.
- Bonduc nut is planted as a live fence in Sierra Leone and Ethiopia.
- Seeds are also used as weights and as counters in board games.
- Oil obtained from the seed is used in cosmetic preparations.
Precautions
- Do not use more than prescribed dose. Taking more medication will not improve your symptoms; rather they may cause poisoning or serious side-effects.
- Caesalpinia bonduc should be used with caution for using this herb in large doses may prove to be toxic.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=514312#null
https://davesgarden.com/guides/pf/go/75920/
http://www.hear.org/pier/species/caesalpinia_bonduc.htm
https://www.cabi.org/ISC/datasheet/10699
https://plants.usda.gov/java/ClassificationServlet?source=display&classid=CABO6
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?id=18059
http://www.bgci.org/plant_details.php?plantID=912
https://www.discoverlife.org/mp/20q?search=Caesalpinia+bonduc&flags=glean:&mobile=close
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/ild-927
http://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/Fever%20Nut.html
https://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/32057
https://uses.plantnet-project.org/en/Caesalpinia_bonduc_(PROTA)
https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CABO6