| Calumba Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Calumba |
| Scientific Name: | Jateorhiza palmata |
| Origin | Kenya, Tanzania, Malawi, Zimbabwe, Mozambique and South Africa |
| Colors | Yellow |
| Shapes | Globoid drupes enclosing a stone akin to the shape of a moon |
| Taste | Bitter |
| Health benefits | Beneficial for diarrhea, dysentery, gastric irritability, snakebites, hernia, ruptures, loss of appetite and anorexia nervosa |
| Name | Calumba |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Jateorhiza palmata |
| Native | Kenya, Tanzania, Malawi, Zimbabwe, Mozambique and South Africa (Kwazulu-Natal). It is cultivated in Mozambique, and cultivated and locally naturalized in many tropical countries, including Ghana, Madagascar, Mauritius, Réunion and also in India and Brazil |
| Common Names | Bitter columba root, Calumbo, Colomba, Colomba root, Colombo, Colombo-root, Foreign colombo, Jateorhiza, Kalamba, Calumba, calumba root, columba, kalumba, kalumb, jateorhiza, guvercin koku otu |
| Name in Other Languages | Arabic: Sakel hamam Catalan: Colombo English: Jateorhiza, calumba root Finnish: Kalumba French: Racine de Colombo German: Kalumba, Kalumbawurzel Hindi: Kalamb-kachri, Kalamb-ki-jar Hungarian: Kalumbagyökér Japanese: Koronbo (コロンボ) Persian: Bikle Portuguese: Calumba, colomba, colombo-de-áfrica Russian: Jatieoriza paĺčataja (Ятеориза пальчатая) Swedish: Kalumba Tamil: Kalamba veru |
| Plant Growth Habit | Tall, dioecious twining climbing perennial vine |
| Growing Climates | Rain-forest; fringing forest |
| Plant Size | 2 – 5 meters long |
| Root | Root of this herb has a starchy evenness, a hollowed center and a dense bark |
| Stem | Annual stems, one or two from each root, are hair with glandular tips |
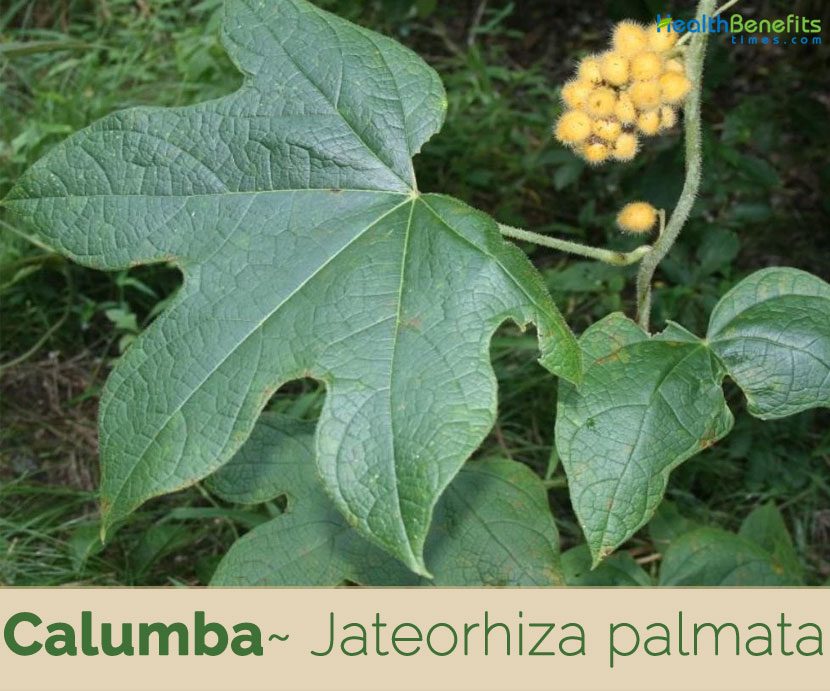
| Leaf | Leaves appear opposite to each other and their petiole is approximately 18 cm to 25 cm in length. The leaf blades measure anything between 15 cm and 35 cm in length and 18 cm and 40 cm in width |
| Flower | Cluster of flowers (inflorescences) of the male plant of the species is about 40 cm in length and possesses green sepals. The female inflorescence of calumba measures approximately 8 cm to 10 cm in length |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Globoid drupes enclosing a stone akin to the shape of a moon. It is about 2.0 cm to 2.5 cm in length and approximately 1.5 cm to 2.cm in width. |
| Propagation | By seed |
| Taste | Bitter |
| Plant Parts Used | Root |
| Available Forms | Dried root pieces, Powder, Pills/tablets, Fresh |
Plant Description
Calumba is a tall, dioecious twining climbing perennial vine that normally grows about 2 – 5 meters long often reaching the tops of trees. The plant is found growing in rain-forest as well as fringing forest. The diameter of calumba root is normally between 3 cm and 8 cm and it has a greenish-black hue. In addition, the root of this herb has a starchy evenness, a hollowed center and a dense bark. Crosswise, the roots have a yellowish color having circulatory bundles arranged in spreading out lines. The annual stems, one or two from each root, are hair with glandular tips and have large bright green membranous leaves.
Leaves
The leaves appear opposite to each other and their petiole is approximately 18 cm to 25 cm in length. The leaf blades measure anything between 15 cm and 35 cm in length and 18 cm and 40 cm in width. They have bristly hairs on both sides, are generally curved, profoundly heart-shaped (cordate) at the bottom and generally have five wide oval-shaped lobes each.
Flower
Calumba is a dioecious plant, representing that each plant has a separate sex. The cluster of flowers (inflorescences) of the male plant of the species are about 40 cm in length and possess green sepals that measure anything between 2.7 mm to 3.2 mm in length and 1.2 mm to 1.6 mm in width. The stamens of the male inflorescences are unbound, but merged at their base with the intricate margins of the petals. On the other hand, the female inflorescence of calumba measures approximately 8 cm to 10 cm in length and possesses a rust-red hued pubertal ovary measuring about 1.0 mm to 1.5 mm.
Fruits
Fertile flowers are followed by globoid drupes enclosing a stone akin to the shape of a moon. It is about 2.0 cm to 2.5 cm in length and approximately 1.5 cm to 2.cm in width.
Worldwide Ethno-medical Uses
| Country | Uses |
| Africa | For diarrhea, dysentery |
| Brazil | For diarrhea, poor digestion, dysentery, dyspepsia, nausea, and as a gastro-tonic, stomachic, bitter tonic |
| Elsewhere | For diarrhea, dysentery, dyspepsia, wounds, and as a tonic |
| Turkey | As an antiseptic, aperitif, gastro-tonic, restorative, vermifuge and for dysentery |
Traditional uses and benefits of Calumba
- The tuber is gathered from the wild for local medicinal use.
- It was especially valued as a treatment for digestive problems for people with a weak stomach in Europe.
- It was used against dyspepsia and diarrhea, being considered especially suitable for people with a weak stomach.
- Root is considered to be anthelmintic, antipyretic, bitter, tonic.
- It is widely used as a treatment against diarrhea and dysentery, gastric irritability, vomiting during pregnancy.
- Traditionally, it has been eaten as a treatment against snakebites, hernia and ruptures.
- Root scrapings are applied onto scarifications made in abscesses to mature them.
- Root is eaten against snakebites and as a vermifuge in Tanzania.
- The Zigua people of Tanzania use it to treat hernia and ruptures.
- Throughout south-eastern Africa the roots are considered tonic and are taken against dysentery and diarrhea, whereas in India they are taken as a bitter tonic with antipyretic and anthelmintic properties, against gastric irritability and vomiting during pregnancy.
- In Europe Jateorhiza palmata is still used in laxative herbal mixtures.
- In Italy and the United States the root has been added to herbal bitters.
- Today it is still respected in Africa and India, especially for treating gastric disorders.
- Root is used for poor digestion, low stomach acid, diarrhea, gas, and loss of appetite.
- This medication is particularly used to cure loss of appetite as well as anorexia nervosa.
- Calumba is particularly useful in treating chronic fatigue syndrome that is usually related to scarce production of stomach acids.
- Calumba is an effective remedy for treating dysentery and in East Africa.
- It has been traditionally used for this purpose as well as to force out worms from the body.
- People in the United States and in Italy add the root of calumba to herbal bitters.
Precautions
- Avoid use during breast feeding.
- Calumba’s side effects include vomiting and stomach pain.
- Calumba ought to be usually avoided by pregnant women; often small doses of this medication have been prescribed to such women with a view to alleviate morning sickness.
- Safety in young children, nursing women, or those with severe liver or kidney disease is not known.
- Taking this herb in excessive doses may result in symptoms of unconsciousness and paralysis.
References:
https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=JAPA2
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jateorhiza_palmata
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/IARPA
http://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Jateorhiza+palmata
https://uses.plantnet-project.org/en/Jateorhiza_palmata_(PROTA)
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/tro-20600480
http://usefulplantsofboyaca.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:580974-1
https://www.botanical.com/botanical/mgmh/c/calumb10.html
https://www.prota4u.org/database/protav8.asp?g=pe&p=Jateorhiza+palmata+(Lam.)+Miers
https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q1722737