| Colonial Bent Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Colonial Bent |
| Scientific Name: | Agrostis capillaris |
| Origin | Northern Africa (i.e. Tunisia), the Canary Islands, Europe, Australia, New Zealand, western and eastern North America |
| Shapes | Seed heads are usually 15 cm long with spreading branches with tiny, brown seeds |
| Name | Colonial bent |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Colonial bent |
| Native | Northern Africa (i.e. Tunisia), the Canary Islands, Europe, Australia, New Zealand, western and eastern North America, Greenland, Central and South America, the sub-Antarctic islands and parts of western and central Asia (i.e. Turkey, northern Iran, Afghanistan, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Kazakhstan and southern Russia). In British Columbia, it is common on southern Vancouver Island and the southwestern part of the province, becoming uncommon further East and North |
| Common Names | Astoria bent, black couch, brown bent grass, brown top, brown top bent grass, burden’s grass, colonial bent, common bent grass, common bent grass, dew grass, English bent, furze top, New Zealand bent grass, Prince Edward Island bent grass, Rhode Island bent, Rhode Island bent grass, Waipu bent, brown-top grass, colonial bent grass, common bent |
| Name in Other Languages | Albanian: Barimza e rënomtë, barimëz Bulgarian: Obiknovena polevitsa (обикновена полевица) Catalan: Agrostis tènue Chinese: Xi ruo jian gu ying (细弱剪股颖), 细弱剪股颖 Croatian: Obična rosulja Czech: Psineček obecný, psinecek tenký Danish: Almindelig Hvene Dutch: Gewoon struisgras English: Browntop, Colonial bent grass, Common bent grass, New Zealand bent grass, Prince Edward Island bent grass, Rhode Island bent, Rhode Island bent grass, Colonial Bent, bent grass, browntop bent, common bent, waipu, black couch Estonian: Harilik kastehein Finnish: Nurmirölli French: Agrostide commune, Agrostide grêle, Agrostide ténue, Agrostis vulgaire, agrostide fine, agrostis capillaire; agrostis commun, agrostis delicat, agrostide des prés, agrostide delicate, agrostide grêle, agrostide vulgaire, traînasse Galician: Feorainn mhín German: Gemeines Straußgras, Rotes Straußgras, Rotstraußgras, gewöhnliches Straußgras, Haarstraußgras, schmaler Windhalm Greek: Agrostis i lepti (Αγρώστις η λεπτή) High Aragonese: Yerba fina Hungarian: Cérna tippan Icelandic: Hálíngresi Irish: Feorainn mhín Italian: Agrostide tenue, Capellini delle praterie , capellini esile capellini volgare, agrostide capillare, agrostide rossa Japanese: Bento gurasu (ベントグラス ), Ito konuka gusa (イトコヌカグサ) Latvian: Parastā smilga Lithuanian: Paprastoji smilga Netherlands: Gewoon struisgras Northern Sami: Gieddeávji Norwegian: Engkvein, Fiinhveen, Fiinhvine, Haarhveen, Haarkjøse, Rø-kjøsa, Vesselkjøsa Polish: Mietlica pospolita Portuguese: Erva-fina, agrostide-tenue, agrostide-comum, agrostis-comum, castanho, panasco, panasco-de-topo Romanian: Păiuș Russian: Polevitsa tonkaia (Полевица тонкая), polevica tonkaâ , polevitsa volosovidnaya (полевица волосовидная), polevitsa litovskaya (полевица литовская), polevitsa obyknovennaya (полевица обыкновенная) Serbian: Obična rosulja (обична росуља), rudacha (рудача) Slovakia: Psincek tenucký, psinček obyčajný Slovenian: Tankolistna šopulja, lasasta šopulja Spanish: Agróstide común, Agróstide tenue, Chépica alemana, Heno ahumado, Hierba fina, pasto quila, pico pardo Swedish: Rödven, Nurmirölli Turkish: Kuş otu, Kahverengi tavus otu, Narin tavus out, karahasanotu Ukrainian: Mitlytsya tonka (мітлиця тонка) Welsh: Maeswellt cyffredin |
| Plant Growth Habit | Low-growing, rhizomatous and stoloniferous perennial grass |
| Growing Climates | Ruderal, disturbed areas, heathland, woodland, scrub and sand dune habitats, heathy woodlands, lowland grasslands, grassy woodlands, dry and damp sclerophyll forests, riparian vegetation and alpine and sub-alpine vegetation, montane peatlands and swamps, urban areas, dry coastal vegetation, moist grasslands, open meadows, agricultural areas, roadsides, and invading disturbed areas, freshwater wetlands |
| Soil | Preference for poorly drained, fine to medium textured soils of pH 6.5 to 7.3 with a moderate level of organic matter (Dale et al., 1965). It is tolerant of temperature extremes. |
| Plant Size | 20-25 cm or 100 cm tall |
| Root | Roots have rhizomes and occasionally stolons |
| Stem | Stems are spreading and grow to 80 cm long. The entire plant is hairless |
| Leaf | Flat, short and narrow measuring 100-150 x 1.5mm. Ribs and regular and margins slightly rough |
| Flowering season | June to August |
| Flower | Spikelets (flower clusters in grasses) are 1.5-3.5mm in length and purplish brown to greenish in color |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Seed heads are usually 15 cm long with spreading branches with tiny, brown seeds |
| Seed | Small seed are oblong to ovate in shape. It has a shiny brown to amber color. It is 1 mm in length |
| Propagation | By seeds and vegetatively by rhizomes and stolon |
| Season | August to October |
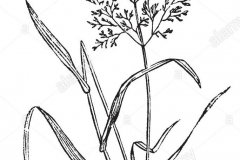
Plant Description
Colonial bent or common bent is a low-growing, matted, rhizomatous and stoloniferous perennial grass that normally grows about 20-25 cm or 100 cm tall. The plant is found growing in ruderal, disturbed areas, heathland, woodland, scrub, sand dune habitats, heathy woodlands, lowland grasslands, grassy woodlands, dry and damp sclerophyll forests, riparian vegetation and alpine and sub-alpine vegetation, montane peatlands, swamps, urban areas, dry coastal vegetation, moist grasslands, open meadows, agricultural areas, roadsides, and invading disturbed areas and freshwater wetlands.
The plant has a preference for poorly drained, fine to medium textured soils of pH 6.5 to 7.3 with a moderate level of organic matter. It is tolerant of temperature extremes. Roots have rhizomes and occasionally stolons. Stems are spreading and grow to 80 cm long. The plant spreads predominantly by underground rhizomes. The entire plant is hairless. The plant has a very fine texture and like most bent grasses grows very dense. Colonial bent is fairly easy to grow from seeds and fertilization of the lawn is not as intense. This grass also takes longer to establish than creeping bent. However it does not require the intense maintenance.
Leaves
Stems (stolons) are decumbent (creeping) and slender and produce long narrow leaves. Leaf blades are smooth on the upper surface and ridged on the underside, 1 to 3 mm wide and bluish green in appearance. The ligule is long, membranous, finely toothed or entire and rounded, auricles are absent.
Flower
The species is characterized by single flowered spikelet in a compact panicle. The panicle in flower is purple to bronze in appearance. The flowering panicles appear from June to August. The panicle persists in winter after the seeds have been shed.
The plant propagates by way of highly abundant seeds and vegetatively by rhizomes and stolons. The large proportion of A. capillaris clones and low proportion of seedlings in populations suggests that much of its reproduction is vegetative. Flowers are wind pollinated, but are also spread by water, humans and vertebrates.
Fruit
Seed heads are usually 15 cm long with spreading branches with tiny seeds. Seeds of Colonial bent are too small to be recognized without magnification. Seeds are ovate, less than 1 mm long, usually awn less with an occasional short, straight awn and silvery in appearance. Seed is set from August to October in the northern hemisphere. Seeds may persist for 5 years or more.
Other Facts
- It is used in garden lawn mixtures and in particular for tennis courts, high-grade lawns, golf course fairways and erosion control.
- It is a food source for herbivores, including rabbits.
- It is a valuable agronomic species because of their ability to produce fodder as well as provide food for grazing animals.
Prevention and Control
Due to the variable regulations around (de)registration of pesticides, your national list of registered pesticides or relevant authority should be consulted to determine which products are legally allowed for use in your country when considering chemical control. Pesticides should always be used in a lawful manner, consistent with the product’s label.
Cultural Control and Sanitary Measures
A. capillaris is highly adapted to grazing and tolerant of burning, so neither of these mechanisms can be used to control the species and can, in fact, result in increased abundance. In cultivated areas, where A. capillaris can become a weed, short rotations with root crops may help reduce this species.
Physical/Mechanical Control
For Agrostis species in general, conventional control including physical removal is considered difficult or not feasible even when they exert a large negative impact on native biodiversity. However, for A. capillaris, mechanical removal by hand pulling, ploughing, grubbing and harrowing can reduce abundance. It can also prevent seeding when applied in spring or early summer before seed set. Manual removal is labor intensive and remaining pieces of broken stolons can re-establish.
Biological Control
There are no known biological control agents available for A. capillaris and the value of the species worldwide as a commercial fodder and lawn grass may preclude any attempts at biological control.
Chemical Control
The graminicide cycloxydim has been used to effectively control A. capillaris in forest tree establishment situations (Clay et al., 2006). A. capillaris is also susceptible to the herbicides dalapon, hexazinone and sethoxydim, the last giving a 100% mean control rate, while glyphosate applied before emergence reduces growth rate. The introduction of glyphosate resistance into A. capillaris by genetic engineering may have implications for the species’ invasiveness, spread and control. Herbicides should only be used with extreme caution, and under expert advice, in sensitive Garry oak ecosystems.
Other Techniques
Prescribed burning is not an effective management method for colonial bent grass as a study in Oregon found abundance of the species to be ten-fold in burned versus unburned areas. Colonial bent grass can also not be managed by cutting or grazing. Due to its low stature, its relative leaf loss is minimal in comparison to other grass species, and it is thus able to maintain its competitive advantage. Grazing on colonial bent grass in cultivated plots was even found to increase the abundance of the species.
Preventative Measures
Soil disturbance and the use of fertilizers should be avoided in natural areas. Equipment, clothing and animals should be checked and cleared for seeds when leaving an infested area. Encourage plant nurseries, gardeners and farmers to stock and use native or non-invasive species, and to avoid using non-native grasses such as colonial bent grass.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=185249#null
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxon/taxonomydetail?id=2017
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Agrostis+capillaris|
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/3830
https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=AGCA5
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Agrostis_capillaris
http://issg.org/database/species/ecology.asp?si=1365&fr=1&sts=&%20ang=EN&ver=print&prtflag=false
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-387729
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/AGSTE