| Khirni Quick Facts | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name: | Khirni | ||
| Scientific Name: | Manilkara hexandra | ||
| Origin | South Asia (China: Hainan and southern Guangxi provinces | ||
| Colors | Initially green turning to reddish-yellow as they mature | ||
| Shapes | One seeded berry, obovoid-oblong or ellipsoid, 1.5 mm long and 8 mm wide | ||
| Taste | Sweet, pungent | ||
| Health benefits | Cures Fevers and Jaundice, Augments Kidney Function, Heals Skin Infections, Alleviates Stomach Ulcers, Enhances Immunity | ||
| Name | Khirni |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Manilkara hexandra |
| Native | South Asia (China: Hainan and southern Guangxi provinces; the Indian Subcontinent: Bangladesh, India, and Sri Lanka; Indo-China: Cambodia, Myanmar, Thailand and Vietnam |
| Common Names | Ceylon Iron Wood, milk tree, wedge-leaved ape flower, Rayan, khirni |
| Name in Other Languages | Bengali : Krikhiyur, Khirani (খিরনি) Chinese: Tie xian zi (铁线子), Tie se English : Ceylon iron wood, Milky tree Gujarati: Khirani (ખિર્ની), Rayana (રાયન) Hindi: Drirh (दृढ़), Khirni (खिरनी), Kshiri (क्षीरी), Rayan (रायन), Kshiri Irula: Palai maram Kannada : Bakula, hale hannu, khiranee, kiraale, kiraanimara, kirani hannina mara, kirani mara, kirhaale, ksheera vriksha, ksheerini, mukula, pete, nn, pakkalada, pakkila Konkani: Karni (कर्णी), Ranjana (रांजण) Malayalam: Krini (കൃണി), paḻamunpāla (പഴമുന്പാല) Pazhamunpaala, Pazhamunpaala, Mullupala, Khirni, khrini, Pazhamunppala, Krini (കൃണി), manilakkara, palamunnippala, palamunpala, elengi, pala, pali Marathi: Karani (करणी), Khirni (खिरणी), Rajana (राजण ), Ranjana (रांजण), Rayan (रायण), Rayani (रायणी), khiranee (खिरणी), kirni, raajana, raini, ranjana, rayan, rajana Nepalese: Khirni (खिरणी) Persian: خیز نی Sanskrit: Kshirini (क्षीरिणी), Nimbabija (निम्बबिज), Rajadana (राजादन), rajadana, rajadanah, dhupeshtha, drdhaskandha, dridhaskandha, guchhaphala, jara, kapishtha, kshirashukla, kshiravriksha, kshiri, kshirika, kshirini, ksiri, ksirika, ksirini, madhavodbhava, madhuphala, nimbabija, nripadruma, phaladhyaksha, rajadani, rajahvam, rajanya, rajaphala, shriphala Sindhi: کيرڻي(وڻ) Tamil: Ulakkaippalai (உலக்கைப்பாலை), palai (பாலை), Kanupala,Kannupala,Ulakkaipaalai, kannupalalai, kanupala, karupala, kirni, palla, patla, pola, ullakai-palai, attukkompuppalai, attukkottuppalai, civa, mesakkotu, metakkotu, pala, palai 1, palai mukil, sivandi, sivani, sukkilam, ulakkaipalai, ulakkaippalai, ulakkaippali, vatuvati Telegu: Ankalu (అంకాలు), Nandivriqshamu (నందివృక్షము), Palachettu (పాలచెట్టు), Ankalu (అంకాలు), kirni, manchipala, manjipaala, nemmi, nunni paala, pala, palapandu chettu, patla, pola, puttapala, mancipala, manjipala, nienni, nunni, pal, pale, palla, pallapandu, palle, pallepaulo Tibetan: Ra dza da na (d), ra dze da na Thai: Ked (เกด) Urdu: Tukhm khirini |
| Plant Growth Habit | Small to medium sized, slow-growing but fairly large glabrous evergreen tree |
| Soil | Prefers a well-drained soil and a pH in the range 6 – 7 |
| Plant Size | About 12 to 25 meters tall and one to three meters in trunk circumference |
| Bark | Bark blackish-grey, longitudinally fissured and cracked, rough; blaze crimson red; exudation milky |
| Wood | Hard, heavy, and durable, weighing 70 pounds per cubic foot |
| Leaf | Simple, alternate, often closely clustered towards the end of branchlets, with conspicuous scars. Petiole is 8-20 mm, slender, slightly grooved above and glabrous |
| Flowering season | August-December |
| Flower | Bisexual, 7 mm across, white, 1 or 2 axillary. Pedicel is thick about 3.5 cm long. Sepals are ovate- triangular, 3-4 mm, yellowish gray velvety. Flowers are white or light yellow, about 4 mm |
| Fruit Shape & Size | One seeded berry, obovoid-oblong or ellipsoid, 1.5 mm long and 8 mm wide |
| Fruit Color | Initially green turning to reddish-yellow as they mature |
| Seed | Ovoid, reddish brown with shining testa |
| Propagation | By seeds |
| Taste | Sweet, pungent |
| Plant Parts Used | Bark, fruits |
| Health Benefits |
|
| Culinary Uses |
|
Plant Description
Khirni is a small to medium sized, slow-growing but fairly large glabrous evergreen tree that normally grows about 12 to 25 meters tall and one to three meters in trunk circumference. It grows in tropical and temperate forests. Bark is blackish-grey, longitudinally fissured and cracked and rough. The wood is hard, durable, and heavy; the density is variously reported as ranging from about 0.83 to 1.08 tons per cubic meter, partly depending on the degree of drying. It is used for heavy structural work, gate posts, and big beams.
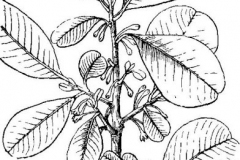
Leaves
Leaves are simple, alternate, often closely clustered towards the end of branchlets, with conspicuous scars. Petiole is 8-20 mm, slender, slightly grooved above and glabrous. Leaf blade is 5-10 cm long and 3-4.5 cm wide, elliptic, elliptic-obovate, obovate or ovate-oblong. Both surfaces are smooth, base broadly wedge shaped to obtuse. Margin is entire, glabrous and coriaceous. Lateral nerves 10-20 pairs are closely pinnate, slender, midrib raised below; intercostae reticulate.
Flower
Flowers are bisexual, 7 mm across, white, 1 or 2 axillary. Pedicel is thick about 3.5 cm long. Sepals are ovate- triangular, 3-4 mm, yellowish gray velvety. Flowers are white or light yellow, about 4 mm. Petals are oblong, about 3 mm. Stamen 6-8, alternating with staminodes, bifid; staminodes shorter than stamen, filaments glabrous, lanceolate; ovary pubescent, 12-celled, superior; style 4-5 mm, subulate; stigma simple. Flowering normally takes place in between August-December.
Fruits
Fertile flowers are followed by one seeded berry, obovoid-oblong or ellipsoid, 1.5 mm long and 8 mm wide. They are initially green turning to reddish-yellow as they mature. Seeds are ovoid and about 1 cm long, reddish brown with shining testa.
Ethno medical uses of Khirni in India
| Place, Country | Parts Used | Ethno Medical Use | Preparation (s) |
| Maharashtra | Fruit | Arthritis, Blood purifier, Heat Burning, Jaundice | Mashed |
| West Bengal | Bark, Fruits | Jaundice, Biliousness | Decoction |
| Andra Pradesh | Leaves | Asthma | Decoction or Infusion |
| Andra Pradesh | Stem Bark | Galactagauge | Infusion |
| Maharashtra | Fruit | Digestive disorder | Mashed |
| Tamil Nadu | Stem Bark, Leaves | Infertility, Veterinary | Infusion |
| Rajasthan | Stem Bark, Fruit | Fever, jaundice, | Decoction, Mashed |
| Madhya Pradesh | Stem Bark, Fruit | Bronchitis, Dysentery | Decoction, Mashed |
| Maharashtra and Gujarat | Stem Bark, Fruit | Alimentary Disorders | Decoction, Mashed |
| Tamil Nadu | Stem Bark, Fruit | Fever, Hallucination | Decoction, Mashed |
| Andra Pradesh | Root | Headache | Infusion or Decoction |
| Kodiakarai | Latex | Toothache | Applied Directly |
| Andra Pradesh | Stem Bark | Dysentery and Diarrhea | Decoction |
| Madhya Pradesh | Stem Bark | Tonic | Decoction or Infusion |
| Madhya Pradesh | Stem Bark | Body ache | Boiled |
Health Benefits of Khirni
Listed below are some of the popular health benefits of Khirni
1. Cures Fevers and Jaundice
Juice derived from the pulp of khirni fruit is bestowed with valuable antioxidants – myricetin and quercetin, which supply significant antipyretic i.e. body temperature lowering traits. Drinking a glass of fresh khirni juice is a well-known remedy for fever and jaundice, vastly diminishing the symptoms of body pain and discomfort.
2. Augments Kidney Function
Khirni fruit is endowed with proteins, which aside from building strong muscles and promoting metabolism, also possess diuretic properties. This fosters normal excretory processes and helps to get rid of toxins, waste matter and undigested food accumulated in the system, by means of optimal kidney activity, thereby preventing kidney disorders.
3. Heals Skin Infections
Vast array of the triterpenoid plant chemicals in khirni make it a superb natural solution to treat skin infections. Additionally, khirni also possesses powerful antimicrobial properties. Applying the paste from fruit extract directly on the skin provides instant relief from rashes, itching and psoriasis, thus enriching its texture and restoring suppleness and radiance to the skin.
4. Alleviates Stomach Ulcers
Khirni fruits encompass noteworthy levels of tannins and saponins – valuable plant compounds that remarkably mend gastrointestinal ulcers. Adding a few slices of khirni fruit to breakfast or having it as a snack in the evening soothes the tummy, by regulating gastric acid volumes and stimulating protective mucosal secretions by the walls of the stomach.
5. Enhances Immunity
Immense quantities of vitamin C are found in khirni fruit, making it an advantageous food for improving the body’s defense mechanism. Antioxidant nature of vitamin C also aids in flushing out harmful free radicals from the system. Moreover, khirni fruit holds considerable antimicrobial potential, shielding the body from bacteria and viruses that trigger diseases.
Traditional uses and benefits of Khirni
- It is a medicinal tree used in the treatment of excess thirst, emaciation, bleeding disorders, ulcer, bronchitis, jaundice, fever, arthritis etc.
- It is used in medicinal herbal drugs to cure various diseases such as jaundice, ulitis, odontopathy, fever, colic dyspepsia, helminthiasis, hyper dyspepsia and burning sensation.
- It is beneficial in swelling, abdominal colic, gout, rheumatism and toxicosis.
- Traditionally Bark is used to treat a wide range of gastrointestinal disorders.
- It improves taste, promotes physical strength and aphrodisiac in nature.
- Stem bark decoction is used as effective remedy in dysentery and diarrhea.
- Mashed fruits are taken to cure diseases like arthritis and jaundice, also used for heat burning, wormicide, and to purify blood by local population of Nawargaon village.
- It purifies blood.
- Leaf extract is used in the treatment of Asthma.
- In toothache, latex of the tree is applied on teeth and gums.
- Root extract is used in treatment of headache.
- To relieve body ache, water boiled with stem bark is used for bathing.
- Extract of stem bark is used as tonic.
- Stem bark infusion is used to promote and increase breast milk.
- Decoction of bark and mashed fruits is used in fever and hallucinations.
- Decoction of bark and mashed fruits are used in sacred groves in Pudukottai district Tamil Nadu for fever and
- It is especially useful in treating gum problems and dental disorders such as bleeding gums, gum inflammation, sudden discharge of blood from gums, odontopathy etc.
- Bark and seed coat are used for strengthening the gum.
- They are useful in hallucinations, loss of consciousness, anorexia, bronchitis, leprosy and vitiated conditions of pitta.
- Seeds are useful in ulcers and the opacity of the cornea.
Other Facts
- Wood is used for heavy structural work, gate posts, and big beams.
- It is also used for turning and carpentry in spite of the difficulties of working with such dense wood.
- This species is often used as a rootstock for the sapodilla (M. zapota) in India.
- Its tender parts are used as tooth brush.
References:
https://en.wikipedia-on-ipfs.org/wiki/Manilkara_hexandra.html
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl/record/kew-120170
https://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/31542
http://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/Ceylon%20Iron%20Wood.html
https://uses.plantnet-project.org/en/Manilkara_hexandra_(PROSEA)
http://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Manilkara+hexandra