| Palm Grass Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Palm Grass |
| Scientific Name: | Setaria palmifolia |
| Origin | China, southern Japan, Taiwan, the Indian Sub-continent and south-eastern Asia |
| Colors | Pale brown (seed) |
| Shapes | 2 mm long and are egg-shaped (i.e. ovoid), but somewhat flattened. |
| Health benefits | Good for irregular menses, skin disorders, measles, freckle and blemish and toothache |
| Name | Palm Grass |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Setaria palmifolia |
| Native | China, southern Japan, Taiwan, the Indian Sub-continent (i.e. India, Nepal, Pakistan and Sri Lanka) and south-eastern Asia (i.e. Myanmar, Thailand, Indonesia, Malaysia, Papua New Guinea and the Philippines).It has been widely introduced to Australia, New Zealand, Pacific Islands and South and Central America |
| Common Names | African palm grass, bristle grass, bristlegrass, broad leaved bristlegrass, broadleaved bristlegrass, Buddha grass, highland pitpit, highlands pitpit, Indian palm grass, knotroot, Malaysian palm grass, palm grass, palm leaf setaria, palmgrass, palm-leaved setaria, pleated pigeon grass, short pitpit, Hailans pitpit |
| Name in Other Languages | Australia: Pleated pigeon grass Chinese: Zong ye gou wei cao (棕葉狗尾草), Zhu tou cao, Zhu ye cao, Zong ye cao, Zong mao, you gou wei cao, zhu ye cao, Zeng ye wei cao, Ruo ye fu, Ji mao, Ji ye cao, Chu mao. Zhu lou cao, Zhu ye cao Dutch: Palmgras English: Highland pitpit, Palm grass, Broadleaved bristlegrass, bigleaf bristlegrass, hailans pitpit, knotroot, palmgrass, short pitpit, Malayan palmgrass, Bristlegrass French: Que de rat German: Palmgras Hindi: Aruna, dhutesaro Indonesia: Lintabung, rumput daun pisang Japanese: Sasa kibi (ササキビ) Malay: Rumput daun pisang, Lintabung (Indonesia) Mizo: Hnahhrat Nepali: Baanspaate Kaaguno (बाँसपाते कागुनो) Papua New Guinea: Kura, pitpit Philippines: Agusas Russian: Shchetinnik pal’molistnyy (щетинник пальмолистный) Samoan: Vao ‘ofe‘ofe Spanish: Pasto de palma, zacate de mula Thai: Ya kap phai (หญ้ากาบไผ่ ) USA/Hawaii: Mau‘u Kaleponi |
| Plant Growth Habit | Large, tufted, clump-forming, long lived, evergreen, perennial grass |
| Growing Climates | Mesic valleys, wet forest, open forests, thicket margins, shady path sides, forest fringes, banks of streams, tropical and subtropical rain forests, wet sclerophyll forests, dry sclerophyll forests, Brigalow forests, sub-humid woodlands, semi-arid shrub woodlands, shady path-sides, roadsides, gardens, disturbed sites and waste areas |
| Soil | Prefers a well-drained but moisture-retentive fertile soil |
| Plant Size | Up to 1.5 m tall, but occasionally reaching up to 2 m in height |
| Leaf | Elongated (i.e. linear-elliptic) leaf blades are 40-80 cm long and 3-12 cm wide and are palm-like with a pleated (i.e. plicate) appearance. These leaf blades have rough (i.e. scabrous) but otherwise entire margins and pointed tips |
| Flowering season | December, January, February, March |
| Flower | The flower spikelets are arranged in loose branched clusters (i.e. panicles) usually 20-50 cm long and 2-10 cm wide. These clusters may be stiff or slightly drooping in nature with numerous slender branches, the lower ones up to 20 cm long. The individual spikelets are 2-4 mm long and are oval (i.e. ellipsoid) or elongated (i.e. lanceolate) in shape and borne on short stalks (i.e. pedicels) 1-4 mm long |
| Fruit Shape & Size | 2 mm long and are egg-shaped (i.e. ovoid), but somewhat flattened |
| Fruit Color | Pale brown |
| Plant Parts Used | Leaves, seeds |
| Propagation | By Division or seed |
Plant Description
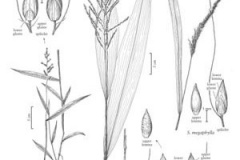
Palm Grass is a large, tufted, clump-forming, long lived, evergreen, perennial grass that normally grows up to 1.5 m tall, but occasionally reaching up to 2 m in height. The plant is found growing in mesic valleys, wet forest, open forests, thicket margins, shady path sides, forest fringes, banks of streams, tropical and subtropical rain forests, wet sclerophyll forests, dry sclerophyll forests, Brigalow forests, sub-humid woodlands, semi-arid shrub woodlands, shady path-sides, roadsides, gardens, disturbed sites and waste areas. The plant prefers a well-drained but moisture-retentive fertile soil. The upright flowering stems (i.e. erect culms) are covered in hairs, particularly near their joints (i.e. nodes). They are generally green in color and quite robust and about 3-7 mm thick.
Leaves
The tufted leaves consist of a roughly hairy (i.e. hispid) leaf sheath and a very large spreading leaf blade. The elongated (i.e. linear-elliptic) leaf blades are 40-80 cm long and 3-12 cm wide and are palm-like with a pleated (i.e. plicate) appearance. These leaf blades have rough (i.e. scabrous) but otherwise entire margins and pointed tips (i.e. acuminate apices). Upper surfaces are mostly hairless (i.e. glabrous), while their undersides are hairy (i.e. pubescent). Where the leaf sheath meets the leaf blade there is a dense row of hairs (i.e. ciliate ligule).
Flowers
The flower spikelets are arranged in loose branched clusters (i.e. panicles) usually 20-50 cm long and 2-10 cm wide. These clusters may be stiff or slightly drooping in nature with numerous slender branches, the lower ones up to 20 cm long. The individual spikelets are 2-4 mm long and are oval (i.e. ellipsoid) or elongated (i.e. lanceolate) in shape and borne on short stalks (i.e. pedicels) 1-4 mm long. They are usually subtended by a long bristle (4-10 mm long). Each of these hairless green spikelets consists of a pair of floral bracts (i.e. glumes) and two tiny flowers (i.e. florets). The lower floret has only male parts (i.e. three stamens) or is sterile, while the upper floret has both male and female flower parts (i.e. it is bisexual). Flowering occurs mainly during summer.
Fruit/ Seed
The mature seeds (i.e. grains or caryopses) are pale brown in color and remain enclosed within the remains of the flower spikelets. These seeds are about 2 mm long and are egg-shaped (i.e. ovoid), but somewhat flattened.
Traditional uses and benefits of Palm Grass
- The plant is used medicinally.
- It is also used for medicinal purposes, e.g. by the Mek tribes in Iranian Jaya, New Guinea.
- In Perak a compound decoction is drunk for irregular menses.
- In the Philippines it is mixed with ashes of burned leaves to treat skin disorders.
- The Mangyans of Mindoro drink decoction of inflorescence for treatment of measles.
- In the Tao Dam forest, Wangkrajae Village in Thailand, rhizome used by natives as ingredient in herbal mix to treat freckle and blemish.
- It is used for toothache in Bougainville.
Culinary uses
- Seeds are boiled or roasted and used as a substitute for rice.
- Hearts of young shoots can be eaten raw, steamed or cooked with rice.
- Very young plants are eaten raw as a side dish with rice.
- Palm Grass has been used in the past as a human food source and may still be in Papua New Guinea.
- Grain of the grass sometimes used as rice substitute.
- In Malaya, tender shoots are eaten as vegetable, raw, steamed, or cooked with rice.
Other Facts
- It is cultivated as an ornamental plant for its palm-like pleated leaves.
- A folk belief in Taiwan holds that the number of latitudinal creases on the leaf predicts the number of typhoons that will hit the area in the coming or current typhoon season.
- It is known locally as typhoon grass.
- It is also used as shading material in plant nurseries.
- In Papua, New Guinea, the species is used for good fortune when playing cards and for hunting birds.
- In New Guinea, leaves used to counter magic spells.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=41262#null
http://www.hear.org/pier/species/setaria_palmifolia.htm
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxon/taxonomydetail?id=33832
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Setaria+palmifolia
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/119079
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/SETPA
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl/record/kew-442588
https://keyserver.lucidcentral.org/weeds/data/media/Html/setaria_palmifolia.htm
http://www.stuartxchange.com/Agusais.html
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Setaria_palmifolia
https://www.nparks.gov.sg/florafaunaweb/flora/5/2/5284
https://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/Palm%20Grass.html
https://www.smgrowers.com/products/plants/plantdisplay.asp?plant_id=741
https://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/223679
http://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Setaria+palmifolia
https://plants.usda.gov/home/plantProfile?symbol=SEPA6