| Peking spurge Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Peking spurge |
| Scientific Name: | Euphorbia pekinensis |
| Origin | China, mainly in the eastern and central provinces |
| Taste | Bitter, Acrid |
| Health benefits | Beneficial for nephritis, edema, fullness of the chest, sticky sputum, conjunctivitis, epilepsy, carbuncle, tubercle, epistaxis, hematemesis, excess menses |
| Name | Peking spurge |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Euphorbia pekinensis |
| Native | China, mainly in the eastern and central provinces |
| Common Names | Da Ji, Peking spurge |
| Name in Other Languages | Catalan: lleteresa pequinesa Chinese: Da Ji (大戟), Jing Da Ji, Hong Da Ji English: Peking spurge Japanese: Taka-tōdai (タカトウダイ) Korean: Dae geuk (대극) Russian: Molochay pekinskiy (молочай пекинский), molochka pekinskaya (молочка пекинская) |
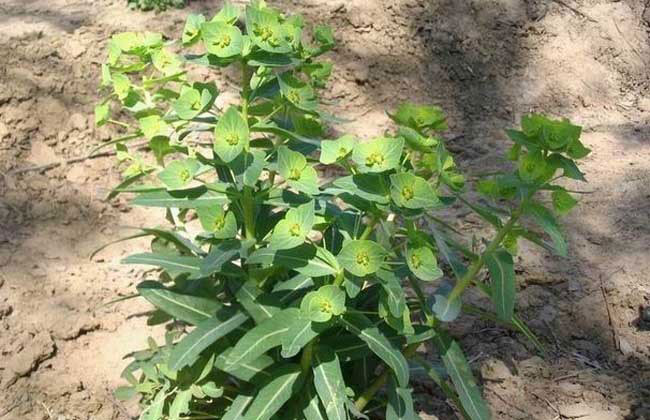
| Plant Growth Habit | Erect annual or flowering herbaceous perennial plant |
| Growing Climates | Grassy places in lowland and mountains |
| Soil | Prefers a light well-drained moderately rich loam in an open position. Succeeds in dry soils |
| Plant Size | Up to 0.60 meters tall |
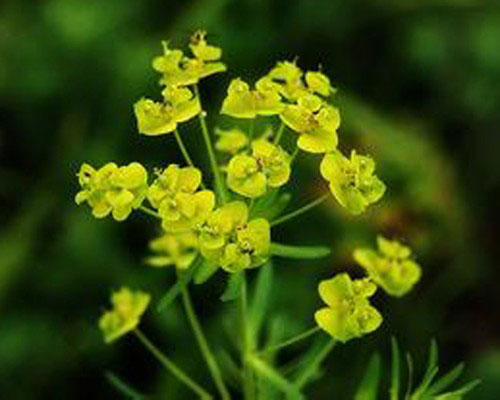
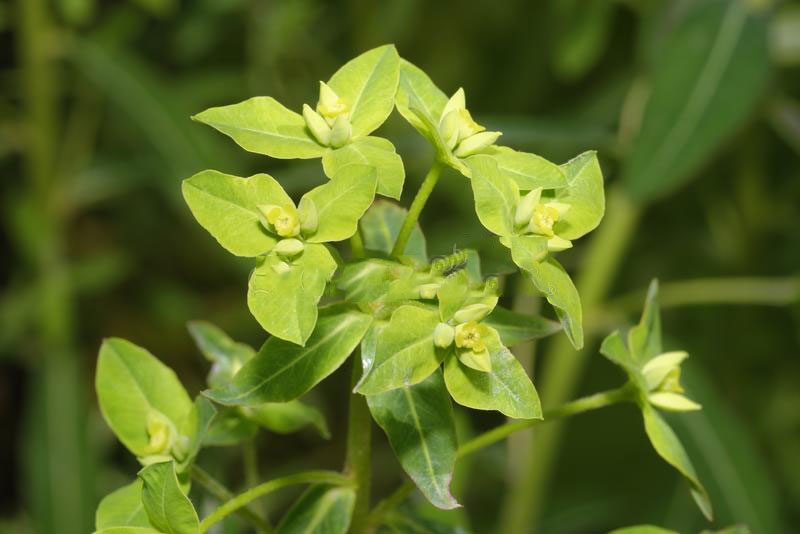
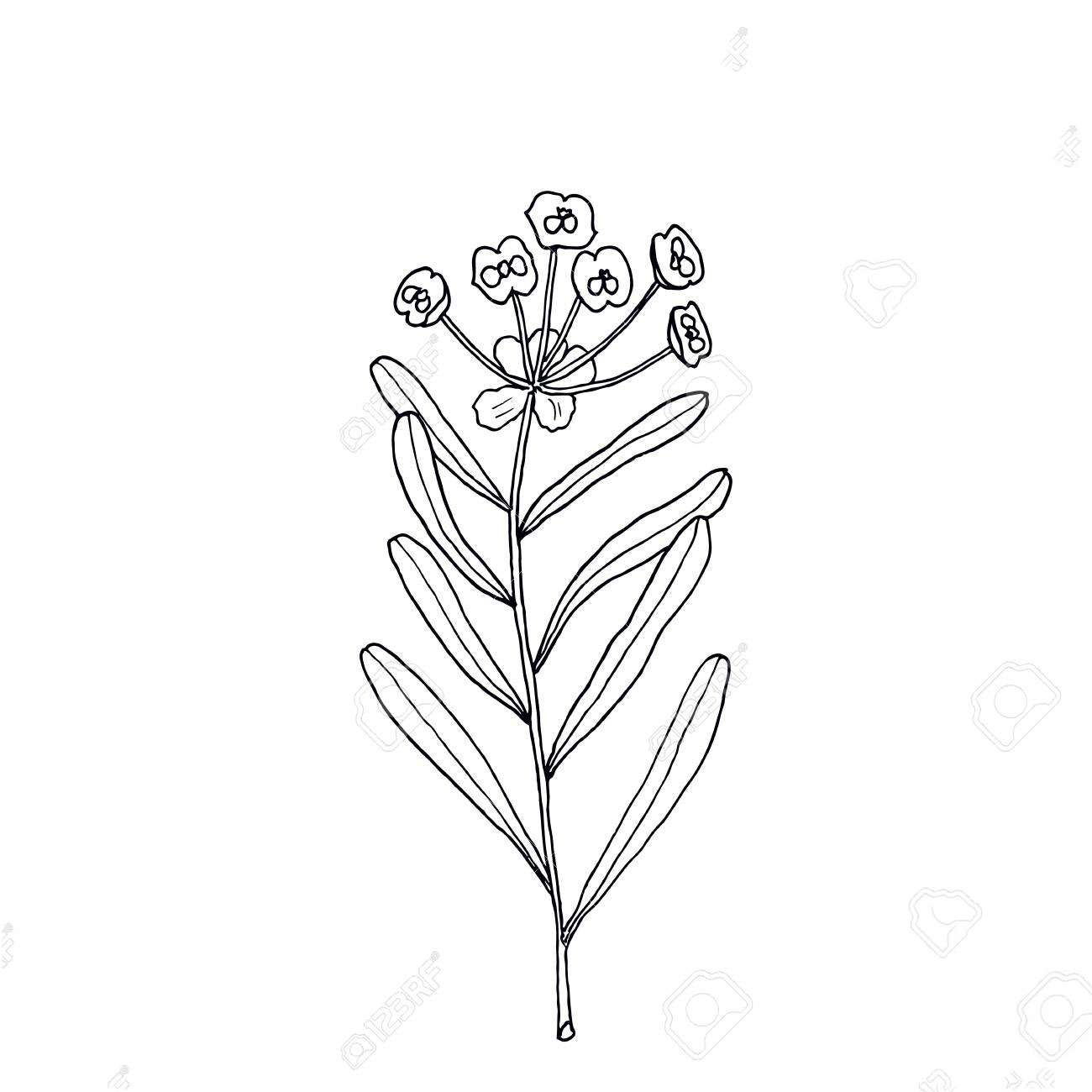
| Leaf | Elongated oval shaped, 3 to 8 cm long and in whorls of five (three or more leaves around the stem at each node) and several peduncles grow from the center and bloom yellow-green flowers. Leaves turn red in autumn. |
| Flowering season | May to July |
| Flower | Flowers are like buds covered by bracts (transformed leaves at the base of flower) and have no petals and calyx. Have four yellow protrusions called leaf glands that produce nectar and have some stamens and one pistil inside |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Fruits have red wart-like protrusions and split open and drop seeds when ripen |
| Taste | Bitter, Acrid |
| Plant Parts Used | Root |
| Other Facts |
|
Flower & Fruit
Flowers are like buds covered by bracts (transformed leaves at the base of flower) and have no petals and calyx. Have four yellow lumps called leaf glands that produce nectar and have some stamens and one pistil inside. In each inflorescence, three male flowers with yellow glands and total buds bloom and give pollen. After that, female flowers bloom. Flowering normally takes in between May to July. Fertile flowers are followed by fruits that have red wart-like protrusions and split open and drop seeds when ripen.
Health benefits of Peking Spurge
Listed below are some of the popular health benefits of Peking spurge
1. Edema
Euphorbia pekinensis root and dried ginger are powdered and taken with ginger soup to treat edema (swelling caused by fluid retention).
2. Pain relieving
Euphorbia pekinensis root can be used externally to relieve toothache.
3. Skin Health
Pills made with Euphorbia pekinensis root, Angelica sinensis, white atractylodes rhizome and fresh pinellia ternata can be taken orally to treat painful sores.
Traditional uses and benefits of Peking spurge
- Da Ji is classified as a toxic herb in Chinese medicine and so is only recommended for relatively serious diseases.
- It is considered to be one of the 50 fundamental herbs and is used as a cathartic to purge excess fluids in conditions such as pleurisy and ascites and for the treatment of kidney problems, especially nephritis.
- Research has shown that it is therapeutically useful in the treatment of ascites and nephritis, but it does produce significant side-effects.
- It should only be used under the supervision of a qualified herbalist.
- Root is antibacterial, diuretic, emetic, emmenogogue, purgative and vasodilator.
- It is used in the treatment of edema, fullness of the chest, sticky sputum, epilepsy, carbuncle and tubercle.
- When used in conjunction with licorice, diuretic and purgative actions are inhibited.
- Externally, it is applied to inflamed sores to reduce swelling.
- It is taken as a cathartic to purge excess fluid in conditions such as pleurisy and ascites (excess fluid in the abdomen), and for the treatment of kidney problems, especially nephritis.
- The fresh juice of the herb can be used alone for epistaxis, hematemesis and excess menses.
- The leaves are used to treat skin irritations.
- The crushed flowers help heal conjunctivitis.
- The roots can be made into a paste to help ease stomach pain if used in small doses, used in larger doses, it will induce vomiting.
- The plant is believed to promote the production of blood platelets.
Precautions
- Sap consists of latex which is toxic on ingestion and highly irritant externally, causing photosensitive skin reactions and severe inflammation, especially on contact with eyes or open cuts.
- Toxicity can remain high even in dried plant material.
- Prolonged and regular contact with the sap is inadvisable because of its carcinogenic nature.
- Avoid use in pregnancy as it causes birth defects.
- It is toxic. Use under an expert supervision.
- This herb should not be mixed with Licorice root (Gancao), and it is contraindicated during pregnancy.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=1026022#null
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Euphorbia+pekinensis
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euphorbia_pekinensis
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/EPHBJ