| Salam panja Quick Facts | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
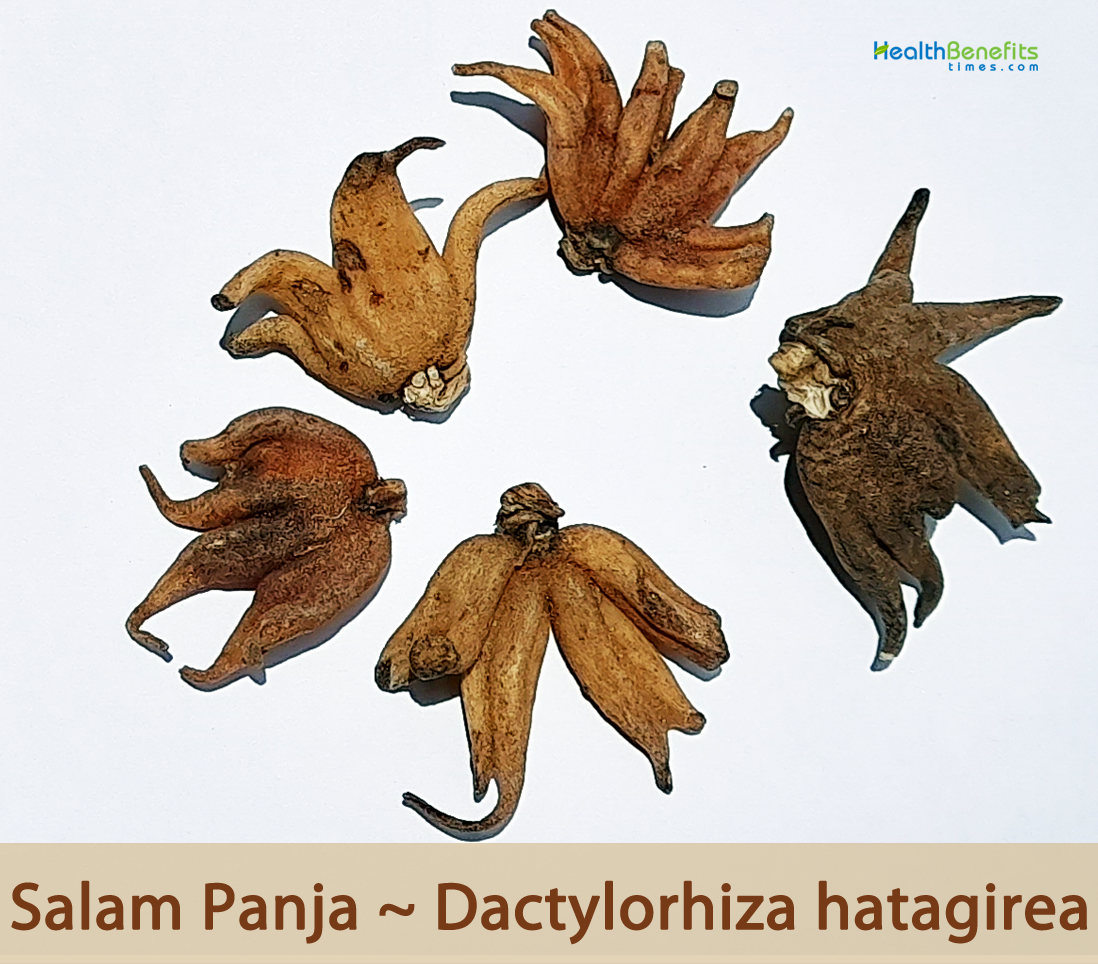
| Name: | Salam panja | |||
| Scientific Name: | Dactylorhiza hatagirea | |||
| Origin | India, China, Pakistan, Iran, Afghanistan, Tibet, Bhutan, Europe, North Africa, Temperate Asia, Mongolia, and Nepal | |||
| Shapes | Loculicidal capsules | |||
| Taste | Sweet | |||
| Health benefits | Male infertility, Gastrointestinal problems, Immunity, Stress, Skin conditions, Erectile dysfunctions and premature ejaculation | |||
| Name | Salam Panja |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Dactylorhiza hatagirea |
| Native | India, China, Pakistan, Iran, Afghanistan, Tibet, Bhutan, Europe, North Africa, Temperate Asia, Mongolia, and Nepal. In India, the plant is found in Jammu and Kashmir, including Ladakh, Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, and Sikkim |
| Common Names | Nar mada, Salap, Panch aunle, Himalayan Marsh Orchid, Marsh Orchids, Salam panja, Hatta had, Spotted Heart Orchid |
| Name in Other Languages | Afrikaans: Moeras orgidee Albanian: Orkide kënetore Amharic: Regiregi orikīdi (ረግረግ ኦርኪድ) Arabic: Mustanqae al uwrkid (مستنقع الأوركيد), khaziyat-ul-salab, salab panja Armenian: Chahchayin kholordz (: ճահճային խոլորձ) Azerbaijani: Bataqlıq orkide Bengali: -Mārśa arkiḍa (মার্শ অর্কিড) Bulgarian: Blatna orkhideya (блатна орхидея) Burmese: Saithkw (သစ်ခွ) Chinese: Zhǎozé lánhuā (沼泽兰花), zhǎng liè lán (掌裂兰) Croatian: Močvarna orhideja Czech: Bažina orchidej Danish: Marsk orkidé Dutch: Moeras orchidee English: Marsh orchid, Himalayan Marsh Orchid, Salampanja, Marsh Orchis, Spotted Heart Orchid Esperanto: Marĉa orkideo Estonian: Sood orhidee Filipino: Marsh orchid Finnish: Marsh orkidea French: Orchidée des marais Georgian: Ch’aobiani orkidea (ჭაობიანი ორქიდეა) German: Sumpforchidee Greek: Orchidéa élous (ορχιδέα έλους) Gujarati: Mārśa ōrkiḍa (માર્શ ઓર્કિડ) Hausa: Marsh orchid Hebrew: סחלב ביצה Hindi: Maarsh aarkid (मार्श आर्किड), Salampanja, salam, salam misri, salam panja, salampanja, salap, salib mistri Hungarian: Mocsári orchidea Icelandic: Mýrubrönugrös Indonesian: Anggrek rawa Irish: Magairlín riasc Italian: Orchidea palustre Japanese: Māshuran (マーシュラン) Javanese: Anggrek rawa Kannada: Javugu ārkiḍ (ಜವುಗು ಆರ್ಕಿಡ್), salamisri Kashmiri: Salem Panja Kazakh: Batpaqtı orxïdeya (батпақты орхидея) Korean: Seubji nancho (습지 난초) Kumaon: Hatajari Kurdish: March orchid Ladakhi: Mbolkp (ཨམབོལཀཔཨ) Ambolakpa Lao: Dok kuany mai (ດອກກ້ວຍໄມ້) Latin: Orchid Latvian: Purva orhideja Lithuanian: Pelkinė orchidėja Macedonian: Močurišna orhideja (мочуришна орхидеја) Malagasy: Mars orkide Malay: Rumput orkid Malayalam: Mārṣ ōrkkiḍ (മാർഷ് ഓർക്കിഡ്), salamisri Maltese: Orkidej tal-bassasa Marathi: Maarsh orkid (मार्श ऑर्किड) Mongolian: Namag tsakhirmaa (намаг цахирмаа) Nepali: Mārśa arkiḍa (मार्श अर्किड), Panch aonle (पाँच आँवले) Norwegian: Myrorkidé Oriya: ମାର୍ଶ ଅର୍କିଡ୍ | Pashto: مارش آرکډ Persian: رکیده باتلاق Polish: Storczyk bagienny Portuguese: Orquídea do pântano Punjabi: Māraśa āraciḍa (ਮਾਰਸ਼ ਆਰਚਿਡ) Romanian: Orhidee de mlaștină Russian: Bolotnaya orkhideya (болотная орхидея) Sanskrit: Mujjataka, munyatakah, salampamisri Serbian: Močvarna orhideja (мочварна орхидеја) Sindhi: دلت آرڪيڊ Sinhala: Vaguru ōkiḍ (වගුරු ඕකිඩ්) Slovenian: Močvirska orhideja Spanish: Orquídea de pantano Sudanese: Anggrek rawa Swedish: Marsh orkidé Tajik: Marşuri mars (маршури марш) Tamil: Catuppu mallikai (சதுப்பு மல்லிகை), salamisri Telugu: Mārṣ ārciḍ (మార్ష్ ఆర్చిడ్), Salamisri Thai: Kl̂wymị̂ bụng (กล้วยไม้บึง) Turkish: Bataklık orkide Ukrainian: Bolotna orkhideya (болотна орхідея) Unani: Buzidan, Salab Misri Urdu: Salap , bolotna orkhideya (دلدل آرکڈ), ood saleeb, salab misri, salabmisri Uzbek: Marsh orkide Vietnamese: Hoa lan đầm lầy Welsh: Tegeirian y gors Zulu: I-marsh orchid |
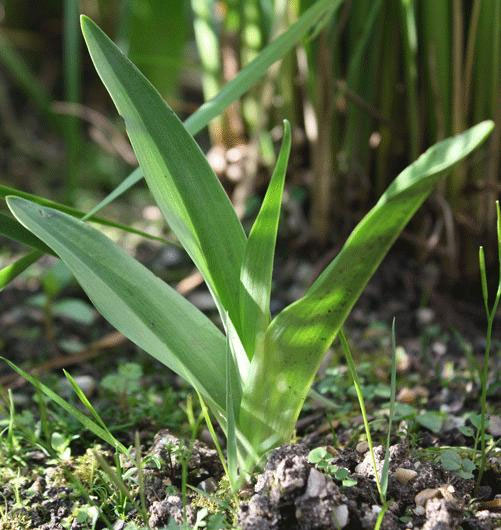
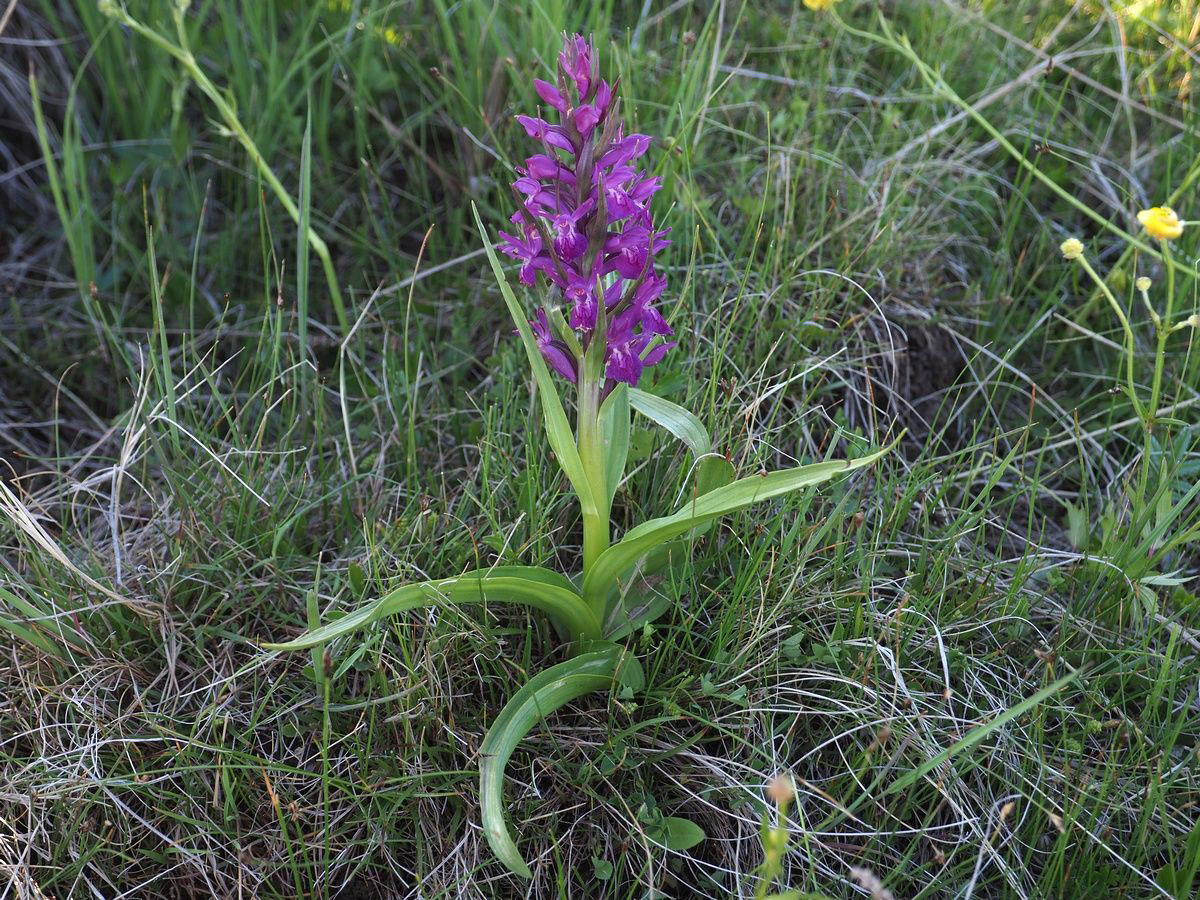
| Plant Growth Habit | Terrestrial glabrous herb |
| Growing Climates | Grows in damp pastures, open areas, shrub land, open meadows, open slopes and marshes |
| Soil | Grow best in moist meadow soils. Soil must be dark grey, granular, sandy loam, micaceous sandy soils at greater depth |
| Plant Size | About 20-25 cm |
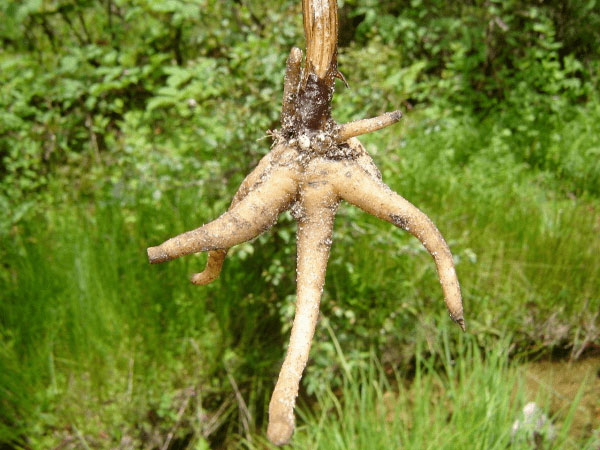
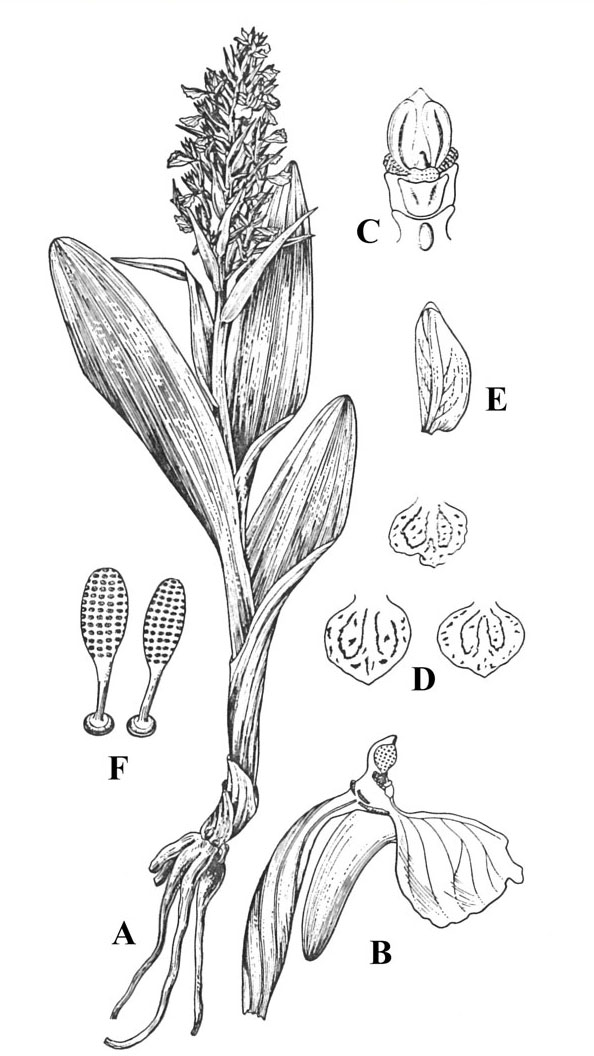
| Root | Roots are tuberous, divided into 2 or 3 lobes |
| Tuber | Tubers slightly flattened, palmately divided into 3-5, finger like lobes |
| Leaf | Leaves are 4-6, cauline, leaf blade oblong to linear lanceolate, 8 -15 cm long and 1.5-3 cm wide, base sheathing, apex obtuse or acuminate. |
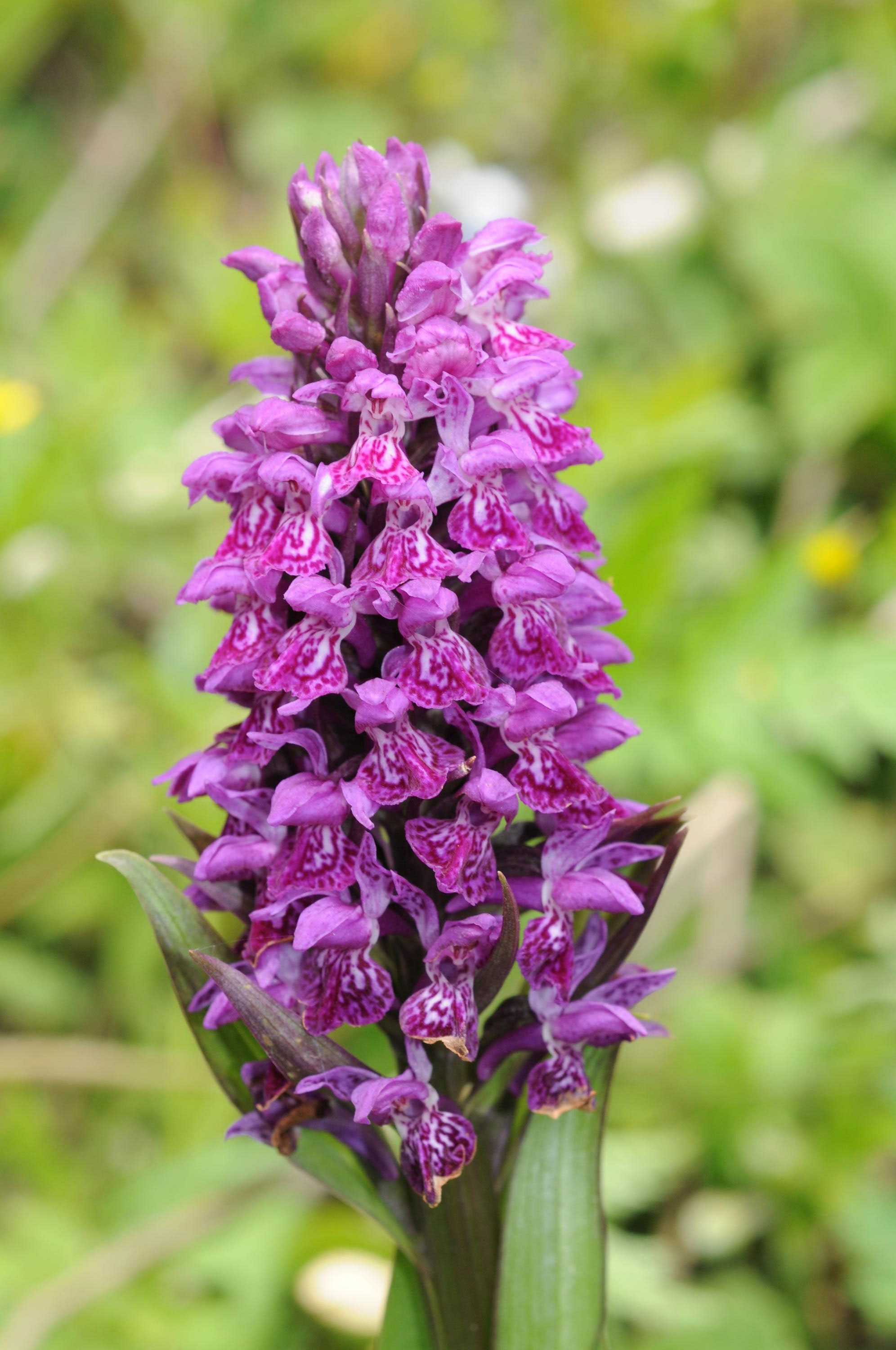
| Flowering season | June–July |
| Flower | Pink purple flowers are borne in upright dense spike inflorescences and are zygomorphic, having fused male and female reproductive organs. Flowers are purple and the bracts green, narrowly lance-shaped, lower longer than the flowers, upper slightly shorter. Flowers are about 1.8 cm long, including the curved spur. |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Loculicidal capsules |
| Propagation | By seeds and tuber cuttings |
| Taste | Sweet |
| Plant Parts Used | Tubers, roots |
| Available Forms | Juice, oil and paste |
| Health Benefits |
|
Ethno Medicinal uses of different part
| S. No | Ailment/Use | Plant Part | Place/Country | Mode of Application |
| 1. | Respiratory (asthma, bronchitis, lungs, and other pulmonary problems) | Leaves and tubers | India (Ladakh, Gharwal Himalaya) Nepal (Dolpa, Rasuwa, Humla, Jumla, and Mustang districts) | · Decoction obtained from the tubers is mixed with boiled water and taken
· Inhalation of stream of plant parts boiled in water · Dried tubers are mixed with other medicinal plants and boiled in water for daily consumption |
| 2. | Neurological (brain tonic, nerve tonic) | Leaves and tubers | India (Gharwal Himalaya), Nepal | · Extract obtained from tubers and leaves is taken in the morning and after dinner
· Decoction of the plant is consumed as juice |
| 3. | Digestive (stomachache, chronic diarrhea, intestinal disorders) | Tubers | India (Gharwal Himalaya, Arunachal Pradesh), Nepal (Dolpa, Rasuwa, Humla, Jumla, and Mustang districts) | · Plant parts are boiled in water and the extract (crude drug) is used
· Tubers of the plant are ground to fine powder, mixed with other medicinal herbs, and taken with milk or water. |
| 4. | Urinary (kidney disorders, burning sensation, and urine discharge) | Tubers | India (Gharwal Himalaya) | Unspecified |
| 5. | Sexual (sexual activity, seminal debility, erectile dysfunction) | Tubers | India (Gharwal Himalaya), Pakistan (Gilgit), Nepal (Dolpa, Rasuwa, Humla, Jumla, and Mustang districts) | Extract of the root is taken on empty stomach and after dinner to increase sexual activity |
| 6. | External uses (headache, wound healing, skin problems) | Tubers | India (Gharwal Himalaya, Kuman Himalayas, Arunachal Pradesh), Nepal (Dolpa, Rasuwa, Humla, Jumla, and Mustang districts) | · Plant parts are crushed, mixed with turmeric, and applied externally
· Powdered roots are spread over wounds to control bleeding · Tubers are ground into fine powder, mixed with mustard oil, and applied on wounds |
| 7. | Others (backache, bone fracture, fever, weakness, general debility, milk flow in lactating mothers) | Tubers and leaves | India (Gharwal Himalaya, Western Himalaya, Manali), Pakistan (Gilgit and Bugrot valley), Nepal (Rasuwa district) | · Tubers are powdered and mixed with mustard oil for use externally
· Plant parts are boiled in water and their extract is dissolved in water and taken after meals. |
Health benefits of Salam Panja
Normally the root of Salam panja is used extensively in Ayurveda for its health benefiting properties. According to Ayurveda, this plant has the ability to calm Vata and Pitta dosha. It is sweet in taste and has cold potency. It is considered as one of the powerful Ayurvedic herbs for treating male infertility. It also has anti-inflammatory, anti-aging, antioxidant, and antimicrobial properties. Here are a few health benefits of the Salam panja.
1. Male infertility
Salam Panja is a wonderful herbal medication used for treating male impotency rising out of low sperm count or lack of sperm motility. Salam Panja helps to increase the sperm count by boosting the testosterone levels in the blood and improves the quality and motility of the sperms. Hence, it is considered an effective treatment for oligospermia and oligozoospermia.
2. Gastrointestinal problems
Salam panja is an excellent herb for dealing with gastrointestinal problems. It combats numerous digestion related problems like indigestion and acidity. It improves the overall health of the digestive system. It also provides relief from stomach aches.
3. Immunity
Salam panja is loaded with essential nutrients and has immunity-boosting properties that help build a stronger immune system. Consuming the root powder of this plant helps to flushes out the toxins from the body. It fortifies the body and provides energy.
4. Stress
Salam panja has the ability to calm the mind and body. It is used as a nervine tonic in Ayurveda. The chemical constituents present in Salam panja helps to reduce the high level of cortisol hormones and bring a calming effect on the person. It also promotes good sleep.
5. Skin conditions
Salam Panja is used to treat certain skin conditions like wounds and ulcers. It helps in the faster healing of wounds by encouraging the regeneration of skin cells and helping the repair processes of the body. Juice of this herb can be consumed to heal cuts, and wounds. This property of Salam Panja is also helpful in the management of gastritis, in which it repairs the damaged mucosa of the stomach and provides relief from hyperacidity.
6. Erectile dysfunctions and premature ejaculation
Salam Panja can be used to treat male health problems like erectile dysfunctions. It increases the strength of the muscles in the penile tissue and also increases the blood supply into the organ thus allowing a man to get an erection. This herb is known to possess a strong penile erection index, which is a measure of how long a man can maintain an erection. Hence, it is considered useful for treating premature ejaculation also.
Traditional uses and benefits of Salam Panja
- Juice extracted from stem of the plant treats inflammation of the gum and teeth.
- Juice helps to cure cuts, wounds and ulcers.
- Root paste of marsh orchid is applied as poultice on wounds and cuts.
- The extract treats intestinal disorder.
- Oil is applied topically on the penile tissue for curing erectile dysfunction and nightfall. It strengthens the muscles in the penile tissues.
- The herb is used for treating fractured bones.
- Salab Punja root is good for building mass.
- It promotes the formation of tissues resulting in increased muscle mass. It increases Body weight and promotes strength.
- It stimulates the physical performance in men. It enhances the stamina, strength and sex drive in men.
- It boosts the production of male hormones called testosterone.
- It promotes the production of Nitric oxide in the muscles of penile tissue.
- It is also used to treat Oligospermia (low sperm count) and Oligozoospermia (lack of sperm motility).
- It treats gastritis and hyperacidity.
- Marsh Orchid repairs damaged mucosa of the stomach.
- Salep obtained from tubers and leaves is used in curing ailments like dysentery, chronic diarrhea, etc.
- It is also useful in treating general debility, emaciation, seminal weakness, neurasthenia, and cerebro-pathy.
- Decoction of the tubers is helpful to relieve colic pain and fever, besides for speckling over cuts, burns, and wounds to stop bleeding.
- Plant is used to cure ailments such as chronic diarrhea, fractured bones, seminal debility, erectile dysfunction, gout, Parkinson’s disease, tuberculosis, and stomachache.
- Root paste is commonly used in promoting growth and blackness of hair.
- It effectively used in treatment of women after child birth via enhancing level of regenerative fluids.
Ayurvedic Health benefits
Libido Loss Male: Take 5 tablespoons Withania Somnifera, 5 tablespoons Asparagus Racemosus, 1.5 tablespoons Dodder, 2 pinches Saffron, 1 tablespoon Anacyclus Pyrethrum, 1 tablespoon Nutmeg and 1/2 tablespoon Marsh Orchid. Grind all ingredients together. Have half teaspoon with milk daily.
Other Facts
- It costs around NRs. 10,000-15,000 per kilo as of late 2015.
- Tubers of D. hatagirea show wide utilization in silk industries for sizing material.
- Plants are grown in gardens for decorative purposes.
- Aesthetically appealing appearance of the flowers makes them suitable for ornamental purposes (placed in flower vases, twisted within hair ponies, making bracelets and necklaces).
- Grounded stem and leaves are used as insect repellant.
- Leaves and stem of the plant are used as fodder for livestock.
- hatagirea helps in improving the flavor and taste, color and appearance, body and texture, and melting quality of frozen milk products.
- Young leaves and shoots are also used as vegetables.
- Extract of the flowers is used in perfume industries to increase fragrance.
- Tubers of the plants are used for witchcraft.
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dactylorhiza_hatagirea
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-55324
http://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/Himalayan%20Marsh%20Orchid.html