| Skunk Cabbage Quick Facts |
| Name: |
Skunk Cabbage |
| Scientific Name: |
Symplocarpus foetidus |
| Origin |
Eastern North America |
| Colors |
Green when young turning to black as they mature |
| Shapes |
Oval-shaped |
| Flesh colors |
Whitish |
| Taste |
Acrid taste |
| Calories |
11 Kcal./cup |
| Major nutrients |
Vitamin C (34.22%)
Vitamin A (25.14%)
Iron (11.75%)
Magnesium (9.52%)
Vitamin B9 (8.00%)
|
Symplocarpus foetidus, commonly known as skunk cabbage, eastern skunk cabbage, swamp cabbage, clumpfoot cabbage, meadow cabbage, foetid pothos and polecat weed is a low growing, foul-smelling tuberous plant of the Aurum family that grows in wetlands around the world. The plant is native to the eastern North America; it ranges from Nova Scotia and southern Quebec west to Minnesota, and south to North Carolina and Tennessee. It is secure as endangered in Tennessee. The skunk cabbage is named so because its leaves look a lot like the leaves of the cabbage. The whole skunk cabbage plant has a strong fetid smell largely depending on the unstable determinant and the smell is normally deteriorated by heat instantly.
Skunk Cabbage is remarkable in that it is able to generate heat when the ground is frozen. In fact, its flowers can warm up to around 70º F. This allows the plant to emerge and bloom when most other spring blooming species are still dormant. The root and underground stem (rhizome) are used to make medicine. The pungent smelling roots of the skunk cabbage have been a popular conventional cure for bronchitis, tight coughs and phlegm or catarrh. Several herbal medical practitioners recommend the skunk cabbage to treat nervous disorders as it is said to have moderate sedative or tranquilizing properties. In earlier times, an indigenous tribe of America also inhaled in the aroma of the mashed skunk cabbage leaves to get relief from headaches.
Plant Description
Skunk cabbage is a low growing, foul smelling tuberous plant that grows about 30-90cm (1-3ft) tall. The plant is found growing in swamps, wet woods, along streams, and other wet low areas and normally prefers moist, wetland soil. Roots are fleshy, contractile and rhizome is usually two inches or little more in length and measure one inch in diameter and 30 cm (1 ft.) thick. Skunk cabbage rhizomes are found in slanting slivers that are compacted and ridged. The rhizomes have a dark brown hue on the exterior and are white or yellowish inside.
Leaves
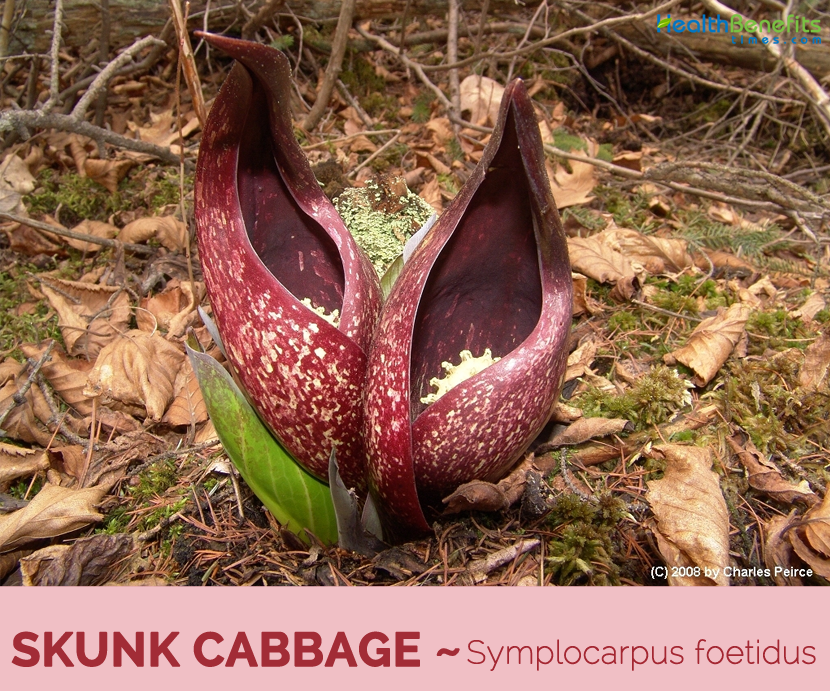
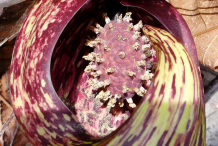
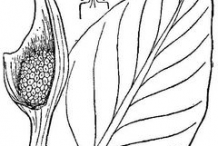
Eastern skunk cabbage has leaves which are very large entire margined with a plastic like appeal, and have a slight wrinkle, about 40–55 cm (15.75–21.5 in) long and 30–40 cm (12–15.75 in) broad. It flowers early in the spring when only the flowers are visible above the mud. The stems remain buried below the surface of the soil with the leaves emerging later. The flowers are produced on a 5–10 cm (2–5 in) long spadix contained within a spathe, 10–15 cm (4–6 in) tall and mottled purple in color.
Flower & fruit
As the spathe gets bigger, it will reveal another part inside, called a spadix. The spadix is a litle knob covered with small flowers. Numerous small, purple flowers grow on a small, oval, fleshy spike (or spadix), covered by a purple and yellowish-green, hood like bract (or spathe). Flowering time is from February to April, before the leaves appear. The whole plant emits a skunk or garlic odor. The plant bears oval-shaped fruit that are green when young turning to black as they mature. The fruit has wrinkled outer skin and whitish flesh.
Traditional uses and benefits of Skunk Cabbage
- It was used in the treatment of respiratory diseases, nervous disorders, rheumatism, and dropsy.
- Skunk cabbage was much used by the native North American Indians mainly for its expectorant and antispasmodic properties to treat bronchitis and asthmatic conditions, a use that is still used in modern herbalism.
- Root is antispasmodic, diaphoretic, diuretic, emetic, expectorant and slightly narcotic.
- Rootstock has been used internally in the treatment of respiratory and nervous disorders, including asthma, whooping cough, catarrh, bronchitis, mucous congestion and hay fever.
- It is occasionally used to treat epilepsy, headaches, vertigo and rheumatic problems.
- Externally, it has been used as a poultice to draw splinters and thorns, to heal wounds and to treat headaches.
- Root hairs or rootlets have been applied to dental cavities to treat toothache.
- Tea made from the root hairs has been used externally to stop bleeding.
- An inhalation of the crushed leaves has been used in the treatment of headaches.
- The leaf bases have been applied as a wet dressing to bruises.
- It is said to be helpful in epilepsy and convulsions during pregnancy and labor.
- Externally, as an ointment, it stimulates granulations, eases pain, etc. and relieves the pain of all external tumors and sores.
- It is helpful for nervous disorders, spasmodic problems, rheumatism, and dropsy.
- Some Native Americans boiled the root hairs to make a wash for stopping external bleeding.
- One tribe inhaled the odor of the crushed leaves to cure headache or toothache (which may be a classic case of a cure worse than the disease).
- Root is poultice for wounds, underarm deodorant; leaf is poultice to reduce swelling, they ate the root to stop epileptic seizures.
- It is very reliable in tuberculosis, chronic catarrh, fevers, whooping cough, epilepsy, convulsions, and pleurisy.
- It is also an excellent remedy in dysentery, convulsions, dropsy, hysteria, epilepsy, and for use during pregnancy.
- It is used in the treatment of cancer, fluid retention, excessive bleeding (hemorrhage), anxiety, snakebite, skin sores, splinters, swellings, and wounds.
- Skunk cabbage is also used to stimulate the digestive system.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VfXdfq7ppvU
Culinary uses
- While not considered edible raw, because the roots are toxic and the leaves can burn the mouth, the leaves may be dried and used in soups and stews.
- Root must be thoroughly dried or cooked before being eaten.
- Traditionally the root was dried for at least 5 weeks or boiled for 3 days before being eaten.
Dosing considerations for Skunk Cabbage
The appropriate dose of skunk cabbage depends on several factors such as the user’s age, health, and several other conditions. At this time there is not sufficient scientific information to determine an appropriate range of doses for skunk cabbage. Keep in mind that natural products are not always necessarily safe and dosages can be important. Be sure to follow relevant directions on product labels and consult your pharmacist or physician or other healthcare professional before using.
Other facts
- Skunk cabbage is protected as endangered in Tennessee.
- The plant is foul smelling when it blooms.
- Odor in the leaves serve to discourage large animals from disturbing or damaging this plant which grows in soft wetland soils.
- The water should be changed at least once during the cooking process.
- It should not be stored for a long time because it loses its medicinal qualities.
- An infusion of the powdered root has been used as a wash to ‘cure a strong smell under your arm.
- Skunk cabbages do not produce seed until they are five to seven years old.
- Skunk Cabbage leaves are poisonous to mammals (including us).
Precautions
- The plant is considered poisonous.
- Calcium oxylate in all parts of the plant is toxic and if consumed makes the mouth and digestive tract feel as though hundreds of needles are being stuck into it.
- However, calcium oxylate is easily destroyed by thoroughly cooking or drying the plant.
- Itching and inflammation possible with root contact.
- Handling the fresh leaves can cause skin to blister whilst excessive doses of the root can bring on nausea and vomiting, headaches, vertigo, dimness of vision and dizziness. Skin hives, rash, and itchy or swollen skin have been reported.
- Avoid during pregnancy and breast feeding.
- Avoid with kidney stones.
- Large doses cause nausea, vomiting, headache, vertigo and dimness of vision.
- It may worsen gastrointestinal ulcers, gastrointestinal inflammation or cause irritation, abdominal cramps, burning, blistering in the mouth and throat, colic, and watery or bloody diarrhea.
- Breathing problems, tightness in the throat or chest, and chest pain have also been reported with use of skunk cabbage.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=811065#null
https://davesgarden.com/guides/pf/go/2593/
http://www.pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Symplocarpus+foetidus
https://www.nps.gov/miss/learn/nature/skunkcabbage.htm
https://www.botanical.com/botanical/mgmh/s/skunkc52.html
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl/record/kew-198911
https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=syfo
http://medicinalherbinfo.org/herbs/SkunkCabbage.html
http://www.bmsch.org/health-library/natural-standard-herbs-and-supplements/article/skunk-cabbage/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Symplocarpus_foetidus
http://www2.fcps.edu/islandcreekes/ecology/skunk_cabbage.htm
www.bentoncountyiowa.org/webres/File/IRVM/…/Skunk%20Cabbage.pdf
http://www.gloucesterva.info/Portals/0/mg/documents/HelpDesk/LocalGardening/Wildflower_Spot/SkunkCabbageFeb2007.pdf?ver=2016-08-14-180527-070
Comments
comments