| Spanish cedar Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Spanish cedar |
| Scientific Name: | Cedrela odorata |
| Origin | Tropical Africa, southern Africa, and Madagascar |
| Colors | Initially green turning to reddish-brown as they mature |
| Shapes | Oblong-ellipsoid to obovoid overhanging capsule about 2 to 4 com long |
| Health benefits | Good for fever, sores, headaches, earache, wounds, malaria, bronchitis, diabetes, diarrhea, vomiting, hemorrhage, and indigestion. |
| Name | Spanish cedar |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Cedrela odorata |
| Native | Extensively planted in tropical Africa, in West as well as East and southern Africa, and in Madagascar. It has been established in Côte d’Ivoire, Ghana, Uganda, Tanzania, Madagascar and South Africa, and in several other tropical countries |
| Common Names | Barbados cedar, Mexican cedar, Spanish cedar, West Indian cedar, cedrela, cigar box cedar, Cedar Wood, Cedro Hembra, cedar, cigar-box tree, Brazilian mahogany, American cedar, Central American cedar, cigar box cedrela, Honduras cedar, Jamaican cedar, Mexican boxwood, stinking mahogany, red cedar |
| Name in Other Languages | Arabic: Sindirilaa ‘uwdwrata (سيدريلا أودوراتا) Brazil: Acaju, capiúva, cedreilro, cedro, cedro-amargo, cedro-amargoso, cedro-aromático, cedro-batata, cedro-bordado, cedro-branco, cedro-bravo, cedro-cheiroso, cedro-de-mato-grosso, cedro-do-amazonas, cedro-do-brejo, cedro-do-paraguai, cedro-fêmea, cedro-manso, cedro-mogno, cedro-rosa, cedro-verdadeiro, cedro-vermelho Bulgarian: Ispanski kedŭr (испански кедър) Burmese: Thit kado Costa Rica: Cedro amargo Chinese: Mo xi ge xiang hong chun (墨西哥香红椿), Xiang hong chun (香红椿 ), Yan yang chun (烟洋椿 ), Mòxīgē xiāngchūn (墨西哥香椿), Yáng chūn (洋椿), Xībānyá bǎimù (西班牙柏木), nan mei xiang chun, yang chun English: Barbados cedar, Cigar box cedar, Mexican cedar, Spanish cedar, West Indian cedar, Red Cedar, Cigar-box Wood, Cedro Hembra, Spanish-Ceda, cedar, cedarwood, cigar box wood, bastard cedar, cigar-box cedrela, false cedar Finnish: Punasetrela French: Cèdre acajou, Cèdre des barbares, Acajou rouge, Acajou-bois, Cedrat, Acajou amer, Acajou, Cedrela, acajou cédrel, acajou femelle, cédrèle odorante, acajou pays, Acajou à planches, acajou senti, acajou á muebles, cèdre, cedrela German: Westindische Zeder, Westindische Zedrele, Jamaica-Zedar, westindische Scheinzeder, cedrela, Westindische Scheinzeder, Zigarrenkistchenholz Haitian: Sèd Indonesian: Suren, Surian, cederwood Italian: Cedrella odorosa, cedro acajou Japanese: Cedoro (セドロ) Macedonian: Mirisliva cedrela (Мирислива цедрела) Malay: Surian (Indonesia) Malaysian: Stinking mahogany Mexico: Culche Myanmar: Thit kado Nicaragua: Cedro real North Frisian: Spoonsk Tseeder Norwegian: Vestindisk seder Persian: سدر اسپانیایی Polish: Cedrzyk wonny Portuguese: Cedro, Cedro-branco, Cedro-rosa, Cedro-vermelho, Cedro-cheiroso, cedro-aromatico, cedro-das-índias-ocidentáis, cedro-do-méxico, mogno-da-américa Quechua: Kanuwa ruya Russian: Tsedrela dushistaya (Цедрела душистая) Spanish: Cedro colorado, Cedro real, Cedro Rojo, Cedro, cedro amargo, cedro hembra, Cedrela, Cedro Rosado, cedro cubano, cédre, cédre espagnol, cedro macho, acajú, cedro hembra del país, redcedar, culche, cedro vermelho, cedro hembra, cedro mexicano, cedro español, cedro dulce, cedro del país, cedro blanco, cedro oloroso Swahili: Mwerezi Swedish: Cigarrlådeträd Thai: Yom-hom Tongan: Sita hina Upper Sorbian: Wonjaty cedrelowc |
| Plant Growth Habit | Monoecious, fast growing, medium-sized to fairly large deciduous, tree |
| Growing Climates | Forests, forest edges, disturbed areas, semi-deciduous to evergreen lowland, roadsides, lower montane rainforest, montane tropical forests and pastures |
| Soil | Not demanding of soil nutrients, tolerating soils high in calcium; it prefers fertile, free draining, weakly acidic soil but tolerates heavy soil |
| Plant Size | 30 -40 meters tall, exceptionally up to 50 meters. The straight, cylindrical bole can be 60 – 120 cm in diameter and unbranched for 15 – 24 meters |
| Bark | Young bark is smooth, grey and becomes deeply fissured with age |
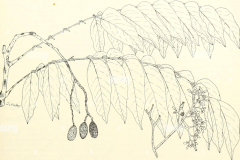
| Leaf | Leaves are alternate, paripinnately compound with 6–14 pairs of leaflets grouped towards the end of the branches, 15–50 cm (5.9–19.7 in) long |
| Flower | Flowers are unisexual, male and female flowers are very comparable in look, regular, 5-merous and aromatic. Pedicel is up to 2 mm long. Calyx is cup shaped, 2 mm long, split on 1 side, shallowly to deeply toothed. Petals are free and imbricate, forming into a long, columnar androgynophore by a medium carina, white or cream tinged red near the margin |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Oblong-ellipsoid to obovoid overhanging capsule with 5 thin, woody valves. They are about 2 to 4 com long, and are borne close to branch tips |
| Fruit Color | Initially green turning to reddish-brown as they mature |
| Seed | Seeds are 2–3 cm long, pale brown and winged at apex |
| Flavor/Aroma | Leaves smelling strongly of garlic or onions Flowers have strong malty smell |
| Plant Parts Used | Bark, leaves |
| Season | March-June |
| Culinary Uses |
|
Plant Description
Spanish cedar is a monoecious, fast growing, medium-sized to fairly large deciduous tree that normally grows about 30 – 40 meters tall, exceptionally up to 50 meters. The straight, cylinder-shaped bole may be 60 – 120 cm in diameter and are unbranched for 15 – 24 meters. Bark surface is rough and fissured, reddish brown mostly towards the base of trunk, greyish greater up. Inner bark is purplish red or pink. Branchlets are superbly to noticeably lenticellate. The plant is found growing in forests, forest edges, disturbed areas, semi-deciduous to evergreen lowland, roadsides, lower montana rainforest, montana tropical forests and pastures. The plant is not demanding of soil nutrition, tolerating soils great in calcium. It favors fertile, well-draining, softly acidic soil but endures heavy soil.
Leaves
Leaves are alternate, paripinnately compound with 6–14 pairs of leaflets grouped towards the end of the branches, 15–50 cm (5.9–19.7 in) long. Stipules are absent and rachis is somewhat hairy or glabrous. Petioles are up to 2 cm long. Leaflets are ovate to oblong-lanceolate, 7–15 cm (2.8–5.9 in) long and 3–5 cm (1.2–2.0 in) wide with the base indirectly shortened and unequal. They are hairless (glabrous) to densely pubescent.
Inflorescence/ Flower
Flowers are borne on large branched inflorescences. Flowers are unisexual, male and female flowers are very comparable in look, regular, 5-merous and aromatic. Pedicel is up to 2 mm long. Calyx is cup shaped, 2 mm long, divide on 1 side, trivially to deeply toothed. Petals are imbricate, creating a stretched, columnar androgynophore by a medium carina, white or cream tinged red near the margin. Stamens 5, free, but adnate to the androgynophore below; anthers are dorsifixed, opening by longitudinal slits. Male flowers consist of rudimentary ovary while female flower consists of non-dehiscing, smaller anthers. First flowering can be probable after 10-15 years.
Fruit
Fertile flowers are followed by oblong-ellipsoid to obovoid overhanging capsule with 5 thin, woody valves. They are about 2 to 4 com long, and are borne close to branch tips. Capsules are initially green turning to reddish-brown as they mature containing several seeds. Capsule ruptures when mature, commonly still attached to the parent tree. Each fruit consist of around 40 to 50 winged seeds. Seeds are 2–3 cm long, pale brown and winged at apex. Fruit development takes around 6 to 10 months.
Traditional uses and benefits of Spanish cedar
- Cedar wood is used in the treatment of headaches, fever, earache, sores and wounds.
- Cold water infusion of the stem bark is used in the treatment of fevers.
- Trunk bark and Root is used to lessen pain and fever.
- Bark is used for treating sores.
- Decoction of the leaves and bark is used to cure headaches.
- Decoction of the leaves is used to heal fevers.
- An infusion is used to cure earache.
- Trunk is gathered to prepare a decoction for abortion.
- Shavings of the wood are utilized in sweat baths for treating skin eruptions.
- Oil achieved from the seed is used to cicatrize wounds.
- Bark is used to treat malaria in Sao Tome.
- Bark immersed in hot water is used to numb foot soles in Tanzania.
- Bark resin is used to treat bronchitis.
- It is also used in the treatment of diabetes and malaria in traditional Suriname medicine.
- Bark infusion is used as a remedy for hemorrhage, diarrhea, and fever, indigestion, anti-inflammation and vomiting.
- Bark decoction is used to heal fever and malaria in Africa.
Other Facts
- Bark is used for making twine.
- Wood is fragrant and certainly termite and rot-resistant.
- It is used in making furniture, light constructions, wooden novelties, doors, ornamental veneer and musical instruments.
- Since it is a long-lived tree and offers an excellent timber, it is an outstanding option for use in reforestation program.
- It is also used for moldings, cabinets, paneling, boxes, plywood, exterior joinery, turnery, weather boards, matchboxes, boat building (especially racing boats), canoes, household tools, and louvered doors.
- Lower grades are appropriate for animal pens, fencing and crates.
- The revolting odor of the wood to insects makes it mostly appropriate for the production of wardrobe and clothing chests.
- It is a virtuous firewood type.
- It is used as an agroforestry variety in coffee and cocoa farming.
- Wood is the traditional option for creating the neck of flamenco and traditional guitars.
- First flowering is predictable after 10-15 years.
Prevention and Control
Due to the adaptable rules around (de)registration of pesticides, your national list of registered pesticides or applicable authority must be referred to regulate which products are lawfully permissible for use within your country while allowing for chemical control. Pesticides must always be utilized in a legal way, reliable with the product’s label.
Regeneration of transition zone forests on Santa Cruz Island, Galapagos, is being checked following the control of C. odorata, and though control is proving effective, eradication is not considered possible at present.
Saplings and seedlings have very shallow root systems and are sensitive to uprooting and root crushing. It is not resistant to fire and therefore mechanical and fire cures might show effective in certain situations. Seedlings can be physically removed, as is practiced in the Galapagos Islands, however larger plants require some form of chemical treatment even though it is noted that they tend not to covert well. In the Galapagos, hack and squirt use of 50% Tordon 22K has been found effective, but for trees >40 cm diameter, a 10% mixture of Tordon or Combo at 20% was found to be operational, or a cut stump cure of 5% Combo for smaller trees. Though an appreciated timber types, control by utilization of the wood might need cautious control of the chain of custody, as trade is planned due to C. odorata being a CITES listed types.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=29014#null
http://www.hear.org/pier/species/cedrela_odorata.htm
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxon/taxonomydetail?id=9685
https://pfaf.org/USER/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Cedrela+odorata
https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/10.1079/cabicompendium.11975
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/CEDOD
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-2707234
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cedrela_odorata
http://www.worldfloraonline.org/taxon/wfo-0000592446
https://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/246708
https://uses.plantnet-project.org/en/Cedrela_odorata_(PROTA)#Synonyms
https://www.srs.fs.usda.gov/pubs/misc/ag_654/volume_2/cedrela/ordota.htm
http://apps.worldagroforestry.org/treedb/AFTPDFS/Cedrela_odorata.PDF
https://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Cedrela+odorata
https://plants.usda.gov/home/plantProfile?symbol=CEOD