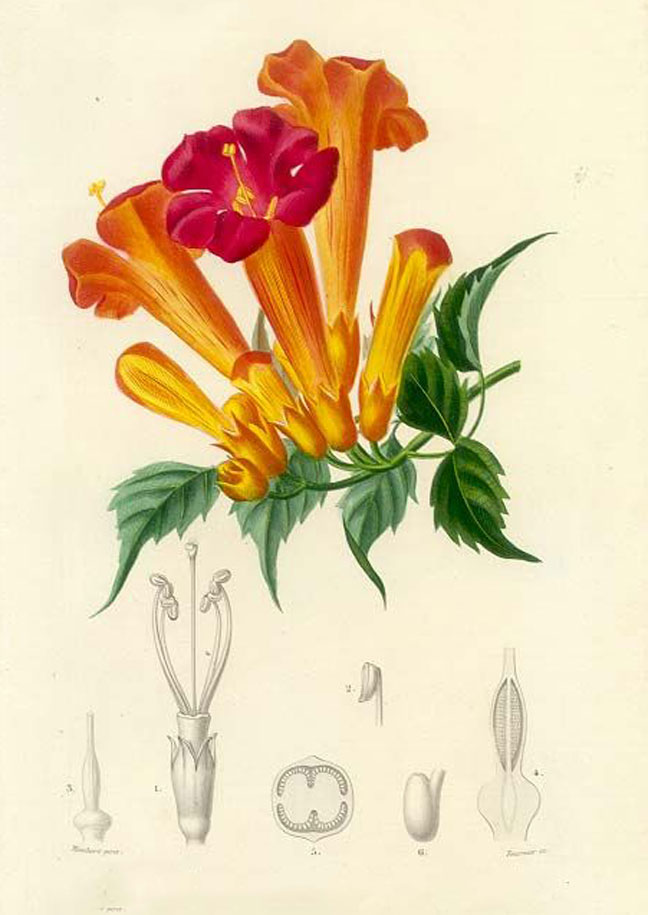| Trumpet vine Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Trumpet vine |
| Scientific Name: | Campsis radicans |
| Origin | Eastern, north-central, and south-central portions of the United States and has become naturalized in New England |
| Colors | Green when young turning to brown as they mature |
| Shapes | Long flat tapered (10-20 cm) capsules, 10-20 cm long which split open when ripe releasing flat winged seed |
| Taste | Sweet, Sour |
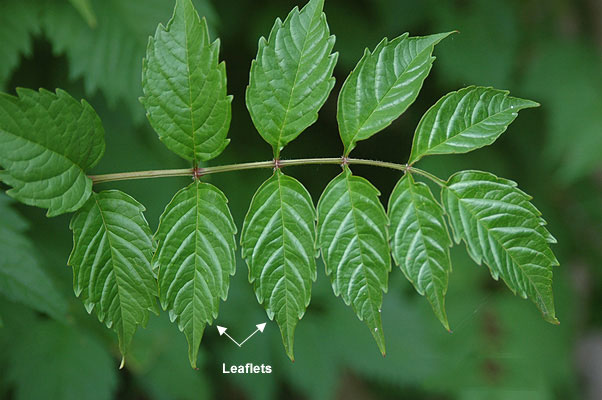
| Leaf arrangement | Opposite/sub opposite |
| Leaf Type | Odd-pinnately compound |
| Leaf Margin | Dentate |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate |
| Leaf Venation | Pinnate |
| Leaf type and Persistence | Deciduous |
| Leaf blade length | 2 to 4 inches |
| Leaf Color | Green |
| Fall color | Orange |
| Fall characteristic | Not Showy |
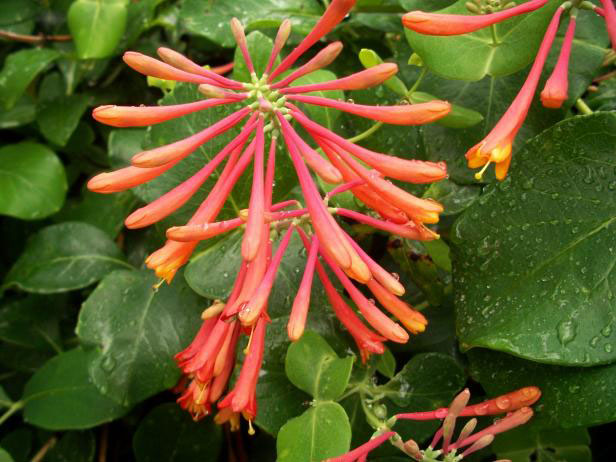
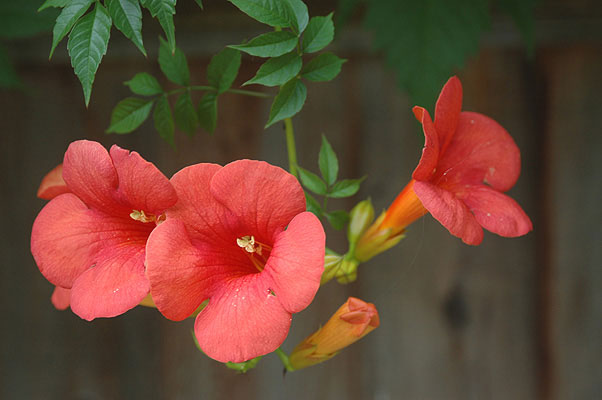
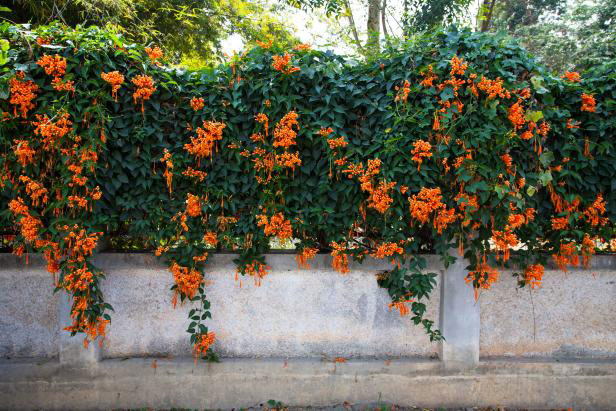
Flower
Periodically, short cymes of 2-8 flowers are produced along the length of the vine. Flowers are up to 3½ inch long and have an elongated funnel form shape that is trumpet-like in appearance. The corolla is orange to reddish orange; along its outer rim there are 5 shallow lobes that curl backward. The tubular calyx is reddish orange, leathery in texture, and 5-toothed. It is much shorter than the corolla. Along the inner surface of the corolla, there are reddish lines that function as nectar guides and 4 inserted stamens. There are extra-floral nectaries at the base of each flower. The blooming period occurs during the summer and lasts about 2 months. The abundance of flowers is variable; there is no floral scent.
| Flower Color | Yellow |
| Flower Characteristics | Summer flowering |
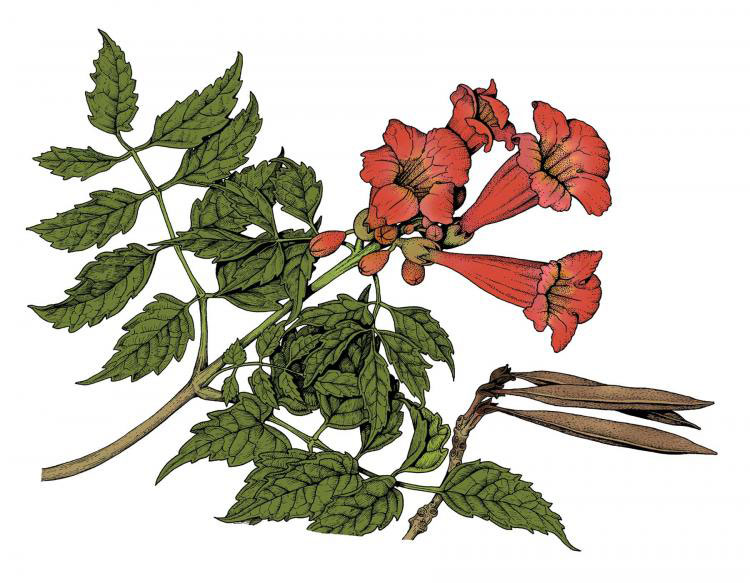
Fruit
Each flower is replaced by an linear elongated seed capsule about 6 inches long, 2-valved, slightly flattened, elliptic in cross-section with noticeable ridges along the sutures between the valves, the valves glabrous, with a leathery texture. As they matures this seed capsule dry and eventually splits apart into two sections to release hundreds of thin brown paper like seeds. The seeds are 6-9 mm long, flattened; the body is elliptic in outline, 2-lobed, brown, with a wing at each end, the wings is papery, light tan, with irregular margins. They are dispersed by the wind.
| Fruit Shape | Pod or pod-like |
| Fruit Length | 3 to 6 inches |
| Fruit Cover | Dry or hard |
| Fruit Color | Brown |
| Fruit Characteristic | Persists on the plant |
Other Facts
- It can be used as a ground cover plant in a sunny position.
- They can be allowed to scramble on the ground and will form an effective ground cover, rooting at intervals along the branches.
- They should be planted about 2.5 meters apart each way.
- radicans is an occasional food source for large mammals and terrestrial birds.
- Showy flowers of trumpet creeper make this plant appropriate for some gardening and landscaping needs.
- It is often used as a cover for fences, arbors, walls, pillars or large trellises and as a ground cover.
- Cigar-like fruit may be considered decorative during winter.
- Vines also provide habitat to ants.
Precautions
- There have been isolated cases reported of people suffering from dermatitis after handling the leaves.
- Avoid its use during Pregnancy.
- Avoid use in case of blood deficiency.
- Eating leaves or flowers may result in minor skin irritation with redness and swelling.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=34309#null
https://davesgarden.com/guides/pf/go/644/
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?id=8799
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Campsis+radicans
http://www.missouribotanicalgarden.org/PlantFinder/PlantFinderDetails.aspx?kempercode=b840
https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CARA2
https://courses.washington.edu/esrm412/protocols/CARA2.pdf
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fp099
http://coastalplainplants.org/wiki/index.php/Campsis_radicans
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-320348
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Campsis_radicans
https://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/265956
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/CMIRA
http://www.naturalmedicinalherbs.net/herbs/c/campsis-radicans=trumpet-vine.php
https://www.wildflower.org/plants/result.php?id_plant=cara2
http://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/Trumpet%20Creeper.html
https://plants.usda.gov/plantguide/pdf/pg_cara2.pdf