| West Indian elm Quick Facts | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
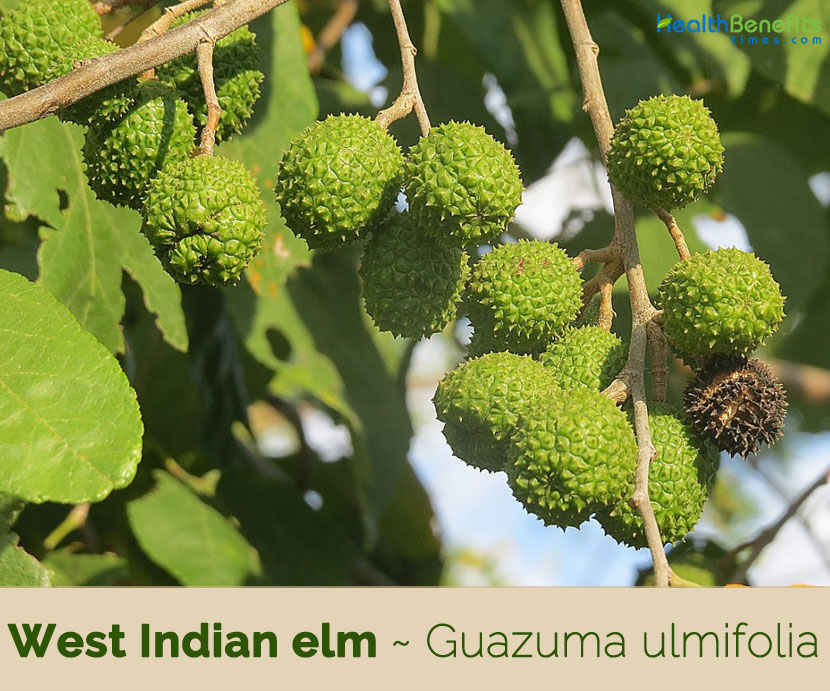
| Name: | West Indian elm | ||||
| Scientific Name: | Guazuma ulmifolia | ||||
| Origin | Caribbean, Central America, Mexico and Colombia, Peru, Ecuador, Bolivia, Argentina, Paraguay and Brazil | ||||
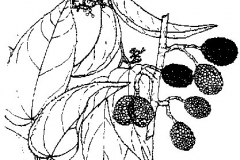
| Colors | Green when young turning to purplish black as they mature | ||||
| Shapes | Globose or ellipsoid capsule, woody, tubercled, 5-celled, 1.2-4 cm long and 1.2-2.5 cm wide, containing numerous, seeds | ||||
| Health benefits | Cholesterol, Slimming, Healthy Hair, Good for Diarrhea, Combat Respiratory Problems, Injury Recovery, Treatment of Ulcers, Fight Venereal Diseases, Fight against Bronchitis, Good for Estomacais Problems, Combat hair implant, Liver Health | ||||
| Country | Uses |
| Belize | For childbirth, diarrhea, dysentery, infections, prostate problems, rashes, skin, uterine problems, sores |
| Brazil | For asthma, blood cleansing, bronchitis, coughs, dysentery, excessive mucous, fever, hair loss, hepatitis, liver problems, parasites (head), pneumonia, skin diseases, syphilis, ulcers, and to increase perspiration |
| Colombia | As a uterine stimulant |
| Cuba | For bruises, burns, colds, flu, hemorrhoids, urinary insufficiency, wounds |
| Dominican
Republic |
For dysentery, fertility (veterinary), lung problems, and to increase perspiration |
| Guatemala | For bruises, dermatitis, erysipelas, fevers, gonorrhea, kidney diseases, skin disorders (irritation, eruptions, inflammation, sores, ulcers), stomachache, stomach inflammation, wounds, and to increase perspiration |
| Haiti | For blood cleansing, cough, diabetes, diarrhea, digestive sluggishness, fever, flu, fractures, scurvy, skin problems, wounds |
| Jamaica | For diarrhea, elephantiasis, leprosy, malaria |
| Mexico | For asthma, chest problems, childbirth, constipation, diarrhea, dysentery, elephantiasis, fever, gastrointestinal problems, hemorrhages, infectious diseases, kidney problems, leprosy, malaria, rashes, skin problems, syphilis, uterine pain, wounds |
| Peru | For diarrhea, dysentery, asthma, bronchitis, dermatitis, elephantiasis, fever, hair loss, hepatitis, kidney disease, leprosy, liver disease, lung problems, malaria, syphilis |
| Venezuela | For syphilis, wounds, and to increase perspiration and lower body temperature |
| Elsewhere | For asthma, bleeding, bronchitis, chest problems, elephantiasis, hair loss, hypertension, kidney disorders, liver problems, obesity, skin problems, stomachaches, and to increase perspiration |
Ethno medical Information on West Indian elm
| Plant Part | Place | Documented Ethnic Use | Type Extract | Route | Used for |
| Bark | Belize |
|
|
|
|
| Bark | Brazil |
|
|
|
|
| Bark | Brazil |
|
|
|
|
| Bark | Dominican Republic |
|
|
|
|
| Bark | Colombia |
|
|
|
|
| Bark | Cuba |
|
|
|
|
| Bark | Guatemala |
|
|
|
|
| Bark | Haiti |
|
|
|
|
| Bark | Jamaica |
|
|
|
|
| Bark | Panama |
|
|
|
|
| Bark | Peru |
|
|
|
|
| Bark | Peru
|
|
|
|
|
| Bark | Mexico |
|
|
|
|
| Bark + Fruit | Mexico |
|
|
|
|
| Bark+ Leaf | Mexico |
|
|
|
|
| Fruit | Haiti |
|
|
|
|
| Fruit | Mexico |
|
|
|
|
| Leaf | Guatemala |
|
|
|
|
| Leaf | Haiti |
|
|
|
|
| Leaf | Peru |
|
|
|
|
| Leaf | Mexico |
|
|
|
|
| Entire Plant | Mexico |
|
|
|
|
| Root | Mexico |
|
|
|
|
| Stem bark | Mexico |
|
|
|
|
Different parts of plant and its uses
Bark: Asthma, bruises, burns, alopecia, constipation, bronchitis, dermatitis, dermatitis, coughs, diarrhea, dysentery, fevers, childbirth, fractures, gastrointestinal pain, elephantiasis, gonorrhea, grippe, hypertension, infections, hemorrhoids, hemorrhage, influenza, leprosy, liver problems, malaria, nephritis, kidney problems, pneumonia, prostate problems, pulmonosis, skin conditions, stomach inflammation, stomach ache, syphilis, ulcers, uterine pain, wounds.
Fruit: Hemorrhage, infection, diarrhea, uterine pain.
Seed: Diarrhea, constipation, astringent, and in stomach troubles.
Leaves: Asthma, alopecia, bruises, skin diseases, dermatitis, ulcers, dysentery, erysipelas, fevers, inflammation, kidney diseases, liver diseases, skin eruptions, sores, wounds.
Root: Childbirth.
Stem bark: Diarrhea
Health benefits of West Indian elm
Listed below are few of the popular health benefits of using West Indian elm
1. Cholesterol
Take some dry West Indian elm leaves. Pour enough hot water, such as making tea. Strain before drinking. In order not to bland, add one tablespoon of honey or sugar.
2. Slimming
Take 7 fresh leaves of West Indian elm and wash them. Add a piece of rhizome bangle, ginger, turmeric or white. Boil one-half cup water until remaining one glass. Once cool, strain and drink it. Mixes should be concurrent with white ginger or turmeric to reduce the effects of gastric irritation.
3. Healthy Hair
It is often used in the manufacture of products such as shampoos, conditioners and creams that prevent hair loss, dandruff and seborrhea. The ingredient still treats oiliness, moisturizes the hair and combat baldness.
4. Good for Diarrhea
The astringent properties from this plant help in the balance of the intestinal flora, often affected by the action of bacteria, viruses, or parasites that cause diarrhea and dehydration.
5. Combat Respiratory Problems
Tea provides outstanding results to treat respiratory problems such as colds, flu, bronchitis, and asthma. The substances contained in the plant contribute to clear the airway, promoting the removal of the viruses and bacteria causing these diseases.
6. Injury Recovery
The tonic properties and analgesic effects of this plant helps relieve the aches and pains caused by bruises, preferring the recovery of the body in less time.
7. Treatment of Ulcers
The consumption of West Indian elm tea is related with the decrease of the symptoms of ulcers, favoring the digestion and avoiding episodes of intoxication.
8. Fight Venereal Diseases
West Indian elm plays an important role for the treatment of venereal diseases such as syphilis.
9. Fight against Bronchitis
West Indian elm tea is helpful in the treatment of various respiratory diseases, such as asthma, bronchitis, and coughs. The drink also helps to relieve symptoms of fever as well.
10. Good for Estomacais Problems
Drink made from its crushed seeds with water is also great to treat stomach problems, diarrhea, ulcer, flu, colds, venereal diseases, and bruises, and is a great diuretic natural.
11. Combat hair implant
This is undoubtedly one of the amazing benefits of West Indian elm. It is an ingredient used in products that seek to deal with problems such as baldness or thinning of hair. The properties present in the plant help to stimulate the hair to grow strong and healthy.
12. Liver Health
Tea made from the bark of the West Indian elm has properties, wound healing, astringent, antiseptic, and stimulates the production of sweat and is great to clear the liver.
Traditional uses and benefits of West Indian elm
- Plant is antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antifungal, antitussive, antiviral, astringent, blood purifier, cardiac, diaphoretic, digestive, diuretic, febrifuge, hemostatic, hypotensive, and oxytocic, vulnerary.
- Bark also consists of a chemical called kaurenoic acid which has been recognized with antibacterial and antifungal properties.
- Plant lowers heart rate and blood pressure, relaxes smooth muscles and stimulates the uterus.
- Various research using leaf and bark extracts have clinically proven remarkable antibacterial activity against several disease-causing pathogens, including Bacillus, Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, E. coli, and Neisseria gonorrhea.
- Applied externally, it is used to bathe wounds, rashes and sores; to treat skin problems, including dermatosis, elephantiasis and leprosy; it is applied to the scalp to arrest hair loss and combat parasites of the scalp.
- The fruit (in Mauritius), the roasted seeds (in Java), and the bark (in India) are officinal remedies against elephantiasis.
- An infusion of the crushed, seed soaked in water, is used to treat diarrhea, dysentery, colds, coughs and venereal diseases.
- The Mixe Indians in the lowlands of Mexico use a decoction of dried bark and fruit to treat diarrhea, hemorrhages and uterine pain.
- The Huastec Mayans of northeastern Mexico use the fresh bark boiled in water to aid in childbirth, for gastrointestinal pain, asthma, diarrhea and dysentery, wounds, and fevers.
- Mayan healers in Guatemala boil the bark into a decoction to treat stomach inflammation and regular stomachaches.
- Indigenous people have long used West Indian elm for asthma, bronchitis, diarrhea, kidney problems, and syphilis in Amazon.
- They use a bark decoction topically for baldness, leprosy, dematosis and other skin conditions.
- In Brazilian herbal medicine practices, a bark decoction is used to promote perspiration, cleanse and detoxify the blood, and to suppress coughs.
- Bark decoction is also prepared and is used topically to promote hair growth, to combat parasites of the scalp, and to treat various skin conditions.
- Dried bark and/or dried leaves are made into tea (standard infusion) and used for kidney disease, liver disease, and dysentery in Peru.
- Dried leaves of the tree are brewed into a tea and drunk for fevers, kidney disease, and skin diseases, as well as used externally for wounds, sores, bruises, dermatitis, skin eruptions and irritations, and erysipelas in Guatemala.
- Fruit is used as a cure whooping cough.
- Decoction of the seeds that have been burned like a coffee can be drunk as cure for constipation.
- Bark is used to induce perspiration, as a tonic and a blood cleanser, and is used to treat a wide range of disorders including, digestive tract problems such as kidney problems, uterine pain, venereal disease and as an aid to childbirth, respiratory tract problems such as asthma, bronchitis, coughs and pneumonia, fever and hemorrhages.
- Beverage of crushed seeds soaked in water is astringent and diuretic in nature which is also used to treat cold, cough, contusions, constipation, diarrhea, dysentery, venereal disease and in various stomach troubles.
- It cures Anorexia, Bronchitis, gonorrhea, leprosy, asthma, high blood pressure, syphilis, baldness and indigestion.
Other facts
- Timber is used for posts, general carpentry, interior construction, furniture, barrel stave, boxes, crates, tool handles, gun-stocks and firewood and charcoal.
- It is an important source of livestock fodder in many areas, particularly during the dry season when pasture grasses are unavailable.
- It is fast-growing, tolerant of full sunlight and provides food for the native fauna.
- Tough, fibrous bark and young stems are used to make rope and twine.
- Mucilaginous sap is used sometimes in sugar fabrication to clarify syrup.
- Heartwood is pinkish to brownish; it is not clearly demarcated from the light brown sapwood.
- Fibrous wood is light in weight; it is not durable, It is used for posts, interior carpentry, light construction, furniture, boxes and crates, shoe horns, tool handles etc.
- The tree can be used for fuel and to make charcoal.
- The charcoal is of high quality.
Precautions
- West Indian elm bark has been documented in several animal studies to have uterine stimulant activity and it should not be taken during pregnancy.
- People with a history of heart problems, those taking heart medications, or those with low blood pressure should not use this plant without supervision and advice of a qualified health care practitioner.
- The plant should be taken internally only in moderation, as large doses can cause nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=21546#null
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?id=312760
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Guazuma+ulmifolia
https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=GUUL
https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/8ae2/a1d8648692c44c2eefe6f98c402d628ca7a5.pdf
https://wikivisually.com/wiki/Guazuma_ulmifolia
http://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Guazuma+ulmifolia
https://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/264307
http://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/West%20Indian%20Elm.html
https://sl.ku.dk/rapporter/seed-leaflets/filer/guazuma-ulmifolia-16.pdf
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/GUZUL
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Guazuma_ulmifolia
https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/f87a/98afee41739efc41d172d1c6bff022f3b357.pdf
https://italisvital.info/cablote-cualote/
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl/record/kew-2834705
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/26124
http://old.worldagroforestry.org/treedb/AFTPDFS/Guazuma_ulmifolia.PDF
https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/154538-Guazuma-ulmifolia
http://www.rain-tree.com/reports/mutamba-tech.pdf