| Yellow Elder Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Yellow Elder |
| Scientific Name: | Tecoma stans |
| Origin | American southwest, from Texas to Arizona |
| Colors | Green when young, turns to brown upon ripening |
| Shapes | Large, elongated (linear), shiny and somewhat flattened (compressed) capsules 10-30 cm long and 5-20 mm wide |
| Taste | Bitter |
| Health benefits | Treat hyperglycemia, gastrointestinal and urinary tract disorders, jaundice, toothaches, headaches, colds, skin infections, and scorpion, snake, and rat bites |
| Name | Yellow Elder |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Tecoma stans |
| Native | American southwest, from Texas to Arizona , and regions of Chihuahua and Sonora, Mexico. It is often found in other warm climates of the Americas such as Florida, and the Caribbean. It can also be found as far south as Argentina |
| Common Names | Ginger-Thomas, Trumpet flower, Trumpet bush, Yellow trumpet bush, Yellow bells, Yellow bignonia, Yellow elder, Yellow trumpet-flower, yellow blossom, Ginger Thomas, golden seal, tecoma |
| Name in Other Languages | Afrikaans : Geelklokkies Arabic: تيكومة واقفة Bengali: Candraprabhā (চন্দ্রপ্রভা), Chandraprabhā phula (চন্দ্রপ্রভা ফুল) Chuukese: Peeal Czech: Protiha vzpřímená Dutch: Gele bignonia English: Ginger-Thomas, Trumpet flower, Trumpetbush, Yellow trumpet bush, Yellow bells, Yellow bignonia, Yellow elder, Yellow trumpet-flower, yellow blossom, Ginger Thomas, golden seal, tecoma Fijian: Bitu Finnish: Keltatekoma French: Bignone jaune, Bignone stans, Bignonia jaune, Bois à enivrer, Bois Caraïbe, Bois pissenlit, Chevalier, Copete, Fleur de saint Pierre, Fresnillo, Herbe de saint Nicolas, Trompette d’or, tecoma jaune German: Eschenblättrige Jasmintrompete, Gelbe Trompetenblume, Aufrechte Trompetenwinde, eschenblättrige Trompetenwinde, gelbblühender Trompetenbaum, gelbe Tecome, gelbe Trompetenwinde, gelber Trompetenstrauch Greek: Louloúdia (Λουλούδια), Louloúdi vignónia (Λουλούδι βιγνόνια) Hebrew: דק פרי זקוף Hindi: Piliya (पीलिया), Sonapati I-Kiribati: Nei Karairai, neikarairai Italian: Bignonia gialla, tecoma giallo Japanese: Kinreiju (キンレイジュ), Kin Suzuki (金 鈴樹),Tekoma sutansu (テコマ・スタンス) Kannada: Gaṇṭe hū (ಗಂಟೆ ಹೂ), Koranekelar Malayalam: Subrahmaṇyakirīṭaṁ (സുബ്രഹ്മണ്യകിരീടം) Maori (Cook Islands): Tekoma Marathi: Ghantiful (घंटी फुल) Nepali: Ghata Pushpa, Saawari Pacific Islands: Piti Persian: تکوما استنس Tikuma al stans, زنگهای زرد , شیپور زرد Polish: Tekoma prosta Portuguese : Amarelinho, Bignonia-amarela, Guarã-guarã, Ipê-amarelo-de-jardim, Ipê-de-jardim, Ipê-mirim, Ipezinho-de-jardim, Sinos-amarelos, estenolóbio, sabugueiro-amarelo Polish: Tekoma prosta Quechua: Sawsaw Russian: Tekoma priamostoiachaia (Текома прямостоячая) Spanish: Bignonia amarilla, Chanté, Guaranguay amarillo, Palo amarillo, Roble amarlllo, Saúco amarillo, Saúco de jardín, Trompeta de oro, Tronadora, saico Amarillo, lluvia de oro, trompeta, trona frente, tronadora, campanillas amarillas, chirlobirlo, flor de San Pedro, fresnilla, Gloria, trompetilla, huevo de iguana, tache Swedish: Gul trumpetbuske Tahitian: Piti Tamil: Sonapatti, Manjarali, Swarnapatti, Sannapatti, cunacci, nagasambagam, sorndpatti, naga chambagam, nakacenpakam, comappatti, ponnarali, tankarali, nakacanpakam, nakakam Telugu: Pachagotla, Suvarna ganneru, swama ganneru, panchaganneru, paccagotla, patcha ganner Thai: Tong u rai (ทองอุไร) Tongan: Piti Tuamotuan: Piti Tuvaluan: Neikarairai Vietnamese: Huỳnh liên |
| Plant Growth Habit | Spreading, fast-growing evergreen, flowering perennial shrub or small tree |
| Growing Climates | Highly disturbed habitats, roadsides, riparian zones (banks of watercourses), open woodlands, grasslands, forest margins, waste areas, rocky places, sandy lake shores and disturbed sites in tropical and subtropical environments and occasionally in native vegetation on coastal sand dunes |
| Soil | Grow in most well-drained soils, including calcareous fill, infertile sands, acidic Ultisols, and volcanic regolith |
| Plant Size | About 8 m, rarely 10 m, and with stem diameters of up to 25 cm |
| Bark | Light gray to brown, with white lenticels when young, then becomes fissured with age |
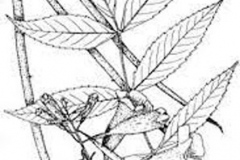
| Leaf | Leaves which are 10-25 cm long are arranged in pairs (oppositely arranged) and are borne on slender stalks (petioles) 1-9 cm long. They are compound (pinnate) with 3-13 leaflets, but usually have 3-7 leaflets |
| Flower | Flowers are bright yellow in color, tubular in shape, and borne on short stalks (pedicels) that are slightly curved or twisted. The flower tube (corolla tube) is 30-50 mm long and has five rounded lobes that are 8-30 mm long |
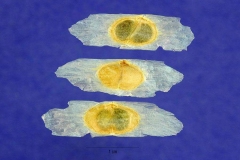
| Fruit Shape & Size | Large, elongated (linear), shiny and somewhat flattened (compressed) capsules 10-30 cm long and 5-20 mm wide pointed at the end |
| Fruit Color | Green when young, turns to brown upon ripening giving untidy appearance |
| Varieties |
|
| Propagation | From seeds or cuttings |
| Taste | Bitter |
| Plant Parts Used | Flower, root, seed, leaves, pods |
Plant Description
Yellow Elder is a spreading, fast-growing evergreen, flowering perennial shrub or small tree that normally grows about 8 m tall, rarely 10 m, and with stem diameters of up to 25 cm. The plant is found growing in highly disturbed habitats, roadsides, riparian zones (banks of watercourses), open woodlands, grasslands, forest margins, waste areas, rocky places, sandy lake shores and disturbed sites in tropical and subtropical environments and occasionally in native vegetation on coastal sand dunes. The plant grows in most well-drained soils, including calcareous fill, infertile sands, acidic Ultisols, and volcanic regolith.
Stem
Stem is solid and cylindrical. The younger stems are smooth, glabrous and greenish in color. They are slightly four-angled in cross-section (quadrangular) and turn pale brown or reddish-brown in color as they age. The bark on the main stem is light brown to pale grey in color, furrowed, and relatively rough in texture, covered in light greyish to brown barks.
Leaves
The leaves which are 10-25 cm long are arranged in pairs (oppositely arranged) and are borne on slender stalks (petioles) 1-9 cm long. They are compound (pinnate) with 3-13 leaflets, but usually have 3-7 leaflets. The leaflets are narrowly egg-shaped in outline with broad end at base (ovate-lanceolate) or elongated in shape (25-100 mm long and 8-30 mm wide) and have a pointed tip (acuminate apex). Their margins are irregularly and sharply toothed (serrated) and they are mostly hairless (glabrous), though both sides of the leaf blade are smooth and mostly glabrous, though a few hairs may be present on the undersides near the midrib.
| Leaf arrangement | Opposite/sub-opposite |
| Leaf type | Odd-pinnately compound; made up of 5 to 13 leaflets |
| Leaf margin | Serrate |
| Leaf shape | Lanceolate to elliptic |
| Leaf venation | Pinnate, brachidodrome |
| Leaf type and persistence | Semi-evergreen, evergreen |
| Leaf blade length | 4 to 10 inches; leaflets are 1½ to 5 inches |
| Leaf color | Yellowish green to dark green |
| Fall color | No color change |
| Fall characteristic | Not showy |
Flowers
The showy flowers are borne in several-flowered clusters (5-15 cm long) that are first produced at the ends of the branches (in terminal clusters), and then later in the leaf forks (axils) near the tips of the branches (in axillary clusters). These flowers are bright yellow in color, tubular in shape, and borne on short stalks (pedicels) that are slightly curved or twisted. The flower tube (corolla tube) is 30-50 mm long and has five rounded lobes that are 8-30 mm long. There are several faint reddish lines in the throat of the flower, which is slightly ridged and hairy. In some varieties the corolla is slightly orange-yellow with pinkish lines in the throat. Flowering may occur throughout the year.
| Flower color | Bright yellow with thin, red vertical lines along the inner throat |
| Flower characteristics | Very showy; trumpet-shaped; somewhat fragrant; emerges in clusters on racemes |
| Flowering | Primarily spring and fall, but also year-round |
Fruit
Fertile flowers are followed by large, elongated (linear), shiny and somewhat flattened (compressed) capsules (10-30 cm long and 5-20 mm wide) pointed at the end. These fruit are initially green turning to brown in color as they mature and finally these two-valve dehiscent capsule splits open to release up to 77 (mean 42) papery-winged seeds which are primarily wind, and to a lesser extent water, dispersed.
| Fruit shape | Elongated; long slender capsule |
| Fruit length | 4 to 10 inches |
| Fruit covering | Dry or hard |
| Fruit color | Turns from bright green to brown when mature |
| Fruit characteristics | Does not attract wildlife; showy; fruit/leaves not a litter problem |
| Fruiting | Primarily spring and fall, but also year-round |
Seeds
The seeds are very flat, oblong in shape measuring up to 7-8 mm long and about 4 mm wide, and together with the transparent wings at each ends the size of the entire seed is about 20 mm long and 6 mm wide.
Types of Yellow Elder
Yellow bells are very similar to orange bells and may also be confused with the garden plants known as golden trumpet vine and shrubby allamanda. It may sometimes also be confused with yellow oleander. These species can be distinguished by the following differences:
1. Orange bells
Orange bells have compound (i.e. pinnate) leaves that are oppositely arranged along the stems. These leaves have several toothed (i.e. serrated) leaflets and are borne on long slender petioles. Its moderately large (3-5 cm across) tubular flowers have reddish-orange outsides. Its fruit are long and narrow capsules (10-30 cm long) that split open when mature to release numerous papery seeds.
2. Golden trumpet vine
Golden trumpet vine has simple leaves that are clustered (i.e. whorled) along the stems. These leaves have entire margins and are borne on short stalks (i.e. petioles). Its flowers are very large (6-15 cm across) and its fruit are rounded and prickly (4-6 cm long) capsules that split open when mature to release numerous winged seeds.
3. Shrubby allamanda
Shrubby allamanda has simple leaves that are clustered (i.e. whorled) along the stems. These leaves have entire margins and are borne on short stalks (i.e. petioles). Its flowers are moderately large (3-6 cm across) and its fruit are rounded and prickly (4-6 cm long) capsules that split open when mature to release numerous winged seeds.
4. Yellow oleander
Yellow oleander has simple leaves that are spirally arranged (densely alternately arranged) along the stems. These leaves are long and narrow (i.e. linear) with entire margins and obscure stalks (i.e. petioles). Its flowers are moderately large (4-6 cm across) and its fruit are large fleshy drupes (25-55 mm across) that are somewhat rounded or slightly triangular in shape.
Traditional uses and benefits of Yellow Elder
- Medicinally active compounds in this plant have been known to treat stomach pains, and be used as a diuretic
- Leaf infusion can be taken orally for diabetes and stomach pains.
- Strong leaf and root decoction is taken orally as a diuretic, to treat syphilis or for intestinal worms.
- South America and Latin America used traditionally for reducing blood glucose.
- Leaves, barks and roots have been used for a variety of purposes in herbal medicine.
- Bark shows smooth muscle relaxant, mild cardio-tonic and chloretic activity.
- Root of the plant is stated to be a powerful diuretic, vermifuge and tonic.
- Grinding of the root of Yellow Elder and lemon juice is reportedly used as an external application and also taken internally in small quantities as a remedy for snake and rat bites.
- Yellow Elder is used for treatment of diabetes, digestive problems, and control of yeast infections.
- Decoction of plant flowers and bark are used for Stomach pain.
- Strong root and leaf decoction of the plant is taken orally to treat Syphilis and Intestinal worms.
- The herb lowers the Blood pressure.
- It can be taken as a tonic to correct stomach ulcers.
- Yellow Elder antioxidant properties control depression, drowsiness, and vomiting.
- You can use coffee water mixed with the Yellow elder flowers and the bark for stomach pain.
- It is used as the main drug for the treatment of diabetes in Mexico and Central America.
- Its roots are used as medicine for snake bites and can be mixed in small quantities with lemon juice.
- Flowers are used as a diuretic.
- Its leaves are used as medicine for piles and pain in Bangladesh.
- It is widely used in traditional Mexican medicine, to treat hyperglycemia, gastrointestinal and urinary tract disorders, jaundice, toothaches, headaches, colds, skin infections, and scorpion, snake, and rat bites.
- Leaves are used throughout Mexico and Central America for diabetes and urinary disorder control.
- Traditionally flowers and bark are used for treatment of various cancers.
- Flowers consist of beta carotene and zeaxanthene to treat eye disorder.
Prevention and Control
Due to the variable regulations around (de)registration of pesticides, your national list of registered pesticides or relevant authority should be consulted to determine which products are legally allowed for use in your country when considering chemical control. Pesticides should always be used in a lawful manner, consistent with the product’s label.
Including various control methods is the most effective approach and includes the prevention of new introductions, dispersal and sales by the nursery trade as well as mechanical and chemical control.
Mechanical Control
Maintaining a vigorous ground cover, preventing overgrazing and rehabilitating disturbed areas remains one of the best methods to prevent establishment and invasion of T. stans. Frequent inspections of pastures and forest margins are necessary to locate seedlings that can be hand-pulled. Larger plants can be uprooted by using a tractor, but resprouting from cut roots can cause rapid reinfestation unless the remaining roots are burnt after drying. Rehabilitation of such disturbed areas after uprooting and burning is essential. Follow-up control to remove the regrowth is necessary for at least a year after initial control.
Chemical Control
Conventional chemical control methods of shrubs and small trees as practiced by most municipalities and counties are not effective against T. stans. Only repeated applications of foliar-applied herbicides are effective but this method is usually not economic. More effective are cut-stump application methods using oil-based or oil/water emulsions of 2, 4-D and picloram mixtures. These are generously applied to the freshly cut stumps by spraying or painting. Soil applied tebuthiuron also gave excellent control 270 days after treatment.
Biological Control
Host specificity tests on two rust fungus species, namely, the microcyclic Prospodium transformans and the macrocyclic P. appendiculatum from Mexico are in progress in South Africa. P. appendiculatum is already present in Brazil and Argentina but is not contributing much to the suppression of populations. Further surveys for additional host-specific natural enemies are planned. A raceme-feeding membracid and the pyralid pod-feeding moth Clydenopteron sp. are to be introduced into quarantine in South Africa for possible biological control.
Other Facts
- Yellow Elder is the official flower of the United States Virgin Islands and the floral emblem of The Bahamas.
- It has many uses in landscapes.
- It is commonly used as a border, barrier, windbreak, container plant, or for the patio.
- The scent and brilliant color provided by the flowers often attract humming birds and bees during bloom season.
- It provides firewood and charcoal.
- The wood is used in the construction of buildings.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=34326#null
http://www.hear.org/pier/species/tecoma_stans.htm
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxon/taxonomydetail?id=80111
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/52951
https://plants.usda.gov/home/plantProfile?symbol=test
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tecoma_stans
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/st625
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/TECST
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-318412
https://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/265983
http://www.missouribotanicalgarden.org/PlantFinder/PlantFinderDetails.aspx?taxonid=277878
http://ijerme.rdmodernresearch.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/01/8.pdf