| Taiwan Cherry Quick Facts |
| Name: |
Taiwan Cherry |
| Scientific Name: |
Prunus campanulata |
| Origin |
Taiwan, China (Guangxi, Guangdong, Hainan, Hunan, Fujian, and Zhejiang)and Vietnam |
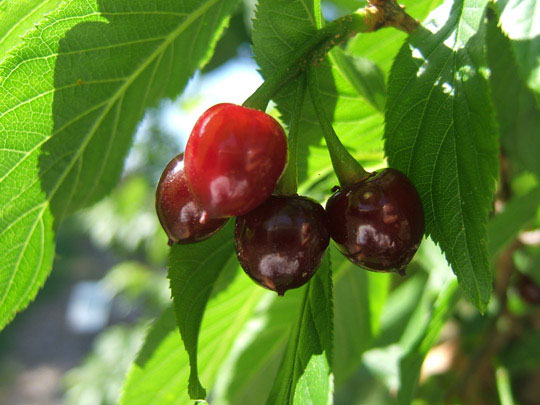
| Colors |
Initially green, turning red and finally black as they matures |
| Shapes |
Small ovoid drupe, 15 mm long and 12 mm wide, glabrous, glossy scarlet, with a smooth stone |
| Health benefits |
Beneficial to stimulate respiration, improve digestion, and promote a sense of well-being |
Prunus campanulata Taiwan Cherry also known as Formosan cherry, Bellflower cherry is a flowering cherry tree in the Rose family (Rosaceae). The tree is native to Taiwan, China (Guangxi, Guangdong, Hainan, Hunan, Fujian, and Zhejiang) and Vietnam and has been presented as an ornamental to Australia, Japan, New Zealand, United Kingdom and the USA. In New Zealand, P. campanulata invades the under storey of relatively complete indigenous forests and is considered invasive in some areas, particularly on the North Island, where it has spread and dominates native vegetation. There, in the region of Northland, it is prohibited to sell, propagate, breed, distribute or otherwise spread P. campanulata and in the Waikato region, the Regional Council needs residents to destroy P. campanulata on personal property. Few of the popular common names of the plant are Formosan cherry, Taiwan cherry, Bellflower cherry, Bell-flowered cherry, Ryukyu cherry, Taiwan flowering cherry, bellflower cherry, Taiwanese cherry and Carmine Cherry.
Plant Description
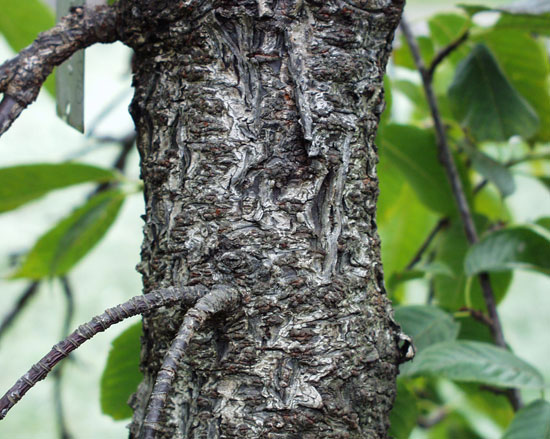
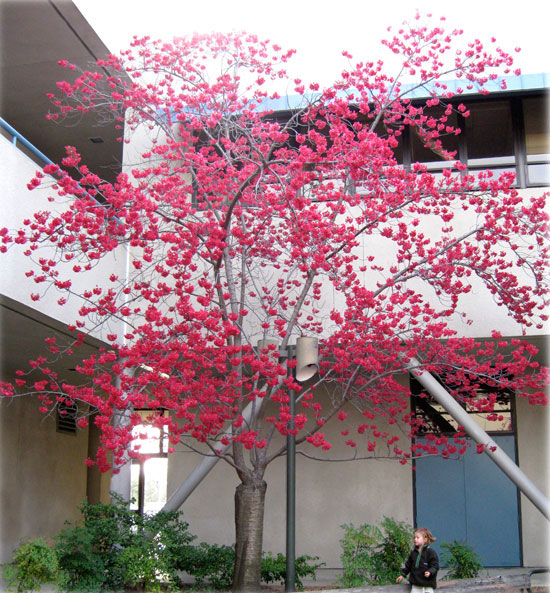
Taiwan Cherry is a small, deciduous, flowering tree that grows about 3–8 m (10–26 ft.) tall. The plant is found growing in broadleaved forests, riparian zones, urban areas, hillsides, in scrub, urban fragments, regenerating secondary bush, and relatively undamaged forest via canopy gaps, edges and riparian margins. The plant thrives in a fertile, light, well-drained moisture-retentive loamy soil. It also prefers some lime in the soil but is likely to become chlorotic if too much lime is present. Bark is dark brown with prominent lenticels (pores in the bark that allow for gas exchange). Branchlets are brown to purplish brown and young branchlets are green and hairy.
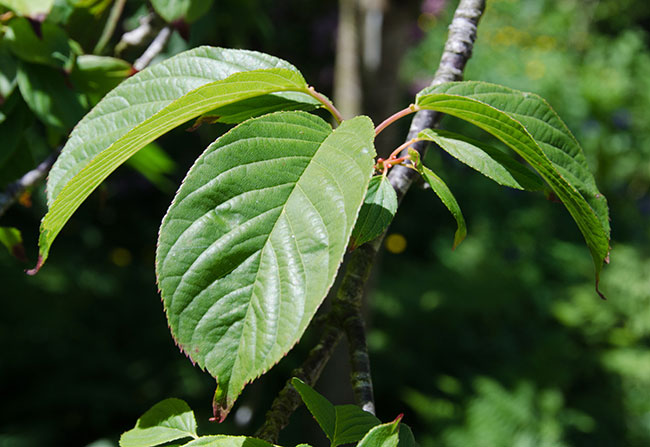
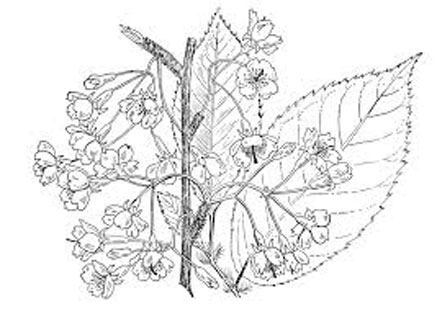
Leaves
Leaves are typically cherry-like and are up to 4-7cm long and 2-3.5 cm wide that are serrated at the edges. They are a bright green color when they emerge in spring, changing to dark green in summer and finally turning bronze during autumn. Leaf petioles are 12-20 mm and hairy, and blades are obovate to broadly elliptical.
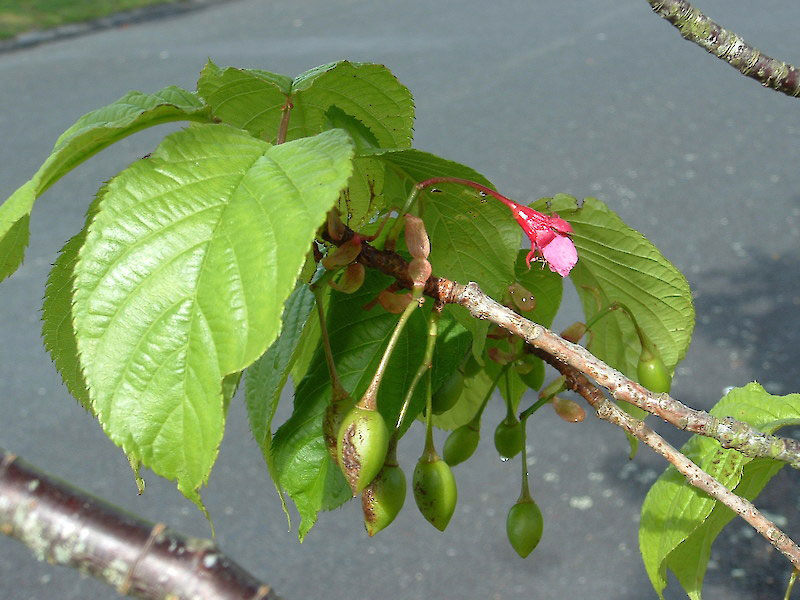
Flower
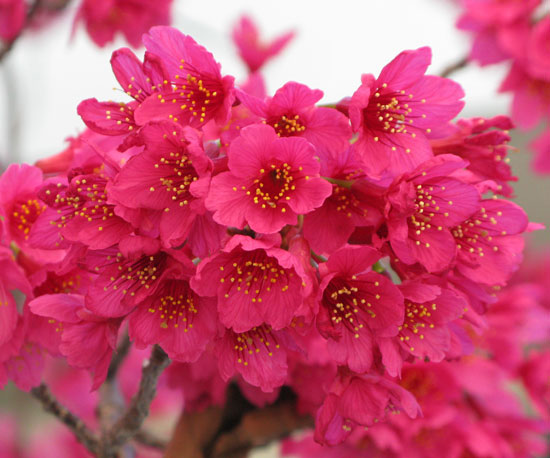
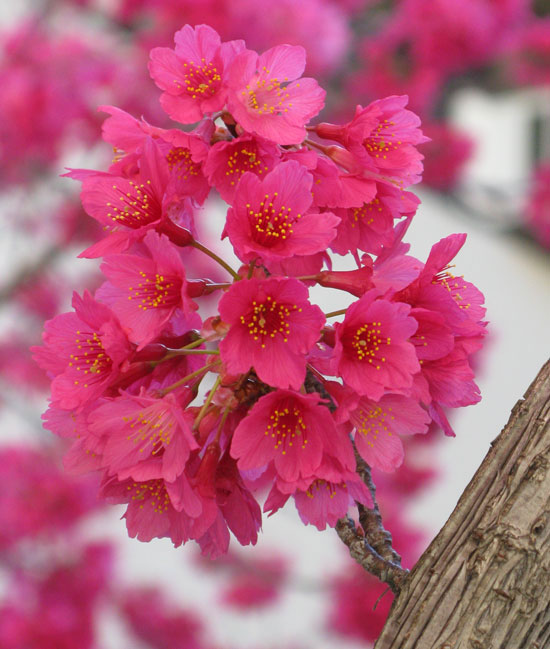
The plant has characteristics deep red, bell-shaped flowers of up to 2.2 cm diameter that hang in clusters in late winter to early spring. Clusters consist of 1-5 flowers on very short shoots which elongate after anthesis. Flowers can appear on the branches before leaves emerge. Sepals are triangular, 3-6 mm, magenta to dark red, glabrous, shiny becoming spreading or reflexed. There are five petals, 5-12 mm in diameter, corolla appearing campanulate and eventually spreading, broadly elliptic-ovate, deep pink to rose-magenta. Flowers have 39-41 stamens, and the style is hairy and usually longer than the stamens. Filaments are flushed magenta to crimson. Flowering normally takes place from July, August and September.
Fruits
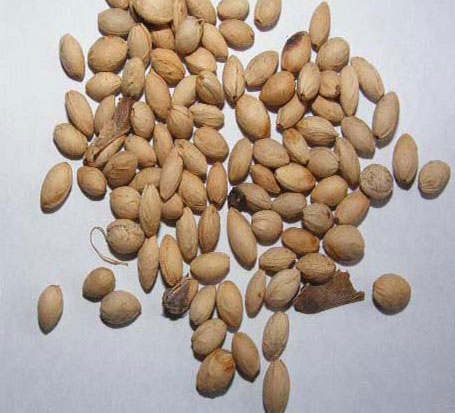
Fertile flowers are followed by small ovoid drupe that is 15mm long and 12mm wide, glabrous, glossy scarlet, with a smooth stone. The fruit is initially green, turning red and finally black as they mature. Seeds are up to 9mm long.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=29tx8gRDe0g
Few Facts about Taiwan Cherry
- It is a popular ornamental tree that has been purposely planted in both private gardens and public areas.
- It is a symbol of Nago in the Ryukyu Islands of Japan.
- The plant is harvested from the wild for local use as a food.
- A green dye can be obtained from the leaves.
- A dark grey to green dye can be obtained from the fruit.
- This invasive plant species is totally banned in the Northland region of New Zealand where it is illegal to distribute, sell, propagate, distribute soil, gravel etc. that contain the seeds or other parts of the plant.
Prevention and Control
Prevention
In Northland, North Island, New Zealand, it is banned to sell, propagate, breed, distribute or otherwise spread P. campanulata and the species is classified as a community pest. In the Auckland region, North Island, it is considered a species requiring further research to determine its effects on biodiversity, and is listed by the Waitakere City Council as an environmental weed posing a risk to conservation, for which eradication is recommended. In Waikato, North Island, it is included in the Regional Pest Management Strategy and classified as a ‘containment pest plant’. The Waikato Regional Council needs residents to eradicate P. campanulata on personal property.
In the regions of Bay of Plenty (North Island), Marlborough (South Island) and West Coast (South Island), P. campanulata is also considered a garden escapee and planting of alternative native species is recommended.
Control
In Northland, New Zealand, it is a sustained control plant, i.e. a widespread pest in suitable habitat that causes adverse effects to the environment. As a result, landowners are responsible for management of the plant and need to act to reduce its impact and spread.
Physical/mechanical control
Prunus campanulata trees should be removed by felling, and seedlings can be dug out. In Northland, New Zealand, it is recommended to pull out seedlings and small plants of P. campanulata and then to apply mulch, and to cut and stump treat more established plants all year round.
Chemical control
Once chopped, stumps of P. campanulata should be treated with herbicide. Follow up treatments should be used to check for subsequent sprouting or seedlings. In Northland, New Zealand, it is recommended to cut P. campanulata trees and to stump treat them with metasulfuron-methyl or picloram all year round, followed by mulching the cut branches and leaves. Another recommended year-round method of chemical control is to cut, drill or ringbark, then inject the trunk at a downward angle with metasulfuron-methyl or picloram. Summer spraying with metasulfuron-methyl or picloram is also recommended for the control of P. campanulata.
Ecosystem Restoration
After physical and chemical control of P. campanulata, sites should be observed for potential growth and seed bank for two years. It is also recommended that a dense cover of native trees or shrubs is planted to produce shade.
References:
https://davesgarden.com/guides/pf/go/64259/
https://www.cabi.org/ISC/datasheet/44268
http://www.iucngisd.org/gisd/species.php?sc=1666
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prunus_campanulata
http://issg.org/database/species/ecology.asp?si=1666&fr=1&sts=&lang=EN
http://floraofalabama.org/Plant.aspx?id=5310#classification
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/rjp-13282
http://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:729533-1
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/PRNCM
https://selectree.calpoly.edu/tree-detail/prunus-campanulata
http://oki-park.jp/sp/kaiyohaku/en/inst/87/126
https://hort.ifas.ufl.edu/treesandpowerlines/prunus_campanulata.shtml
Comments
comments