| Black Plum (Java plum) Quick Facts |
| Name: |
Black Plum (Java plum) |
| Scientific Name: |
Syzygium cumini |
| Origin |
It is widely distributed in subtropical and tropical Asia to Queensland. It is native to India, Sri Lanka, Myanmar and the Andaman islands. |
| Colors |
Dark purple, oblong |
| Flesh colors |
White or purple |
| Taste |
Sour and sweet |
| Calories |
81 Kcal./cup |
| Major nutrients |
Vitamin C (21.44%)
Carbohydrate 21.01 g (16.16%)
Magnesium (4.76%)
Vitamin B6 (3.92%)
Phosphorus (3.29%)
|
| Health benefits |
Diabetic treatment, Antioxidant activity, Lower apoptosis, Antioxidant activity |
Other common names for Black Plum are Jamun Fruit, Indian Blackberry, Damson Plum, Jambolan, Java Plum, Jambolan Plum, Portuguese Plum, Malabar Plum, Purple Plum, Jambu, Jambul, Jamun, Jambas, Kala jamun, Rajaman, Neredu, Naval, Jamali, Nerale, Java plum and Black berry. The scientific name of Black plum is Syzygium cumini. Naturally the tree grows in India, Himalayas, Malaysia, Sri Lanka and Australia. It got introduced to Fiji, Cook Islands, Guam, French Polynesia, New Caledonia, Florida, Hawaii, Palau, Niue, China, Tonga, Palau, Malaysia, Indonesia, Australia, Christmas Island, India, Africa, South America and Caribbean.
The tree is tall which usually grows from 5 to 20 meters tall. Leaves are thick, wide having a pinnate bone. The tree produces ellipsoid or oblong berries as a fruit. Berries are green at first which turns into purple. The fruit tastes sour and sweet. The plant could be grown in semi-shade or no shade. It prefers wet or moist soil and is also able to tolerate drought.
Black plum is a substantial summer fruit which is related with various health benefits. It provides relief from stomach pain and acts as anti-scorbutic, carminative and diuretic. The polyphenolic compounds found in Black plum are helpful for heart diseases, cancer, asthma, diabetes and arthritis. It is also effective against bowel spasm, flatulence, dysentery and stomach ailments. It is consumed as a tonic to promote sexual activities. Black plum possesses anti-diabetic features. It converts starch into energy and normalizes level of blood sugar. Due to its low glycemic index in Black plum, it is suitable for sugar patients as well. It reduces the diabetic symptoms such as thrusting and frequent urination. This fruit contains adequate amounts of Vitamin C and iron. Iron helps to promote the count of haemoglobin and also acts as blood purifier. Iron content is helpful in menses where women experience blood loss.
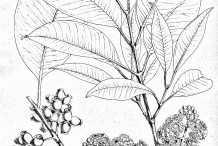
Plant
Black plum is a large and evergreen tree which is much branched and grows from 5 to 20 meters tall having trunk diameter of 60 to 90 cm, terete branches, scaly bark and canopy spread of 10 meters. Leaves are coriaceous, opposite, elliptic oblong measuring 5 to 15 cm long by 2.5 to 8 cm wide, narrow, acuminate. Petioles are 1 to 2.5 cm long. The fragrant flowers occur in clusters and are axillary on flowering branches. Flowers are pinkish or white which measures 12 mm wide. Calyx is copular measuring 4 to 6 mm wide and 8 mm long. Petals are caduceous, slightly rounded, coherent and white to rose pink. Flowers are replaced by an ovoid to ellipsoid fruit which measures 2 to 2.5 cm long. Fruits are green which turns to pale greenish to white to deep purplish to black when ripe. Pulp is astringent, juicy, white to pale lavender in color with one large and green seed.
Health Benefits of Black Plum
Black plum belongs to family Myrtaceae. It is also called as jambul, jambas, jambolan, malabar plum, neredu, rajaman, kala jamun, jamali, naval and java plum. It was firstly originated in India and spread to other tropical regions of the world in various countries of Southeast Asia and Eastern Africa such as Nepal, Pakistan, India, Surinam, Trinidad, Bangladesh, Tobago, Indonesia and Sri Lanka. Though various varieties could be found, common variety is oblong shaped and bluish or deep purple colored.
- Diabetic treatment
Black Plum is used for treating various diseases especially diabetes and associated complications. The plant possesses several compounds which are found to be the characteristics of plant. The pharmacological activities on diabetes were carries out with seed. There are not so much works with pharmacological actions of phytochemical constituents of Black plum. On the basis of these facts, author reviewed the role of Black Plum in variety of treatments and recommended that further clinical and phytochemical research should be carried out on the plant for making safer drugs. (1)
- Antioxidant activity
The study findings concluded that some medicinal plants have antioxidants and might be effective as preventive agents in pathogenesis of diseases. The methanol extracts are considerably effective radical scavengers in comparison to those who use less polarity solvent. It indicates that antioxidants of different polarity could be found in leaves of Black Plum. Still more research is needed on use of Black plum essential oil and extracts as preservative agents in various foods. Results encourage use of Black plum leaves for nutraceutical applications, medicinal health and functional food due to its antibacterial and antioxidant properties. (2)
- Lower apoptosis
Study confirms apoptotic and inhibitor effect of Black plum extract on cervical cancer cell lines. This fruit possess gallic acid whichy has anti-HIV, anti-adenoviral, anti-carcinomic, anti-peroxidant, chemopreventive and apoptotic activities. It is a topoisomerase-I-inhibitor. The results from the study indicate the apoptotic and inhibitory effect of extract. Anti-viral effect is confirmed by further experiments. Further research is required for identifying efficacy, mode of action and safety issues. (3)
- Antioxidant activity
The results obtained from the study confirmed that leaves of Black plum gall extracts as antioxidant and justified ethnobotanical approach in search for novel bioactive compounds. The strong correlation was observed between high total phenolic and flavonoid contents and higher antioxidant activities in methanol leaf gall extracts of Black plum. The findings supported that extracts obtained with the use of high polarity solvent are effective radical scavengers. Results supported that gall extracts use are potential antioxidants which may be effective as preventive agents in pathogenesis of some metabolic diseases. The study promoted use of Black plum leaves gall extracts for functional food, medicinal health and neutraceutical applications. (4)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XcmQFiz0IlI
Other medicinal uses
- Bed Wetting
Give 1 teaspoon of ground seeds with water.
- Nightfall
Consume 4 gm of seed powder with water twice a day (in the morning and evening).
- Blood Dysentery
Drink the mixture of 20 gm of powdered seeds and ½ cup water twice a day.
Or,
Boil 10 gm of bark and 500 ml water till it reduces to 1/4th. Let it cool down. Take about 20 to 25 ml of this mixture 3 times a day.
- Diarrhea
Grind leaves by adding a little rock salt. Make a pill and take this each in the morning and evening.
- Hoarseness
Grind seeds by adding honey to make pills. Use two pills for 3 to 4 times in a day.
- Dental & gum infections
Mix ash of each Black plum leaves and almond shells. Then add peppermint (little) for making a tooth powder which helps to clean teeth and stop bleeding.
Or,
Rub leaves ashes on teeth and gums. This stops bleeding and also makes teeth strong.
Or,
Wash mouth with Black plum juice if suffering from pyorrhea.
- Ringworm
Apply the diluted juice on affected area of ringworm.
- Excessive urination
Powdered seeds help to provide relief from excessive urination.
- Conjuctivitis
Boil 400 ml water by adding 15 to 20 soft leaves till it reduces to 100 ml. Let it cool and then with the use of this decoction wash eyes.
- Throat ailments
Drink 10 to 15 ml juice of Black plum to provide relief.
- Bleeding piles
Grind leaves for making 20 ml juice. Then add some sugar in it. Take three doses every day for providing relief.
Or,
Grind 10 gm of leaves. Add it to 250 ml of cow’s milk. Take 3 doses every day for 1 week by stirring well. This helps to stop bleeding.
- Bloody diarrhea
Mix 2-3 gms of powdered bark with 2 tsp honey. Add to milk and drink.
- Gas & bloated stomach
Take 10 ml of jamun vinegar for relief in water.
- Vomiting
Boil 500 ml of water by adding few pieces of mango. Boil it till the water reduces to 1/4th. Cool it down and drink 10 ml to stop vomiting.
- Heal wounds
Place 2 to 3 gm of powdered bark on wound to heal the wound faster.
Traditional uses
- In traditional medicine, it is used as an aid for diabetes mellitus.
- Fruit is useful for dysentery and bilious diarrhea.
- Prepare water diluted juice and use it as a gargle for sore throat.
- It is used as a lotion for ringworm of scalp.
- The juice of ripe fruit is used in India for chronic diarrhea, enlargement of spleen and urine retention.
- Seeds are used for digestive problems.
- Leaves are used for strengthening gums and teeth, treat stomachache, leucorrhoea, skin diseases, strangury, fever, constipation and prevent blood discharges.
- In India, leaves are used as poultice for skin problems.
- Leaves are steeped in alcohol which is used for diabetes and dysentery.
- In Philippines, decoction made from powdered bark is used internally in diarrhea, dysentery and dyspepsia.
- Decoction prepared from bark is used for cleansing ulcers.
- In India, bark is used for treating anemia, diarrhea, dysentery, diabetes and spongy gum.
- Bark and leaves are used to control gingivitis and blood pressure.
- Roots are used to treat epilepsy.
- Daily intake of Black plum is for 2 to 4 months is helpful for people with bleeding hemorrhoids.
- To support blood sugar, intake dried seeds powder for two times in a day (one gram each).
- Fruit helps to lower excessive salivation.
- The decoction of seeds with honey helps to prevent fatigue and thirst caused due to physical strain.
- Apply seeds mixed with little oil on boils or other skin problems.
- Intake Black plum with roasted cumin seed powder and black salt for treating acidity.
- Take one teaspoon each of honey, Black plum juice and amla juice daily in the morning for treating anemia, eliminate sexual weakness, increase memory and eliminate body weakness.
Precautions
- Avoid road side Black plum as it is contaminated from lead and heavy metals.
- Pregnant women and breast feeding mother should avoid it.
- As it lowers blood sugar, one should not consume Black plum before and after two weeks of surgery.
- Do not consume Black plum in an empty stomach.
- Does not intake milk after consuming Black plum.
- Over consumption of Black plum results in fever and body ache.
- Its excessive uses it not helpful for chest and throat.
- Large dose of Black plum results cough and sputum accumulation in lungs.
- People with high vatta should avoid the consumption of Black plum.
How to Eat
- Fruits are consumed fresh when ripe or made into sauces, wine, jams and vinegar.
- Juice is good for syrup, sherbet and squash.
- Unripe fruits are used to make vinegar.
- Fruits are processed into desserts.
- Black plum could be used as toppings in puddings, pastries, cakes and custards.
- Pulp is used for making chutneys and jams.
Other Facts
- All parts of Black plum have variety of uses.
- Wood is water resistance. Thus it is used for making agricultural implements and bullock cart wheels. It is also used for building houses.
- The planks made from this wood supports water pumps located in wells.
- Leaves are used as a fodder for sheep, cattle and goats.
- Bark is used in dyeing and tanning industries.
- Flowers are rich in nectar which attracts bees and produce a high quality honey.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=505419#null
http://www.hear.org/pier/species/syzygium_cumini.htm
http://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Syzygium+cumini
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/52426
http://www.gyanunlimited.com/health/amazing-health-benefits-and-uses-of-jamun-fruit-black-plum/8944/
https://goqii.com/blog/amazing-health-benefits-and-uses-of-jamun-fruit/
http://fitlife.expertscolumn.com/15-health-benefits-jamun
https://drhealthbenefits.com/herbal/leaves/health-benefits-jamun-leaves
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0963996911000949
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/jamun-black-plum-controls-blood-sugar-levels-ayurveda-hospital
https://hubpages.com/health/Black-Plums-Or-Jamun-Health-Benefits-And-Uses
Comments
comments