| Chives Quick Facts |
| Name: |
Chives |
| Scientific Name: |
Allium schoenoprasum |
| Origin |
Native to Asia and Eastern Europe |
| Colors |
grayish green (Leaf) |
| Shapes |
Long, round and hollow, similar to onions, but smaller in diameter 8-20 inches long. |
| Calories |
30 Kcal./cup |
| Major nutrients |
Vitamin K (177.25%)
Vitamin C (64.56%)
Vitamin A (31.14%)
Vitamin B9 (26.25%)
Iron (20.00%)
|
| Health benefits |
Birth Defects, Immune System Booster, Heart Health, Vision Health, Detoxify the Body, Digestive Issues |
Chives scientifically known as Allium schoenoprasum are bulbous hardy perennial plants of the genus Allium in the Liliaceae, or Lily family, cultivated for their onion or garlic -flavored leaves and for their attractive and edible flower heads, rather than for their bulbs as with most other Alliums. The term chives is said to be derived from the Latin cepa, meaning onion. Chives are considered to have originated from Asia and Eastern Europe and have been used in cuisine for a recorded 5000 years. Some popular common names of Chives are Garlic chives, Chinese leeks. Garden or Onion Chives, Garlic Chives, Album, Curly Mauve, Forescate, Marsha, Pink Giant, Profusion, Snowcap is some of the popular varieties of Chives which are mainly grown for their delicious leaves. Apart from that it is also called nira in japan, Civette in France, Schnittlauch in German, Erba cipollina in Italy and Cebollino in Spain. Chives make good container plants and therefore are a must for any kitchen windowsill herb garden.
Plant
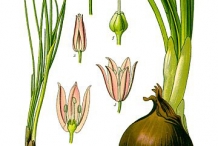
Chives are a bulb-forming herbaceous perennial plant sized approximately 30–50 cm (12–20 in) tall, flower stalks grow up to 30 inches high and spread 6 inches or more wide. It is found growing in clump and prefer cool climates or temperatures. It prefers full sun and thrive in well drained, moist, fertile soil rich in organic matter. The plant grows in dense clumps of slender bulbs, each bulb producing hollow tubular leaves. Chives plant bears underground bulb which is slender, conical, 2–3 cm (3⁄4–1 1⁄4 in) long and 1 cm (1⁄2 in) broad, and grow in dense clusters from the roots. Through the bulb arise a hollow and tubular, up to 50 cm (20 in) long and 2–3 mm (1⁄16–1⁄8 in) across, with a soft texture stem (scapes). Leaves are long, round and hollow, similar to onions, but smaller in diameter 8-20 inches long. Flowers are usually pale purple, and star-shaped with six petals, 1–2 cm (1⁄2–3⁄4 in) wide and produced in a dense inflorescence of 10-30 together, before opening, the inflorescence is enclosed by a papery bract. Flower normally blooms from June and July. Seeds develop from the flower which is small angular black seeds that are enclosed in a small, three-valved capsule.
Leaves
Leaves of chive plant normally grow from thickened underground stems that may be semi-bulbous in nature. Leaves of all Chive plants are linear, but leaves of common chives and giant Siberian chives are tubular, while those of garlic chives and Siberian garlic chives are flattened. Common or onion chives bears plentiful rosy-lavender flower heads resembling red clover during late May and June, garlic chives bears pretty white flower heads in flattened umbels in August/September. Leaves of chive plant have flavor that may vary from nutty, mild sweet flavor to very pungent. The soft-textured, blue-green leaves appear in spring just before the plant blooms and will continue to produce new leaves throughout the growing season so the plant remains fresh-looking. Plants may remain evergreen in mild climates, but in cold climates the foliage is killed over the winter. Flower stems, that rise from the base, grow somewhat taller than leaves and bear small clusters of mauve or purple flower heads. Chive leaves are extremely delicious and full of essential nutrients so it is found used in several delicacies from ancient time.
History
Chives are considered to have originated from Europe and Asia and possibly North America, but there is some disagreement on whether it is actually native or naturalized there. It has been grown in Europe since the middle Ages, both for medicinal and culinary purposes, and as long as 4,000 years ago by the Chinese. Today the leaves are naturally used as a culinary herb with a mild onion flavor.
Nutritional value
Apart from their distinctive moderate taste Chive is a good source of nutrients, vitamins and minerals. Consuming 100 gram of chives offers 212.7 µg of Vitamin K, 58.1 mg of Vitamin C, 218 µg of Vitamin A, 105 µg of Vitamin B9, 1.6 mg of Iron, 0.157 mg of Copper and 0.373 mg of Manganese. Moreover many Amino acids like 0.037 g of Tryptophan, 0.128 g of Threonine, 0.139 g of Isoleucine, 0.195 g of Leucine and 0.163 g of Lysine are also found in 100 gram of the Chives.
Health benefits of Chives
Chives are small bulb-forming herbaceous perennial plant growing in clumps, probably originated in Europe and Asia. The plant grows best in full sun and a well-drained soil. Vitamin K and vitamin V rich vegetable is extremely nutritious and delicious and is found used in fresh salads, combined with egg and omelet recipes, cream cheese, as a flavored garnish on soups and potatoes.
1. Digestive Issues
Chives consist of allyl sulfides and other unique organic compounds that are effective for easing digestive discomforts. Apart from that chives also have antibacterial features which help to eliminates wide range of bacteria which may result in havoc on gastrointestinal system. Chives help to increase the nutrient uptake efficiency of your gut, ensuring that you get as many of the nutrients from your food as possible.(1)
2. Detoxify the Body
Chives have mild diuretic properties, and along with other free-radical scavenging and anti-bacterial qualities, chives are a perfect way to detoxify the body. By encouraging urination, chives helps to eliminate excess toxins, fat, water and salts keeping the organ systems running efficiently and clearing out any hazardous substances that could damage the entire system.
3. Vision Health
Chives includes of Carotenes specifically lutein and zeaxanthin that are directly liable for decreasing oxidative stress in the ocular system and postponing the appearance of cataracts in the eye. They are also helpful to prevent macular degeneration, keeping your eyes healthy well into your old age.(2)
4. Heart Health
Chives consists of allicin which is one of the most important organic compound and is closely related in reducing level of bad cholesterol in the body and improves the heart health. Allicin when connected with vasodilatory effects of the potassium present in Chives, helps to lower the blood pressure level. Apart from those chives also consists of another organic compound quercetin which has been directly associated to lowering cholesterol levels and plaque in the arteries, efficiently preventing atherosclerosis and lowering your risk for stroke and heart attacks.(3)
5. Immune System Booster
Considerable amount of vitamin C is found in Chives which is proven effective to boost the efficacy of the immune system by encouraging the production of white blood cells and stimulating the production of collagen that is an essential component in the creation of new blood vessels, cells, tissues, and muscles.(4)
6. Birth Defects
Folic acid is extremely important for pregnant mothers who want to safeguard the health development of their infant. Folic acid prevents neural tube defects in newborn infants, and chives are a rich source of folic acid for careful mothers.(5)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=S2wvrGzo7v0
How to Eat
- Chives are used in sauces, in fresh salads, combined with egg and omelet recipes, cream cheese, as a flavored garnish on soups and potatoes.
- Mix chives with softened butter and add a dollop to grilled steak, chicken or veal.
- Chopped leaves are used to garnish sour cream and a classic addition to baked potatoes.
- Chives are used fresh and are a common addition to egg dishes, baked potatoes, and cream soups.
- Fresh Leaves are outstanding for making herbal vinegars and butter.
- Mix 2 tablespoons of chopped fresh chives into half a cup of softened butter, reduced-fat cream cheese or a mixture of both for tasty herbed spread.
- Cut fresh and chopped fine are used in green salads, cucumber salad, or sprinkled on sliced tomatoes.
- Leaves and bulbs are used to garnish and flavor soups and salads, and in omelets, soft cheeses and sauces such as remoulade and ravigote.
- Flowers also have a mild onion flavor, and are sprinkled into salads.
- Leaves are cut into small segments and are used as seasoning or garnish sprinkled on the food just before serving.
- In Swedish midsummer celebrations they are an ingredient of the gräddfil sauce with the traditional herring.
- In Poland and Germany, chives are served with quark cheese.
Other Traditional uses and benefits of Chives
- Chives consists of considerable amount of vitamin C, potassium and folic acid are a good addition to modern recipes to restore vital nutrients that are lost in cooking.
- It is good to promote good digestion; comfort stomach upset and prevents bad breath.
- They have a diuretic effect which will lower high blood pressure.
- Romans believed chives can relieve pain from a sunburn or sore throat.
- Chives, chopped and sprinkled on food, are supposed to aid digestion and encourage hunger.
- Chinese chives have long been used as an herbal medicine for recovery from fatigue.
- Chives are reported to have a beneficial effect on the circulatory system.
- The mild anti-inflammatory properties in chives can lower the chance of getting rheumatoid arthritis if consumed every day.
Other Facts
- It was believed that hang bunches of dried chives around your house can ward off disease.
- For a lovely arrangement of long, cylindrical vegetables such as asparagus, carrots or green beans, tie the vegetables into small bundles using chive leaves as strings.
- Although chives are repulsive to insects because of their sulfur compounds, their flowers can entice bees.
- Violet flowers are often used in ornamental dry bouquets.
- Rumanian Gypsies used chives as part of their fortune telling rituals and when dried bunches of chives were hung in the house it was supposed to drive away disease as well as evil influences.
Precautions
- Taking an excessive amount of chive may cause an upset stomach.
- Prevent using chive as medication in case you are pregnant or even breast-feeding.
Chives – Allium schoenoprasum Facts
Chives are an herbaceous perennial plant sized approximately 30–50 cm (12–20 in) tall, native to Europe and Asia. It prefers full sun and thrive in well drained, moist soil rich in organic matter. Due to its distinctive taste it is found used in several food items from ancient times.
| Name |
Chives |
| Scientific Name |
Allium schoenoprasum |
| Native |
Asia and Eastern Europe |
| Common/English Name |
Garlic chives, chinese leeks |
| Name in Other Languages |
Hmong: Ndoh dah
Mandarin Chinese: jiu tsai
Chinese: gil choy
French: Civette
Cantonese Chinese: gow choy
German: Schnittlauch
Japanese: nira
Italian: Erba cipollina
Spanish: Cebollino |
| Plant Growth Habit |
Bulb-forming herbaceous perennial plant |
| Growing Climate |
Grows well in clump and prefer cool climates or temperatures. |
| Soil |
Thrive in well drained, moist, fertile soil rich in organic matter. |
| Plant Size |
30–50 cm (12–20 in) tall, flower stalks grow up to 30 inches high and spread 6 inches or more wide |
| Bulb |
slender, conical, 2–3 cm (3⁄4–1 1⁄4 in) long and 1 cm (1⁄2 in) broad, and grow in dense clusters from the roots |
| Stem or Scapes |
Hollow and tubular, up to 50 cm (20 in) long and 2–3 mm (1⁄16–1⁄8 in) across, with a soft texture |
| Leaf Shape & Size |
Long, round and hollow, similar to onions, but smaller in diameter 8-20 inches long. |
| Leaf Color |
Grayish green in color |
| Leaf Flavor |
Flavor can vary from nutty, mild sweet flavor to very pungent. |
| Flowering Season |
June and July |
| Flower |
Pale purple, and star-shaped with six petals, 1–2 cm (1⁄2–3⁄4 in) wide, and produced in a dense inflorescence of 10-30 together, before opening, the inflorescence is surrounded by a papery bract. |
| Seeds |
Small angular black seeds that are enclosed in a small, three-valved capsule. |
| Varieties/Types |
Garden or Onion Chives, Forescate, Garlic Chives, Snowcap, Album, Curly Mauve, Pink Giant, Marsha, Profusion |
| Major Nutrition |
Vitamin K (phylloquinone) 212.7 µg (177.25%)
Vitamin C (Ascorbic acid) 58.1 mg (64.56%)
Vitamin A, RAE 218 µg (31.14%)
Vitamin B9 (Folate) 105 µg (26.25%)
Iron, Fe 1.6 mg (20.00%)
Copper, Cu 0.157 mg (17.44%)
Manganese, Mn 0.373 mg (16.22%)
Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) 0.138 mg (10.62%)
Magnesium, Mg 42 mg (10.00%)
Calcium, Ca 92 mg (9.20%) |
| Health Benefits |
- Birth Defects
- Immune System Booster
- Heart Health
- Vision Health
- Detoxify the Body
- Digestive Issues
|
| Calories in 1cup (100gm) |
30 Kcal |
References:
http://www.herbinfosite.com/?page_id=346
http://www.nda.agric.za/docs/Brochures/Chives.pdf
http://www.cenlaherbsociety.com/uploads/Beths_Chive_Presentation_Outline_and_Compilation.pdf
http://www.herbsociety.org/factsheets/chives.pdf
http://www.nicksgardencenter.com/images/iwm/herb-herbert/herbs/chives.pdf
http://www.ctahr.hawaii.edu/sustainag/extn_pub/veggie%20pubs/Garlic%20Chive,%20Chinese%20Chive,%20Gow%20Choy.pdf
http://wimastergardener.org/files/2015/12/chives.pdf
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chives
http://www.foodreference.com/html/f-chives.html
Comments
comments