| Mangrove trumpet tree Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Mangrove trumpet tree |
| Scientific Name: | Dolichandrone spathacea |
| Origin | Southeast Asia, South India, and Sri Lanka to New Caledonia |
| Colors | Green at first, turning brown as they mature |
| Shapes | Long, flattened, curling bean-like pods that are 25-60 cm long, 2 to 2.5 centimeters thick and contain many see |
| Health benefits | Support oral thrush, bronchitis, gastrointestinal diseases, asthma, vomiting, inflammation, diarrhea, chlorosis, cholera, diuresis and hematemesis |
| Name | Mangrove trumpet tree |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Dolichandrone spathacea |
| Native | Southeast Asia, South India, and Sri Lanka to New Caledonia |
| Common Names | Mangrove trumpet tree, Singapore mangrove, Tui |
| Name in Other Languages | Bangla: Gaṛaśiṅgā (গড়শিঙ্গা) English: Mangrove trumpet tree, Singapore mangrove French: Bignone de Malaysie Hungarian: Lóhúsfa Kannada: Arkuvoddi Malay: Kaju, Kaju pelok, Kaju pelumping, Poko kulo Malayalam: Neerpongilium, neerpongiliyam, nirpongilium Marathi: Samudrashingi Myanmar: Tha khut ma, Hnin gut, Tha khut Philippines: Pata, tangas, tanghas, tivi, tiwi, tue, tui, tuwi Russian: Bignoniia dlinneyshaia (Бигнония длиннейшая) Sinhalese: Diya danga (දිය දග) Sri Lankan: Diyadanga Tagalog: Tiwi, Tua, Tui Tamil: Kaliyacca, Mankulanchi, Pannir,Vilpadri, attukkompoti, attukkompotiyai, kanbillai, kanpilaicceti Thai: Khaena (แคนา), Khaepa (แค ป่า), Khaena, Khæ thale (แคทะเล) Vietnamese: Quao, Quao nước Visayan: Tanghas, Tanhas |
| Plant Growth Habit | Attractive, evergreen tree |
| Growing Climates | Undisturbed lowland forest, secondary formations, mangroves, along tidal streams, along rivers, in swamps, occasionally also in the sandy soils of keranga forest |
| Soil | Usually found on sandy to muddy soils in the wild, rarely on limestone, but in cultivation it tolerates a wide range of soils. Although its natural habitat is swamps, it can adapt to drier sites. Plants are tolerant of salt-laden winds. It can also tolerate waterlogged soil that is freshwater or brackish |
| Plant Size | Up to 20 meters tall with a bole up to 40 cm in diameter |
| Trunk | Cylindrical, short and often crooked |
| Bark | Grey to dark brown, shallowly ridged and fissured, slightly scaly |
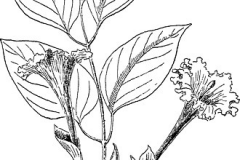
| Leaf | Leaves are compound, opposite to sub-opposite, usually imparinnate, 30 to 40 centimeters long with 9–11 leaflets and petiole up to 8 cm long, lenticels prominent, petioles and rachis furrowed on upper surface. Leaflets are opposite, lanceolate to ovate lanceolate, membraneous, terminal leaflet 10–17 cm long and 4–5 cm wide |
| Flower | Flowers are borne on short, terminal, few-flowered racemes in clusters of 2-10 flowers. The flowers in the cluster bloom one at a time and are very fragrant. Calyx is 4 to 5 centimeters long, spathe like, and split down one side to the base. Corolla is fragrant, white, with a rather slender, cylindrical tube 15-20 centimeters long with ruffled edges, becoming funnel-shaped or bell-shaped above, 5 to 7 centimeters in diameter |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Long, flattened, curling bean-like pods that are 25-60 cm long, 2 to 2.5 centimeters thick and contain many seeds |
| Fruit Color | Green at first, turning brown as they mature |
| Seed | Pale white to dark grey, small about 12–19 mm long and 6–9 mm wide, rectangular to square, with a corky wing |
| Plant Parts Used | Bark, leaves, seeds |
| Propagation | By seed |
| Culinary Uses |
|
Plant Description
Mangrove trumpet tree is an attractive, evergreen tree that normally grows up to 20 meters tall with a bole up to 40 cm in diameter. Old trees have massive trunks that are fluted at the base. Trunk is cylindrical, short and often crooked. Bark is grey to dark brown, shallowly ridged and fissured, slightly scaly. The plant is found growing in undisturbed lowland forest, secondary formations, mangroves, along tidal streams, along rivers, in swamps, occasionally also in the sandy soils of keranga forest. It is usually found on sandy to muddy soils in the wild, rarely on limestone, but in cultivation it tolerates a wide range of soils. Although its natural habitat is swamps, it can adapt to drier sites. Plants are tolerant of salt-laden winds. It can also tolerate waterlogged soil that is freshwater or brackish.
Leaves
Leaves are compound, opposite to sub-opposite, usually imparinnate, 30 to 40 centimeters long with 9–11 leaflets and petiole up to 8 cm long, lenticels prominent, petioles and rachis furrowed on upper surface. Leaflets are opposite, lanceolate to ovate lanceolate, membraneous, terminal leaflet 10–17 cm long and 4–5 cm wide, laterals are smaller, base asymmetrical, apex acuminate, midrib depressed on adaxial surface, peltate scales present on both surfaces when young, 0–5 extra-floral nectaries on abaxial surfaces, occasional on adaxial, domatia present as hair tufts. Young leaves are slightly pinkish and somewhat sticky. At times the tree may be nearly leafless.
Flower
The plant produces bisexual flowers that develop on flowering shoots. Flowers are borne on short, terminal, few-flowered racemes in clusters of 2-10 flowers. The flowers in the cluster bloom one at a time and are very fragrant. Calyx is 4 to 5 centimeters long, spathe like, and split down one side to the base. Corolla is fragrant, white, with a rather slender, cylindrical tube 15-20 centimeters long with ruffled edges, becoming funnel-shaped or bell-shaped above, 5 to 7 centimeters in diameter. The flower is composed of a long thin tube that expands near the opening and spreads abruptly into 5 rounded lobes with frilly edges.
The flowers in the cluster bloom one at a time and according to Corners “very fragrant” while Tomlinson describes it as “a pervasive scent”. According to Hsuan Keng, the flower opens in the early morning and closes at noon, but according to Corners, it blooms at dusk and the flower drops off at sunrise or earlier, while Tomlinson says they bloom in the early evening and the flower usually lasts for only one day. According to Tomlinson, nectar accumulates copiously at the base of the trumpet tube. Suggestions for pollinators include very long-tongued moths (Corners); long-tongued ‘nocturnal animals’ probably hawk moths (Tomlinson). Apparently, no pollinators have been observed so far. Self-pollination also occurs.
Fruit
Fertile flowers are followed by long, flattened, curling bean-like pods that are 25-60 cm long, 2 to 2.5 centimeters thick and contain many seeds. The pods are green at first, turning brown as they mature. The seeds resemble small rectangular wheat biscuits; they are pale white to dark grey, small about 12–19 mm long and 6–9 mm wide, rectangular to square, with a corky wing. They float readily and are probably dispersed by water and not wind.
Traditional uses and benefits of Mangrove trumpet tree
- In Southeast Asia, the leaves and barks of the Mangrove trumpet tree are used as traditional herbal medicine which is used to treat bacterial infections such as oral thrush, bronchitis, and gastrointestinal diseases.
- Leaves are used in the treatment of thrush.
- Seeds, combined with ginger and Pavetta root are administered in spasmodic affections.
- Tea prepared from the leaves is thought to cure mouth related diseases and infections.
- Its seeds are given with ginger in cases of convulsive affections.
- In the Philippines, poultice of fresh leaves and bark is applied against flatulence to women after childbirth.
- Seeds are powdered, and taken for nervous complaints.
- In Java, leaves are used for making mouthwash.
- Leaf decoction is used for various infections of the mouth.
- It has a reputation as abortifacient.
- In Palau, for yaws (frambesia), bark is squeezed together with young stem and flower stalk of Croton sp., and the sap is poured in heated coconut oil; when cooled, applied to affected part of the body.
- In the Philippines, Mangrove trumpet tree is used to treat nervous diseases and flatulence.
- Its bark is applied on antipyretic, asthma, vomiting, inflammation and diarrhea.
- Flower and fruit were used as chlorosis, cholera, diuresis and hematemesis.
Other Facts
- The showy and fragrant flowers are very short-lived, opening at dusk and falling off the tree at sunrise.
- Bruised leaves have an aromatic but disagreeable aroma.
- Seeds are covered by a corky coating; they float and are dispersed by seawater.
- Blackish, coarse fiber is obtained from the bark.
- The pale, white wood is durable, light in weight, soft and easily worked.
- It is used for small household goods, toys, floats and wooden shoes.
- The wood is used for fuel.
- Its leaves and fruits can be substitutes of betel leaves.
- Timber is light and good for carving.
- The Javanese use the wood to make saddles, while the Filipinos use it to make wooden shoes and fishing net floats.
- In Indonesia, the wood is used to make traditional masks.
- Bark is used as fish poison. Some reports that a decoction of bark in dogs has no ill effects.
- The wood is used for making charcoal, matchsticks and toys.
- The wood is light and thus was preferred by the Javanese for making saddles.
- It is also used in floats for fishing nets and for wooden shoes in the Philippines.
- It is used as firewood, and also for making traditional ‘wayang kulit’ (shadow puppet) masks in Indonesia.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=507297#null
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxon/taxonomydetail?id=14450
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/DQLSP
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-320759
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dolichandrone_spathacea
http://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Dolichandrone+spathacea
https://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/225716
http://www.stuartxchange.com/Tiwi.html
https://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/Mangrove%20Trumpet%20Tree.html
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/19468
https://plants.usda.gov/home/plantProfile?symbol=DOSP3