| Ulluco Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Ulluco |
| Scientific Name: | Ullucus tuberosus |
| Origin | Peru, Bolivia, Ecuador, and to a lesser extent in Colombia, Venezuela, Argentina, and Chile |
| Shapes | Subglobose capsule, 2-2.5 mm long, 1-seeded and indehiscent |
| Taste | Combination of beet and potato (Tuber) |
| Health benefits | Removes skin spots, Eliminates acne problems, Prevents and protects us against rheumatism, Eliminates stretch marks, Eliminates stretch marks, Removes the scars, Delays cell aging, Anti-inflammatory and antibacterial food, Relieves and cures digestive problems, Fights Alzheimer’s, Good for growing children and pregnant women |
| Name | Ulluco |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Ullucus tuberosus |
| Native | Peru, Bolivia, Ecuador, and to a lesser extent in Colombia, Venezuela, Argentina, and Chile |
| Common Names | Papa lisa, olluco, melloco, ruba, chugua, ulluco , papalisa , ulloco, olluma, Oca quina, Ullucu, Chigua, Chuguas, Hubas, Michini, Miguri, Muchuchi, Olloco, Ryba, Timbos, Tiquino, Ulluma, Illako, Michurui, Micuche, Rubia, Melloco, melloca, papa chola, papa verde, ulluma |
| Name in Other Languages | Aymara: Ulluma, Ulluco, Ullucu, Ulluku Catalan: Ulluco Czech: Melok hlíznatý English: Tuberous basella, Ulluco Finnish: Ulluco French: Baselle tubéreuse, Baselle tubéreuse cultivée, ulluque German: Olluco, Knollen- Baselle Lithuanian: Gumbinis uliukas Polish: Olluco Portuguese: Uluco Quechua: Ollucu, Ulluco, Ullucu, Ulluku, Oca quina Russian: Ullyuko (Уллюко) Spanish: Camarones de tierra, Chigua, Chuguas, Lisas, Melloco, Mucuchi, Olloco, Olluco, Ulluco, Papa lisa, Papa lisas, Ulluco, Ulluma, Rubas, Rubia, Ruba, Tiquiño, Timbos, Tuna ullush, Ulluca, Ulluma, Uljuku, hubas Swedish: Ulluko Ukrainian: Uĺjuko buĺbonosna (Ульюко бульбоносна) |
| Plant Growth Habit | An erect, twining, procumbent, fleshy, glabrous , perennial plant |
| Soil | Thrives even in relatively poor soils, but loose, light soils benefit you at harvest time. Moderately acidic soils are ideal, but ulluco doesn’t seem to be too particular |
| Plant Size | Up to three feet (91 cm) in diameter and typically reach a maximum height of about fifteen inches (38 cm) before sprawling |
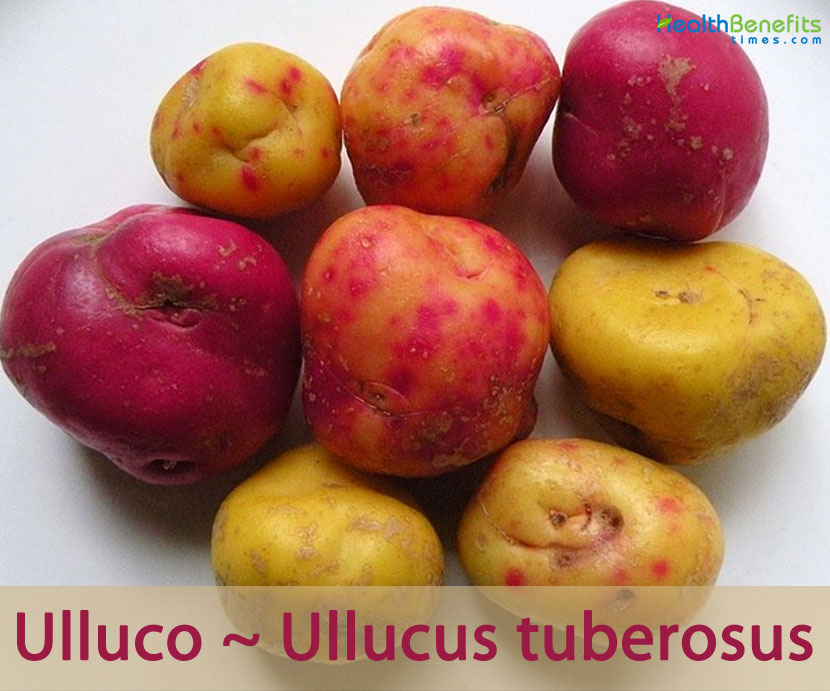
| Tuber Shape and Size | Small, potato shaped, and (2-10 cm) or sometimes elongated (2-15 cm) multi colored tubers |
| Tuber Color | Vividly colored in yellow, orange, red/purple, green, or white, sometimes with spots |
| Tuber Skin | Soft and thin |
| Flesh Color | White or yellow |
| Texture | Much firmer texture than potatoes |
| Stem | Range green to red, are angular in cross section, and often have different coloration at the edges. |
| Leaf | Alternate, fleshy and simple. Petiole is erect and grooved. Blade is cordate to reniform, 5-20 cm long and 5-12 cm wide and shiny |
| Flower | Bisexual, star-shaped, small, with 2 circular red sepals and a 5-lobed, small, green-yellow corolla |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Subglobose capsule, 2-2.5 mm long, 1-seeded and indehiscent |
| Propagation | By stem or tuber cuttings |
| Taste | Combination of beet and potato |
| Plant Parts Used | Tuber, leaves |
| Health Benefits |
|
| Traditional Medicinal Use |
|
| Other Facts |
|
Plant Description
Ulluco is an erect, twining, procumbent, fleshy, glabrous, perennial plant that normally grows up to three feet (91 cm) in diameter and typically reaches a maximum height of about fifteen inches (38 cm) before sprawling. Wild forms are more creeping with branches up to several meters long producing much smaller tubers. The plant thrives even in relatively poor soils, but loose, light soils benefit you at harvest time. Moderately acidic soils are ideal, but ulluco doesn’t seem to be too particular. Stems range from green to red, are angular in cross section, and often have different coloration at the edges.
Leaves are alternate, fleshy and simple. Petiole is erect and grooved. Blade is cordate to reniform, 5-20 cm long and 5-12 cm wide and shiny. Inflorescence an axillary raceme, but in cultivation flowering is rare; flowers are bisexual, star-shaped, small, with 2 circular red sepals and a 5-lobed, small, green-yellow corolla. Fertile flowers are followed by a subglobose capsule, 2-2.5 mm long, 1-seeded and indehiscent.
Tuber
Ulluco are small, potato shaped, and (2-10 cm) or sometimes elongated (2-15 cm) multi colored tubers that are produced in an extremely wide range of colors. The skin can be one color or multicolored with small discrete spots or larger patches of different colors. Colors can be red, yellow, green, white, pink, burgundy, yellow and red, yellow and green, yellow with red spots and red with yellow spots. Tubers also show variation in colors among the same cultivar. They have waxy skins and the bright colors mean they almost look like plastic decorations. Inside, the tubers are yellow or white, with a clear distinction between skins and inside. Tubers are cooked in a variety of different ways in South America with many countries having regional dishes. Principally the tubers are boiled and served with sauces or used in stews with meat and other vegetables. Contemporary dishes include ulluco tubers in salads. Ulluco leaves (which taste like spinach) are also eaten in soups and salads. Dehydrated ulluco are usually eaten in soups and stews in the Peruvian highlands. They can be eaten fresh or dehydrated by freeze drying and can be stored for years.
History
Ulluco tubers are native to the high altitudes of the Andes Mountains in the northwestern part of South America. They primarily grow in an area from southern Venezuela to northern Argentina but can also be found in Chile and parts of Brazil. They are believed to have originated in the Andean high plains in Bolivia, Peru and Ecuador. They have been a part of the Andean people’s diet for over 10,000 years, evidenced by the remnants of Ulluco found in a cave in Peru. Native Ecuadorians have used the raw tuber topically to treat skin conditions and recommend eating it to ease stomach and digestive discomfort. The leaves of the Ulluco plant are edible and are prepared and used like spinach. Outside of the Andes region, Ulluco can be found in New Zealand, where they have been cultivated for over 20 years and are called ‘earth gems.’ One farm in the United Kingdom is cultivating them and canned or jarred Ulluco may be spotted in Latin markets in the United States and Europe.
Health Benefits and uses of Ulluco
The benefits offered by Ulluco are extensive, mentioned below are some of the benefits granted by the properties and medicinal and healing uses of the Ulluco
1. Removes skin spots
Ulluco consists of good amount of Vitamin C, which offers lightening properties and control the appearance of spots on the skin. Besides preventing the negative effect of the sun’s rays it strengthen the natural protective barrier of the skin.
2. Eliminates acne problems
Cut small piece of Ulluco, and apply the cut part to the face with acne, serving as a scar, using it frequently will notice an improvement in the texture of the skin, closing pores and regenerating damaged skin.
3. Prevents and protects us against rheumatism
Ulluco is used to treat rheumatism, bronchial infections and erysipelas. Making an infusion of its leaves, add honey and lemon juice to serve, wait for it to cool a bit and take it. It is very good and helps to calm the intense cough.
4. Eliminates stretch marks
It has a natural healing effect, functioning as a product that removes stretch marks of pregnancy or sequelae of weight gain, thanks to the B vitamins that the ulluco has.
5. Removes the scars
Ulluco has healing properties that help protect the skin. It is used to treat acne, chicken pox, burns and stretch marks.
6. Delays cell aging
B vitamins contained in Ulluco, favors the skin, nails and hair; avoiding premature aging and the presence of wrinkles.
7. Anti-inflammatory and antibacterial food
The juice of the smooth potato, is good in mineral salts helping to expel toxins from the body, it helps to relieve the inflammation of muscles and joints.
8. Relieves and cures digestive problems
Leaves were used habitually by the inhabitants, as a food or in infusions, for constipation, stomach pain and tranquilize indigestion. It is also effective in pets or animals to alleviate their digestive problems.
9. Fights Alzheimer’s
Tuber consumption is very necessary for the elderly people suffering from Alzheimer’s, since it contains B complex, which helps to overcome mental problems and reduce anxiety.
10. Good for growing children and pregnant women
This small yellow tuber has a high content of Zinc and Calcium, important nutrients in the growth stage of a child and calcium for women who are in the gestation stage.
Culinary uses of Ulluco
- Tuber can be consumed after being cooked.
- Ulluco is a staple food in South America, being used in most of the ways that potatoes are used, indeed when boiled and fried they taste very much like potatoes.
- In the Andes a popular dish called ‘chuño’ is made by alternately freezing and drying the tubers.
- Tubers are usually eaten in indigenous soups and stews, but more contemporary dishes incorporate them into salads along with the ulluco leaves.
- In the pickled form, it is added to hot sauces.
- The leaves of ulluco are also edible and can be used like spinach.
- They are used whole as a garnish, grated, pureed, or ground to thicken soups and stews.
Ulluco Soup
Ingredients
- ½ kg of Ulluco
- 4 white potatoes girls
- 1 diced onion
- 200 grams of green beans peeled
- 200 milliliters of evaporated milk
- 1 corn
- 200 grams fresh cheese
- 2 tablespoons of oil
- 1 tablespoon ground Peruvian yellow pepper
- 2 tablespoons ground garlic
- 2 eggs
- 1 twig of huacatay
- Parsley
- Ground oregano
- Salt to taste
Directions
- Wash and chop the Ulluco in julienne. Cut the sliced corn, peel and chop the potatoes in half.
- In a large pot, add oil, garlic, onion, and sauté for 3 minutes, and then add the Peruvian yellow pepper and sauté for 3 more minutes.
- Add 7 cups of water, the Ulluco in julienne, the potatoes, the corn and salt to taste let cook for 30 minutes, then the beans, the huacatay and let cook 15 minutes more
- In a bowl beat the eggs, chop the cheese into squares and cut the leaves of the parsley into thin pieces
- At the end of the 15 minutes of cooking add the beaten egg, milk, cheese, parsley, oregano. Put out fire.
- Serve and enjoy Bon appetite! It can be accompanied by a delicious purple chicha.
Ulluco Locro
Ingredients
- ½ kg of Ulluco
- ¼ kg of pumpkin
- 2 white potatoes
- 1 diced onion
- 250 mg of fresh cheese
- 250 ml of peas
- 400 mg of evaporated milk
- 3 tablespoons ground yellow chili
- 2 teaspoon ground garlic
- 2 tablespoons of vegetable oil
- 4 branches of cilantro
- Pepper and cumin
- Salt to taste
Directions
- In a saucepan, cook the Ullucus and pumpkin with water for 25 minutes. Do not flush the cooking water and crush the Ullucus in a separate container.
- In another pot add oil, ground garlic, onion, yellow pepper, pepper and cumin sauté for 5 minutes.
- Then add 4 cups of cooking water of, squash and crushed Ullucus, peas and salt to taste. Add diced potatoes and cook for 20 minutes.
- If the Mel locos of Locro are thickening, add a little more water. Chop the cheese into squares and the leaves of the cilantro into thin pieces.
- When finished add milk, cheese, coriander and put out the fire. It can be accompanied with a portion of rice.
- Serve and enjoy Bon appetite! It can be accompanied by delicious refreshment from Camu Camu.
Ulluco Saltado with chicken
Ingredients
- ¾ kg of Ulluco
- ½ kg of chicken pulp
- 3 red tomatoes
- 3 red onions
- 2 tablespoons ground garlic
- 2 tablespoon ground yellow chili
- 3 tablespoons of vegetable oil
- 2 spoons of olive oil
- 1 tablespoon white vinegar
- 1 tablespoon of soy sauce
- Parsley
- Ground oregano
- Pepper and cumin
- Salt to taste
Directions
- Wash and cut the Ulluco in julienne, in the same way tomatoes and onions. And chop the leaves of the parsley.
- In a pot, with water cook the Ulluco for 20 minutes then let it dry. In a cutting board, cut the chicken pulp in medium julienne.
- In a large pan, add the vegetable oil, the garlic, the yellow pepper, the chicken and sauté for 5 minutes. Add vinegar, soy sauce, onion, Ullucus, tomato, ground oregano, pepper, cumin and salt to taste, let simmer for 10 minutes.
- Between the 10 minutes of cooking add the parsley, at the end of the time put out the fire
- This delicious Melloco of Saltado with Chicken can be accompanied with a Portion of rice.
- Serve and enjoy Bon appetite! It can be accompanied by delicious refreshment from Camu Camu.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=506585#null
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Ullucus+tuberosus
http://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Ullucus+tuberosus
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/55568
https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ullucus_tuberosus
https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=ULTU
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/ULLTU
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-358073
https://uses.plantnet-project.org/en/Ullucus_tuberosus_(PROSEA)