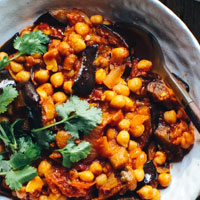| African Eggplant Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | African Eggplant |
| Scientific Name: | Solanum macrocarpon |
| Origin | West Africa, but is now widely distributed in Central and East Africa |
| Colors | Green, ivory, or a purple and white color with dark stripes when young turning to yellow or a yellow-brown as they matures |
| Shapes | Round, the top and the bottom are flattened out and have grooved portions with a length of 5–7 cm and a width of 7–8 cm |
| Flesh colors | Pale yellow or ivory |
| Taste | Distinctly bitter taste that becomes more bitter as it ripens |
| Health benefits | Beneficial for cardiac diseases, throat pain, bronchitis, body aches, asthma, toothaches, abscesses and ear infections |
| Name | African Eggplant |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Solanum macrocarpon |
| Native | West Africa, but is now widely distributed in Central and East Africa. Through an introduction from West Africa, the plant also grows in the Caribbean, South America, and some parts of Southeast Asia |
| Common Names | Mock Tomato, Bitter Tomato, Ethiopian nightshade, Scarlet Eggplant, African eggplant, eggplant Gboma, ornamental eggplant, Tomato-fruited eggplant, red-fruited eggplant, orange-fruited eggplant, eggplant White, Nightshade, gboma, gboma eggplant, local garden egg |
| Name in Other Languages | Danish: Afrikanska aegplante Dutch Afrikaanse aubergine, Antroewa English: African eggplant, eggplant Gboma, ornamental eggplant, Tomato-fruited eggplant, red-fruited eggplant, orange-fruited eggplant, eggplant White, Nightshade, gboma, gboma eggplant, local garden egg Esperanto: Antruvo French: Anghive, Aubergine africaine, Aubergine d’Afrique, Aubergine Amer Orangea Aubergine, Aubergine ornementale, Aubergine gboma, Gboma, Grosse anghive, grosse aubergine amère German: Afrikanische Eierpflanze, Afrikanische Aubergine Ghana: Etruopue, Ntoropo Indonesian: Terong engkol Italian: Melanzana petonciano Japanese: Sennari nose Malaya: Terong Santana, Terong rapoh, Terong engkol (Indonesia), Terong kelapa Nigeria: Ipere Ibo Portuguese: Berinjela-Africans, Beringela-africana Sierra Leone: Busiburaxe, Kabate, Kabeli, Kpola, Kpoloi, Paili Spanish: Berenjena Sundanese: Terong gayung Swahili: Ngogwe, nyanyi, nyanyi Chung Swedish: Afrikanska äggplanta, Afrikansk äggört Uganda: Ntengo, Nume ya Kyalo Vietnamese: Cà pháo |
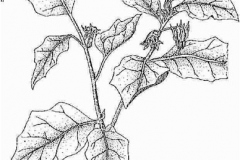
| Plant Growth Habit | Erect, often much branched, annual to perennial herbaceous plant |
| Growing Climates | Evergreen forest edges, floodplains, riverbanks, cultivated ground, in dry or sometimes moist situations |
| Soil | Tolerant of a wide range of soil conditions, but grow best in fertile, humus-rich conditions |
| Plant Size | Up to 2 m (6.6 ft.) in height |
| Branches | Can become more or less woody, especially at the base; they are unarmed, or with occasional prickles |
| Stem | Blackish-violet stem is woody at the base |
| Leaf | Alternate leaf pattern with the blade width of 4–15 cm and a height of 10–30 cm; the shapes of the leaves are oval and lobed with a wavy margin. |
| Flower | Flowers have a diameter of 3–8 cm and are located on short stalked inflorescence that can contain 2 to 7 flowers. The lower portion of the plant carries bisexual flowers while the upper portion contains male flowers |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Round, the top and the bottom are flattened out and have grooved portions with a length of 5–7 cm and a width of 7–8 cm; the stalk of the fruit is 1–4 cm long and is either de-curved or erect |
| Fruit Color | At a young stage the color of the fruit is green, ivory, or a purple and white color with dark stripes; when ripe, the fruit turns yellow or a yellow-brown |
| Flesh Color | Crunchy and pale yellow or ivory |
| Seed | Seeds have a length of 3-4.5 mm, a width of 2-3.5 mm, and are shaped in an obivoid or reniform |
| Taste | Distinctly bitter taste that becomes more bitter as it ripens |
| Plant Parts Used | Roots, Fruits, young leaves |
| Precautions |
|
Calyx
Calyx densely clothed with stalked and long-radiate stellate hairs to glabrous, prickly or unarmed, in fruit strongly enlarged, appressed to and often enveloping it, very prickly. Tube 3–4 cm long, campanulate; lobes foliaceous, 8–15 mm long, elongating to 4 cm in fruit, lanceolate-subulate, sub-acuminate.
Corolla
Corolla is bluish to purple or occasionally white, 1. 6–2.5 cm across, broadly campanulate to rotate-stelliform; lobes are broadly triangular, abruptly ending in a short, hairy mucro, densely clothed with long-radiate hairs on the median region outside and with a few stellate hairs on the midrib to quite glabrous inside.
Stamens
A stamen filament is 1–2 mm long; anthers are 5–8 mm long, oblong to lanceolate in outline or broadly lanceolate-ellipsoid, emarginate at both ends or cordate basally.
Ovary
Ovary is 1. 5–2.5 mm in diameter, globose, glabrous except for a few sparse, minute, glandular hairs near the top and 4–6-locular.
Style
Style is 7–10 mm long, much shorter in male flowers, robust, recurved to the apex, sparsely hairy often with a few uni-radiate hairs and also or only with a few glandular ones near the base.
Fruits
Fruits are round, the top and the bottom are flattened out and have grooved portions with a length of 5–7 cm and a width of 7–8 cm. The stalk of the fruit is 1–4 cm long and is either de-curved or erect. At a young stage the color of the fruit is green, ivory, or a purple and white color with dark stripes; when ripe, the fruit turns yellow or a yellow-brown. The fruit contains many seeds and it is partly covered by the calyx lobes.
Seeds
Seeds are pale yellow-brown or yellowish, 3–4 mm long and 2.5–3 mm wide, oblique or flattened lenticular, subreniform, conspicuously or minutely reticulate all over.
- Fruit is used as a laxative, and as a means to treat cardiac diseases in Nigeria.
- Flowers are chewed on to clean teeth.
- Leaves are heated and then are chewed to ease throat pain in Sierra Leone.
- Roots are boiled and the juice is then consumed to kill any hookworms in the stomach in Kenya.
- Root is also used for bronchitis, body aches, asthma, and speed up the process of healing wounds.
- Seeds are crushed to treat toothaches.
- Crushed leaves are taken to treat stomach troubles.
- Decoction of the leaves and roots is used to treat abscesses and ear infections.
- The plant (parts not specified) is used to treat digestive problems and anemia
Culinary Uses
- Fruit can be eaten raw.
- It is more commonly picked before it is fully ripe and cooked as a vegetable or used in soups and sauces.
- Young leaves and young fruits are cooked and consumed as a vegetable.
- Leaves are boiled or steamed and used as a side dish with rice.
- They can be added to soups and sauces.
Recipe
Nepali Style African Eggplant
Ingredients
- 1½ pounds African eggplant, sliced into quarters
- ¼ cup vegetable or olive oil
- 1 tablespoon cumin seeds
- 1 medium onion, chopped
- 3 cloves garlic, minced
- 1 pound potatoes, cut into to ¼-inch slices
- 1 teaspoon ground turmeric
- 1 inch fresh ginger, minced
- 1 to 2 red Thai chilies, minced
- 1½ cups vegetable broth or water
- ½ pound tomato, chopped
- ½ cup chopped cilantro
- ¼ cup green onion
- Salt and pepper
Directions
- Bring a large pot of salted water to a boil. Boil the eggplant for about 4 minutes and transfer to an ice bath or cool with cold water in a strainer. Set aside.
- Heat the oil over medium heat in a large, nonstick sauté pan. Add the cumin seeds and fry until they become fragrant, about a minute. Add the onions and cook until transparent, about 5 to 8 minutes.
- Add the potatoes and turmeric, seasoning with salt and pepper. Mix well so that the potatoes and onions take on a golden-orange hue, and separate any potato slices that stick together. Fry, stirring often, until the potatoes brown and soften, about 10 to 12 minutes.
- Add the garlic, ginger and fresh chilies. Cook just until fragrant, about a minute. Add the eggplant and broth and adjust the seasoning. Reduce the heat to medium-low and simmer until the eggplant and potatoes are tender, about 12 to 15 minutes. Just before you remove the pan from the heat, stir in the tomatoes, cilantro and green onion. Check seasoning and serve hot, over rice.
African Garden Egg Curry Sauce
Ingredients
- 1 tbsp. coconut oil
- 1 tbsp. red curry paste
- 1 onion small
- 2 garlic peeled and crushed
- 30 g ginger root grated
- 200 g African garden egg whole
- 100 g green beans both ends cut off
- 100 g baby corn cut into 1-inch long pieces
- 250 g coconut milk
- 150 g tomato passata
- 1 scotch bonnet pepper de-seeded
- salt to taste
- pepper to taste
- 1 lemongrass stick
Directions
- Heat a skillet on the hob and when hot, add the coconut oil, and let sizzle. Then add the chopped onions, garlic, and grated ginger and fry while stirring constantly, for 3 – 5 minutes until the onions are soft and translucent.
- Add the red curry paste, and continue frying and stirring until the spices are fragrant. This should take another 2 – 3 minutes.
- Add the coconut milk and tomato passata. Stir to combine. Then add the vegetables – garden egg, green beans, baby corn, including the lemongrass sticks and the peppers. Cover and reduce heat and allow simmering for fifteen minutes.
- Gently scoop out all the garden eggs into a bowl. To a third of the garden eggs, chop them into quarters, and return to the pan to simmer. To the rest of the garden eggs, use a masher and mash the garden eggs, and then return to the sauce. Allow to simmer for another 10 minutes. Remove from heat and serve.
East African Eggplant Curry with Chickpeas
Ingredients
- 1 medium eggplant (1 pound 2 ounces), unpeeled
- 3 tablespoons vegetable oil
- 1 medium onion, chopped
- 4 large garlic cloves, minced
- 1 or 2 jalapeño peppers, minced; or 2 to 3 teaspoons diced canned roasted jalapeño peppers
- 1 tablespoon minced peeled fresh ginger
- 2 teaspoons ground cumin
- 1/2 teaspoon turmeric
- 1/4 to 1/2 teaspoon dried hot red pepper flakes, or to taste
- 2 cardamom pods (optional)
- salt to taste
- 1 pound ripe tomatoes, peeled, seeded, and coarsely chopped; or 1 28-ounce can plum tomatoes, drained and chopped
- 1 tablespoon tomato paste
- 1/2 cup water
- 1 1/2 to 2 cups cooked chickpeas (garbanzo beans), drained
- cayenne pepper to taste
Directions
- Cut eggplant into 1/4-inch dice.
- In a heavy, wide casserole, heat oil, add onion, and cook over low heat for 7 minutes or until soft but not brown.
- Add garlic, jalapeño peppers, ginger, coriander, cumin, turmeric, pepper flakes, and cardamom. Cook mixture, stirring, for 1 minute.
- Add eggplant and salt, and mix well over low heat until eggplant is coated with spices.
- Add tomatoes and bring to a boil over high heat.
- Mix tomato paste with water, and stir into mixture. Cover and simmer over low heat, stirring often, for 20 minutes.
- Add chickpeas and simmer 10 to 20 more minutes or until eggplant is very tender and mixture is thick.
- Taste and adjust seasoning, adding cayenne pepper if desire.
- Remove cardamom. (Stew can be kept, covered, 3 days in refrigerator.) Serve hot.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=505838#null
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?id=102157
https://wikivisually.com/wiki/Solanum_macrocarpon
https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=SOMA7
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/SOLMA
http://www.tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Solanum+macrocarpon
https://uses.plantnet-project.org/en/Solanum_macrocarpon_(PROTA)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solanum_macrocarpon
http://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:819941-1
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/50534