| Toothache Plant Quick Facts |
| Name: |
Toothache Plant |
| Scientific Name: |
Acmella oleracea |
| Origin |
Brazil |
| Shapes |
Achenes are obovoid, 3-angled, 3 mm long, tip slightly depressed |
| Taste |
Pungent taste |
| Health benefits |
Impotency and erectile dysfunction, Pharyngitis and sore throat, Pyorrhea, Toothache, Common cold, Childhood apraxia of speech (CAS) and Delayed Speech Development, Premature ejaculation, Paralysis, Nervous and vascular weaknesses, Epilepsy, Hemiphlegia, Headache, Indigestion, Flatulence,Infections, Facial Neuralgia, Fever, Tonsillitis and sore throat, Congestion, Chronic catarrh, Intestinal worms, Rheumatism and Arthritis, Urinary infections, Irregular Menstrual Periods, Xerostomia, Sciatica, Stammering, Dullness, Inflammation, Throat infection,Bad breath, Hiccups |
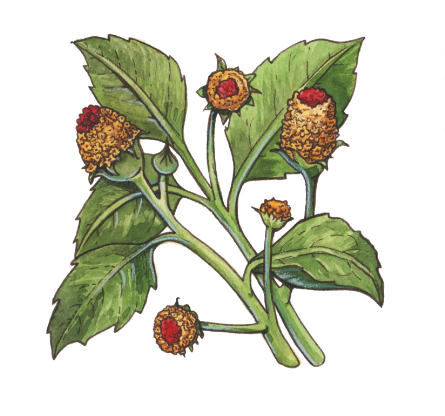
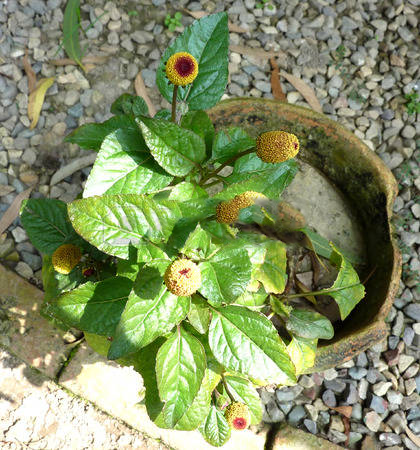
Acmella oleracea commonly known as Toothache Plant is a species of flowering herb in the family Asteraceae. Other popular common names of the herb are Brazil Cress, Eyeball Plant, Para Cress, Peek-ABoo Plant, Perennial Para Cress and Spot Flower. In Brazil it is called jambu and in Maharashtra it is called ‘अक्कलकाढा ‘. The plant is native to Brazil. It has been introduced across the tropics, and in Africa, escapes from cultivation have been reported. The plant is now grown both in the tropics and subtropics including America, Northern Australia, Africa, Southeast Asia, India and Sri Lanka. It is grown as an ornamental and it is used as a medicinal remedy in various parts of the world. A small, erect plant, it grows quickly and bears gold and red inflorescence. It is frost-sensitive but perennial in warmer climates.
Plant description
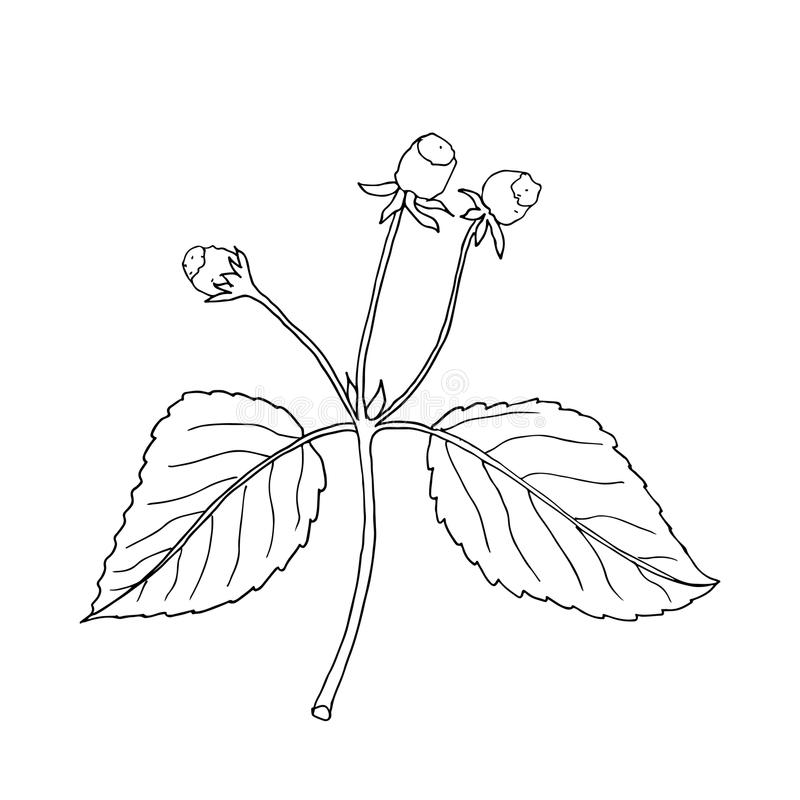
Toothache plant is an erect, or decumbent, stout, branched, annual herb that grows about 20–80 cm tall with erect stems not usually rooting at nodes. The plant is found growing in moist, damp environment, in villages, pastures, rice fields and cultivated areas, along ditches, marshy meadows, open waste places, old clearings, on open hillsides and the rocky shores of rivers, and along roadsides and normally prefers well-drained, black (high organic content) soil. The plant is frost-sensitive but perennial in warmer climates. Water regularly, but do not over water, as it can be prone to mildew and mold. This plant can also be grown in containers. Leaves are opposite, glabrous, simple, broadly ovate to triangular, 5–11 cm long, 4–8 cm wide, base truncate, apex acute, margin serrate.
Flower & Fruit
Flower-heads are disc-like, solitary, borne in panicles carried on 2.5-16cm long stalks in lead axils or terminal. Heads are 8.4-12.5mm tall, 6.9-10mm in diameter. Receptacle (thickened part of a flower stalk) is 5-8 mm tall, 1.1-3mm in diameter. Involucral bracts (a series or bracts beneath or around a flower) are 9-12, ovate-lanceolate, 6mm long. Disc florets are 90-200, tubular, minute, and 4- or 5-lobed. Flowers are followed by Achenes (a type of simple dry fruit) that are obovoid, 3-angled, 3mm long, tip slightly depressed, margins scabrid. Pappus of 2 sub equal bristles, longer on 0.5-1.1mm long, shorter one 0.4-0.9mm long.
Flower is mainly ornamental but the flower heads contain a great amount of an analgesic agent known as Spilanthol. This is specially used to numb toothaches and gum aches as well. Ancient tribes of Central America have used the Spilanthes flower as a vegetable and also for its medicinal value. It was a remedy for toothache, digestive problems and also throat and gum disease. In India, it was used as an additive in tobacco for flavor. Its characteristic pungent and strong taste has given it a space in the kitchens around the world, often consumed as tea, but as a condiments in some communities of northern brazil, in salads in the United States and added to steamed vegetables, soups and meats in India.
History
Even today the origin of A. oleracea is unknown. There is a scarcity of records of the plant from the wild. but one hypothesis postulates that this is due to a long periods of cultivation of Acmella alba in South America. Collections in Brazil and Peru support this hypothesis. According to this idea, after a long period of cultivation, A, oleracea may have spread in the tropics, but also there is a possibility that the Portuguese may have introduced the plant to the Indian Ocean Islands and then, around 1900, it spreads to Africa by Indian Laborers.
Health Benefits of Toothache Plant
Toothache Plant is used to treat the oral diseases, fever, rheumatic pain and other ailments. The flower head and leaves are used for medicinal purposes which have a pungent taste, tingling and numbness. The leaves of Toothache Plant are used in Japan to treat joint pain, gout, rheumatism and arthritis. It is used for toothaches due to its anesthetic properties. The plant parts could increase the salivation and also cure the headaches. The mouth soreness could be treated with the dried flower head. The urinary stones could be helped by decoction of plant. The whole plant should be boiled in water which helps to treat dysentery. Scabies and psoriasis could be treated if the paste of the plant is used as lotion.
1. Loss of Libido
Toothache Plant possess libido stimulant, aphrodisiac and spermatogenic properties. The secretion of androgens and its production is influenced. Alkyl-amide found in Toothache Plant root expands the production of testosterone. Toothache Plant boost the fertility, improves lipido in male and increase spermatozoa count. It triggers the desire and raises the supply of blood to the genitals. It enhances libido and also increases sexual urges.
2. Impotency and erectile dysfunction
It performs the similar function as SILDENAFIL but does not increase the blood pressure. It should be used with Kaunch Beej (Mucuna Pruriens) and Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) to obtain the benefits to the maximum. It triggers the circulation of blood in the urogenital area and provides the longer and stronger erections. It is also effective to treat the nervous and vascular weaknesses or disorders.
3. Pharyngitis and sore throat
10 grams of Toothache Plant root should be boiled with 250 ml of water. This water should be used to gargle in order to alleviate pharyngitis. It is also effective for gum disease and toothache.
4. Toothache
Massage with the mixture of Toothache Plant root powder and camphor which helps to relieve toothache. It could also be used with Vaividang (Embelia ribes), Ajwain Khurasani (Hyoscyamus Niger) and black pepper. Toothache Plant’s tooth powder could be made by drying the whole plant in shade and then grinding it to make powder. Alum and clove powder should be mixed. Toothache Plant tooth powder is prepared.
5. Pyorrhea
The pyorrhea could be treated with the mixture of mustard oil and Toothache Plant’s root powder.
6. Common cold
The common cold could be alleviated if Anacyclus pyrethrum root powder is used with long pepper and black pepper. It possesses antiviral properties which alleviates the symptoms of flu and nasal congestion.
7. Childhood apraxia of speech (CAS) and Delayed Speech Development
The tongue should be massaged with the mixture of honey and 125 mg of Toothache Plant’s root powder. This helps to improve the speech in children. It would be much effective when 125 mg Vacha is added to the mixture.
8. Premature ejaculation
It vitalizes the nerves which are responsible for the sexual performance of men and ejaculation and also assist to delay ejaculation.
9. Paralysis
The presence of nervine and stimulating properties of Toothache Plant enhance the nerves and also assist to recover from Paralysis.
10. Nervous and vascular weaknesses
The presence of flavonoids in Toothache Plant strengthens the vessels and nerves and also prevents the disorders such as nervousness, phobias, vertigo, nausea etc. which is caused by the Nervous and Vascular weaknesses.
11. Epilepsy
The presence of nervine properties in Toothache Plant could control the epilepsy which is a nervous and neurotic disorder. The mixture of vach powder and Toothache Plant powder should be taken twice in a day.
12. Hemiphlegia
The condition of hemiphlegia could be improved with an application of root extracts of Toothache Plant.
13. Headache
It could relieve headache due to the presence of analgesic properties. The paste of Toothache plant should be applied on forehead. Or the juice which is extracted and few drops should be put in each nostril.
14. Indigestion
Toothache Plant’s roots possess sialagogue and cholagogue properties which enhances digestion with the secretion of saliva and digestive juices such as acids, bile etc.
15. Flatulence
The flatulence and gas could be relieved with the carminative property of Toothache Plant.
16. Infections
Toothache Plant possess the anti-bacterial and anti-microbial properties which prevents the water borne and air borne infections.
17. Facial Neuralgia
The extract of Toothache Plant root lessens the swelling in the artery and relieves the pain by lowering the pressure on nerves.
18. Fever
The presence of febrifuge properties helps to eliminate infections which leads to fever and lowers the temperature of body. Massage with the root powder which is cooked in olive oil so that it leads to sweating and assist in high temperature.
19. Tonsillitis and sore throat
The presence of antiviral property counteracts with the infections which is the cause of sore throat and tonsillitis.
20. Congestion
Toothache Plant’s root extract expand the tracheal, nasal and bronchial passages which eases the respiration.
21. Chronic catarrh
Toothache Plant stimulates the inner throat and alleviates the infection and inflammation by expelling the old catarrh.
22. Intestinal worms
Toothache Plant’s root possess the vermifuge effects of alkaloids which eliminates the intestinal worms.
23. Rheumatism and Arthritis
Toothache Plant possess flavonoids and alkaloids which relieves the rheumatism and arthritis by counteracting the uric acid and vitalizing the circulation of blood.
24. Urinary infections
The presence of diuretic properties in Toothache Plant enhances the digestion, provides relief from flatulence and weight loss.
25. Irregular Menstrual Periods
The Emmenagogue property helps to regulate the menstrual cycles and clears the obstructed periods.
26. Xerostomia
The oral intake of Toothache Plant’s roots helps to cure dry mouth. It increases the production of saliva by vitalizing the saliva glands and also cures this problem.
27. Sciatica
The application of Toothache Plant’s root powder in almond oil provides relief from sciatica.
28. Stammering
Toothache Plant is useful to treat stammering which is a nervous disorder. The mixture of honey, one gram Toothache Plant and black pepper should be rubbed on the tongue which causes the salivation and cures the dryness of tongue. It should be used for 1-2 months to obtain the results.
29. Dullness
The application of Toothache Plant’s root activates the neuron which helps to treat dullness.
30. Inflammation
Toothache Plant effectively reduce the inflammation in the body.
31. Throat infection
Jamun leaves, Toothache Plant’s flower and mango leaves should be boiled with water. This solution should be used to gargle.
32. Bad breath
The decoction should be prepared by boiling the Toothache Plant flower and leaves in water. This decoction should be used to drink or gargle.
33. Hiccups
Toothache Plant’s flower should be chewed or gargled which cures the hiccups. Or one gram of Toothache Plant powder should be licked with honey.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6iEvFWgHGyM
Medicinal benefits of Toothache Plant
- Aids in Menstrual problems: Drink 100 ml decoction of Toothache plant twice a day. It normalizes the menstrual cycle.
- Helpful in Paralysis: Grind Toothache Plant’s roots and mix it with the oil of Mahua plant. Massage with this on the affected areas. It heals paralysis. Take 500 gm of Toothache Plant’s root powder and mix it with honey. Licking it twice a day is very beneficial in Paralysis.
- For Stomach problems: Mix equal amount of Toothache Plant’s root powder with fig and peepal powder. Give 1/2 teaspoon of this mixture, every morning and evening after the meals. It cures all forms of stomach disorders.
- Treats Asthma: Make a powder of whole Toothache Plant. Strain it finely through a muslin cloth. Inhaling this powder cures different breathing problems like asthma, dyspnoea etc.
- Aids in Heart diseases: Take bark of Arjuna tree and Toothache Plant powder in equal quantities. Grind them and give 1/2 teaspoon of this mixture, twice a day. It makes your heart stronger and also abides any strokes.
- Helpful cure in Halitosis: Take equal quantities of Toothache Plant, roasted alum, black pepper and rock salt. Grind these into a fine powder and use as tooth powder in brushing your teeth. It curbs Halitosis and cures all types of tooth and gum problems.
- Treats Headache: Make a paste of Toothache Plant’s root and apply it on the forehead treats headache in eased way. OR Chew the root of Toothache Plant, it treats headache caused due to cold.
- For Sciatica: Mix Toothache Plant’s root powder with walnut oil. Massage it on the painful areas. It help cure Sciatica.
- Abides Laziness and Dullness: Whenever you feel dull, take 1 gm. powder of Toothache Plant with 2-3 cloves. OR Take 100 ml decoction of Toothache Plant, it eradicates Laziness.
- For Hiccoughs: Take 1 gm. of Toothache Plant powder with honey.
Traditional uses and benefits of Toothache Plant
- Flowers and leaves of Toothache Plant have a pungent taste supplemented by tingling and numbness and have been used as a spice for appetizers and as widespread folk medicine for stammering, toothache, and stomatitis and throat complaints.
- Leaves of Toothache Plant have been used traditionally as tonic and in the treatment of rheumatism, gout and sialagogue.
- Plant has anesthetic action and is used for toothache in the East.
- Plant is used as a sialagogue to increase salivation and stimulation for curing headaches, paralysis of the tongue and affections of the throat in India.
- Dried flower heads are used for sore mouth of sprue in Java.
- Decoction of the plant can be taken internally as a diuretic and able to resolve stones in the bladder, while a decoction of the roots can be used as a purgative.
- Decoction of the plant is used as vulnerary and also regarded as an antiscorbutic.
- Plant is also used as a cure for dysentery and rheumatism and to enhance the immune system.
- It is used against blood parasites, especially against malaria, both prophylactic and curative.
- Decoction or infusion of the leaves and flowers is a traditional remedy for stammering, toothache, and stomatitis.
- If you have a toothache rub a leaf on the gum area of the toothache, the area tingles and then goes numb within a few seconds.
- It is also used for sore gums, teething babies, and mouth ulcers.
- Leaves can be rubbed on cuts, hard to heal sores and acne.
- For people who suffer with thrush, candida, frequent viruses, fungal and auto-immune diseases, eating the leaves in salads or sandwiches, can be of real benefit.
- Chewing the leaves of this herb stimulates saliva production; it is useful for treating fevers, particularly during summers.
- Internal use of the herb also encourages phagocytosis.
- Leaves of toothache plant are also used to cure bacterial as well as fungal skin afflictions.
- Herb also promotes healing of wounds and protects people from common colds and flu.
- Toothache plant works to augment digestion, relieve flatulence, enhances appetite and also aids in curing vomiting and nausea, as it revitalizes the salivary glands to secrete more saliva.
- It is supposed that the extract of toothache plant helps to alleviate muscle strain when it is applied externally on the affected area.
- It is also reported to diminish wrinkles and facial lines, which are occasionally caused by contracted or tense facial muscles.
- Applying the Acmella extract is said to cause the facial muscles to relax and thus reduce the noticeable wrinkles, “crow’s feet”, ageing lines as well as other related problems.
Culinary Uses
- Leaves and young shoot tips are eaten raw or cooked.
- In the United States, the leaves are used raw as a pungent flavoring for salads and in India as a cooked vegetable in soups and meats.
- In the Indian Ocean islands (Comoros, Madagascar, Réunion, Mauritius), the main use of the leaves is as a steamed vegetable.
- Both fresh and cooked leaves are used in the culinary dishes of the indigenous people in Brazil particularly in the provinces of Acre, Amazonas, Pará and Ceará.
- In the state of Pará, paracress it is often consumed with chillies and garlic. Paracress is used in a fried duckmanioc dish called ‘tucupí’.
- Another dish where paracress is used is ‘tacacá’, a soup thickened with manioc juice that contains dried shrimps and sometimes freshwater fish.
- Leaves and young shoots are served raw in ‘lalab’ served with other vegetables and eaten with a sambal in Java indionesia.
- Leaves of another closely related species S. paniculata are used as cooked vegetables in Assam by the Bodo community and in Southeast Asia.
- Flowers are also edible.
- Leaves and flower heads are cooked as vegetables and used in curries in Thailand.
- Flowers are used as spice for foods and dentifrice flavoring in Japan.
- Consumption of portions or whole flower buds known as Buzz Buttons, Szechuan Buttons, Sansho Buttons and Electric Buttons has been reportedly used to offset the intense heat of chilies and peppers.
- Benwick reported that a dish of eel basted in a thick, sweet sauce with Szechuan Button flowers and roast pineapple won ‘Sushi of the Year’ honors in Britain’s annual Sushi Awards, sponsored by Eat-Japan.
- These buds are also used in drinks, cocktails, sorbets and an Alaskan halibut curry dish.
- Buds and oleoresins are used as flavoring in chewing tobacco in India.
- Both fresh and cooked leaves are used in dishes such as stews in northern Brazil, especially in the state of Pará.
- Leaves can be cooked in coconut milk.
Other Facts
- Acmella oleracea is widely grown as an ornamental (and occasionally as a medicinal) in various parts of the world.
- Crushed plant is used as a fish poison in India.
- Peptides derived from A. oleracea plant extracts are used in a cosmetic composition (in anti-wrinkle cream and anti-aging formulations) to help regenerate the dermal matrix and accelerate repair of functional wrinkles.
- Flower heads have been used as a spice for appetizers by the Japanese, and spilanthol- rich extract.
- Essential oil of the plant was used as a flavoring material for dentifrices, mouthwash, and chewing gum and breathe fresheners.
- Toothache plant is sometimes called the “eyeball plant” because the flowers look like eyeballs.
- Plant is an ingredient in pesticides and is effective in killing mosquitoes.
References:
https://davesgarden.com/guides/pf/go/997/
http://www.hear.org/pier/species/acmella_oleracea.htm
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/gcc-142218
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acmella_oleracea
https://www.mskcc.org/cancer-care/integrative-medicine/herbs/spilanthes-acmella-jambu
Comments
comments