| Chai Hu Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Chai Hu |
| Scientific Name: | Bupleurum chinense |
| Origin | East Asia |
| Shapes | Small, cylindrical |
| Taste | Bitter (Root) |
| Name | Chai Hu |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Bupleurum chinense |
| Native | East Asia |
| Common/English Name | Chai hu, Thorowax root, Hare’s ear root, saiko |
| Name in Other Languages | English: Chinese thoroughwa, Bupleurum, Hare’s-ear; Swedish: inesisk harört; |
| Plant Growth Habit | Perennial herb |
| Soil | Well-drained |
| Plant Size | 39 inches (1 m) tall |
| Root | Bright yellow |
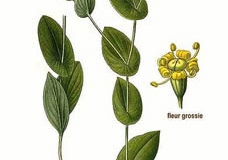
| Leaf | Long sickle-shaped, broad linear to lanceolate |
| Flower | Greenish-yellow |
| Fruit shape & size | Small, cylindrical |
| Root Taste | Bitter |
History and folklore
Called thorowax root, chai hu (China), saiko (Japan), segl-hareøre (Danish) and hare’s ear root (UK), this plant is commonly used in Chinese herbal medicine in combinations. Used since the first century BC for fever, pain, dizziness, debility, and emotional instability. Also a primary part of Japanese (Kampo) medicine today and a common medicine for insomnia in Taiwan.
Plant description
Basal leaves are lanceolate, upper lamina broad and lower narrowed into petiole. Fruit is oblong and 3-4 mm long. The herb has broad linear to lanceolate shaped leaves that are arranged in an alternative array along the stem. An elliptical or flat shape indicates the seed capsule that form on the herb following floral bloom. Traditionally it is used as herbal tonic for improving functioning of liver. It strengthens the functions of digestive tract.
Health Benefits of Chai Hu
1. Liver detoxification
Liver is the largest internal organ in the body which is responsible for various tasks such as neutralizing toxins. Liver forms bile that assists body in absorbing and utilizing fats and fat soluble vitamins properly. The environmental facts which toll on the liver are eating processed foods, drinking alcohol and taking certain medications and pollution. It is used for liver detoxification and improves overall health of liver.
2. Treats Cirrhosis and Liver Cancer
Cirrhosis is a slowly progressing liver disease in which healthy liver tissue is replaced with scar tissue which blocks blood and flow of bile through liver and prevents proper functioning. Cirrhosis is caused due to excessive alcohol consumption and chronic infection with hepatitis C virus. The severeness of disease causes makes it fatal.
3. Supports Adrenal Gland Function
Chai Hu is used with licorice and panax ginseng to aid and also stimulate adrenal gland function. It is helpful for patients having history of long term use of corticosteroid drugs which takes a major toll on adrenal health. It aids adrenal glands and helps harmonize body and improve energy levels by combatting adrenal insufficiency.
4. Relief from Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a disorder in which nerve cell activity in the brain is disturbed resulting seizures. Chai Hu is included in two similar Chinese formulas: Sho-saiko-to and Saiko-keishi-to. These formulas include cassia bark, peony root, ginger root, pinellia root, Asian ginseng root, jujube fruit, Asian skullcap root and licorice root. Trials have shown that both herbal formulas provide relief to epilepsy patients.
5. Combat Ovarian Cancer
The study evaluated apoptotic, anticancer and antioxidant properties of Chai Hu root extract which impressively induce strong and dose dependent cancer killing effects. The extract has anticancer effects which fosters programmed cell death of cancer cells, DNA fragmentation and disruption of energy metabolism of cancer cells. It combats ovarian and liver cancer.
6. Treats Depression
These days, it has become common to take mood stabilizing drugs for depression or anxiety. But the drugs have various side effects. The herbal formula Chai hu shu gan san, is a herbal formula which includes Chai Hu for stagnation of liver qi. It is effective for treating depression which occurs at the time of premenstrual syndrome and menopause.
What scientists say
In humans: Initial pilot studies, in combination with cinnamon and ginger, showed chai hu clinically improved mood in 90 depressed insomniac females, and lowered measures of inflammation. Widely studied in several universities in Japan (such as the Faculty of Medicine, Miyazaki University) in combination with six other medicinal plants that make up the Japanese medicine yokukansan, it clinically improves behavioral symptoms such as irritability, anxiety, apathy, delusions, hallucinations, and psychosis (in autism-related disorders), in schizophrenia (controlled study), Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, vascular and Lewy body dementia.
In the lab: Extracts and saikosaponins are antidepressant, sedative and antiepileptic in several lab models. Saikosaponins stop the stimulatory actions of caffeine and methamphetamine. Affects reward (dopamine and noradrenaline) signals.
Key ingredients: Saikosides/saikosaponins (triterpene saponins) show sedative effects in the lab. Also contains bioactive bupleurumol, flavonoids, and coumarins. Essential oil from the root contains 30 percent hexanal (also in olives and pears), the aroma of freshly cut grass.
How to take it
In China, the ground dried root of chai hu is used at the daily dose of 3 to 9 g by decoction. The root is cooked in boiling water (decoction 15 g in 750 ml) to make tea or soup 250 ml 3 times daily.
Safety
May increase effects of central nervous system (CNS) depressants (sedatives and tranquilizers). Large doses produce drowsiness and may increase bowel movements. Overdose causes nausea and vomiting and liver damage. Caution: one related species is toxic (Bupleurum longiradiatum).
Medicinal uses
- It lowers liver, kidney and upper respiratory tract inflammation.
- It boosts natural defense system of the body.
- It lowers depression and anxiety by inhibiting stress hormones that influence mood.
- It alleviates dizziness, flank pain, irritability, indigestion, chest pain, nausea, emotional instability, menstrual problems and bloating.
- Take it internally for malaria, uterine, blackwater fever and rectal prolapse, sluggish liver, haemorrhoids, abdominal bloating etc.
Side effects
- It causes side effects such as intestinal gas, increased bowel movements and drowsiness.
- When combined with other herbs, it causes serious lung and breathing problems.
- People with bleeding disorder, autoimmune disease and diabetes should avoid this herb.
- People having surgery should stop taking this herb before two weeks as it could increase the chances of bleeding.
- It might lower the effectiveness of immunosuppressant drugs.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=29604#null
https://draxe.com/nutrition/bupleurum/
https://www.anniesremedy.com/bupleurum-chinense-bupleurum.php
https://www.acupuncturetoday.com/herbcentral/bupleurum.php
https://herbpathy.com/Uses-and-Benefits-of-Bupleurum-Cid2942