A saturated triglyceride, also called a saturated fat, is a triglyceride in which most of the fatty acids are saturated. Saturated fatty acids (SFA) contain carbon atoms linked by single bonds and hydrogen on all available arms; they have a relatively high melting point and tend to be solid at room temperature. SFA are obtained from animal storage fats and their products, e.g. meat fat, lard, milk, butter, cheese, and cream. Fats from plant origin tend to be unsaturated with the exception of coconut oil and palm oil. Some manufactured margarines and spreads contain significant amounts of SFA. Plasma low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, and 6 plasma cholesterol, tends to be raised by SFA. High intakes of SFA are associated with atherogenesis and cardiovascular disease. However WHO have recommended lowering intake of saturated fat for enhancing overall health and lowering the chances of cardiovascular diseases. Various articles reviewed that diet with low saturated fat lowers the chances of cardiovascular diseases, diabetes and death.
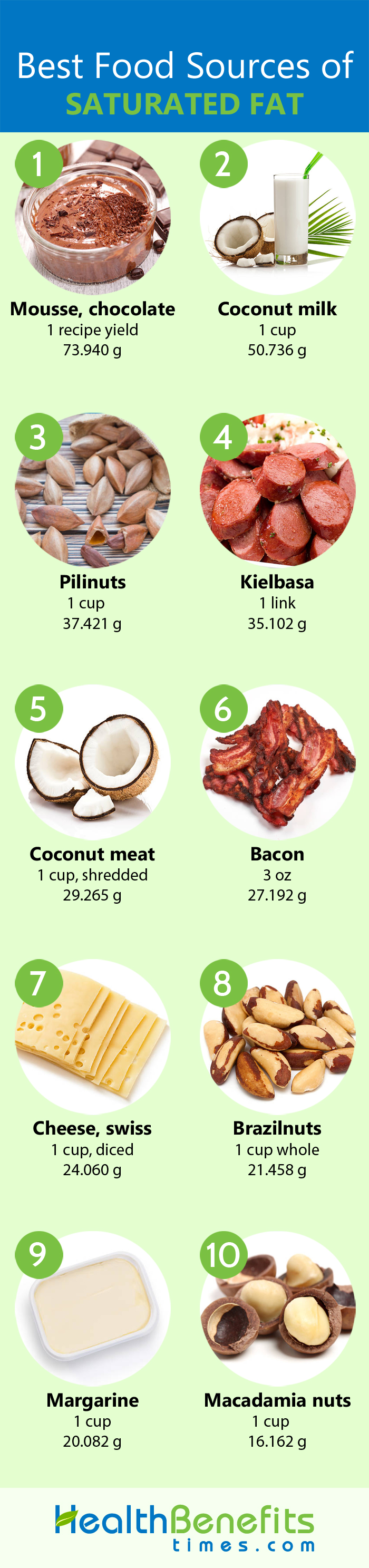
Dietary Sources of Saturated Fat
| Food name | Weight (g) | Saturated Fat (g) |
| Chocolate mousse | 808 | 73.940 |
| Coconut milk | 240 | 50.736 |
| Pilinuts | 120 | 37.421 |
| Kielbasa | 370 | 35.102 |
| Coconut | 93 | 29.265 |
| Bacon | 85 | 27.192 |
| Fontina cheese | 132 | 25.339 |
| Muenster cheese | 132 | 25.229 |
| Swiss cheese | 132 | 24.060 |
| Brazilnuts | 133 | 21.458 |
| Margarine | 232 | 20.082 |
| Feta cheese | 150 | 19.950 |
| Macadamia nuts | 134 | 16.162 |
| Ice cream | 148 | 15.358 |
| Mozzarella cheese | 228 | 15.146 |
| Croissant | 171 | 14.265 |
| Salami | 113 | 13.436 |
| Blood sausage | 100 | 13.400 |
| Cashew nuts | 137 | 12.545 |
| Peanuts | 144 | 11.367 |
Health Benefits of Saturated Fats
Now let us take a view on health benefits offered by saturated fats:
- Promote cardiovascular health
Saturated fat has a crucial role in maintaining cardiovascular health. With an addition of saturated fat, it lowers lipoprotein levels which correlate with chances of heart disease. Research concluded that women diet with consuming greatest percentage of total fat in diet as saturated fat loses most weight.
- Strong bones
Saturated fat is demanded for calcium for effectively incorporated into bone. The foremost research experts in dietary fats and human health show that 50 percent of fats in diet as saturated fats.
- Liver health
Saturated fat protects liver from medications and alcohol including acetaminophen and other drugs which are used commonly for arthritis and pain.
- Lung health
The airspaces of lungs have to be coated with thin layer of lung surfactant for proper functioning. Lung surfactant has fat content of 100 percent saturated fatty acids. Substitute of these critical fats by other types of fat makes faulty surfactant and causes breathing difficulties.
- Brain health
Brain comprises of cholesterol and fat. Fatty acids in brain are saturated. The diet rich in healthy saturated fats feeds brain its raw materials which are required to function optimally.
- Nerve signals
Saturated fats are available in lard, butter, palm oil and coconut oil which are required for direct function such as signaling messengers which influence metabolism including critical jobs as appropriate release of insulin.
- Strengthen immunity
Saturated fats are available in coconut oil and butter which plays a crucial role in immune health. Insufficient saturated fatty acids in white blood cells hampers its ability to recognize and destroy foreign invaders such as bacteria, viruses and fungi.
- Maintain cholesterol balance
Saturated fats promote cholesterol and triglyceride levels. The study shows that triglyceride and cholesterol levels found in blood after 3 different high fat meals varied according to chain length of fatty acids in meals. High level of triglycerides with stearic acid, an 18-carbon chain length fatty acid which is common in cocoa butter and animal fat. Palmitic acid having 16 carbons found in high concentrations in palm oil resulted in highest post meal triglyceride levels. Diet with myristic and lauric acid found in palm and coconut oil with 14- and 12-carbon chains respectively formed smallest rise in triglycerides. Research shows that high density lipoprotein levels are good form of cholesterol which promoted more from shorter chain fatty acid meals.
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Saturated_fat
https://healthyeating.sfgate.com/health-benefits-saturated-fats-7131.html
