 Docosahexaenoic acid is an omega-3 fatty acid which is a primary structural component of human brain, skin, cerebral cortex and retina. It is named as 22:6(n-3). It has 22 carbons and 6 double bonds. It can be synthesized from alpha-linolenic acid or obtained directly from maternal milk (breast milk), fish oil, or algae oil. Its trivial name is cervonic acid and systematic name is all-cis-docosa-4,7,10,13,16,19-hexa-enoic acid. Commercially, DHA is manufactured from microalgae: Crypthecodinium cohnii and another of genus Schizochytrium. DHA manufactured with the use of microalgae is vegetarian. In strict herbivores, DHA is produced internally from α-linolenic acid which is a shorter omega-3 fatty acid formed by plants while carnivores and omnivores obtain DHA from diet.
Docosahexaenoic acid is an omega-3 fatty acid which is a primary structural component of human brain, skin, cerebral cortex and retina. It is named as 22:6(n-3). It has 22 carbons and 6 double bonds. It can be synthesized from alpha-linolenic acid or obtained directly from maternal milk (breast milk), fish oil, or algae oil. Its trivial name is cervonic acid and systematic name is all-cis-docosa-4,7,10,13,16,19-hexa-enoic acid. Commercially, DHA is manufactured from microalgae: Crypthecodinium cohnii and another of genus Schizochytrium. DHA manufactured with the use of microalgae is vegetarian. In strict herbivores, DHA is produced internally from α-linolenic acid which is a shorter omega-3 fatty acid formed by plants while carnivores and omnivores obtain DHA from diet.
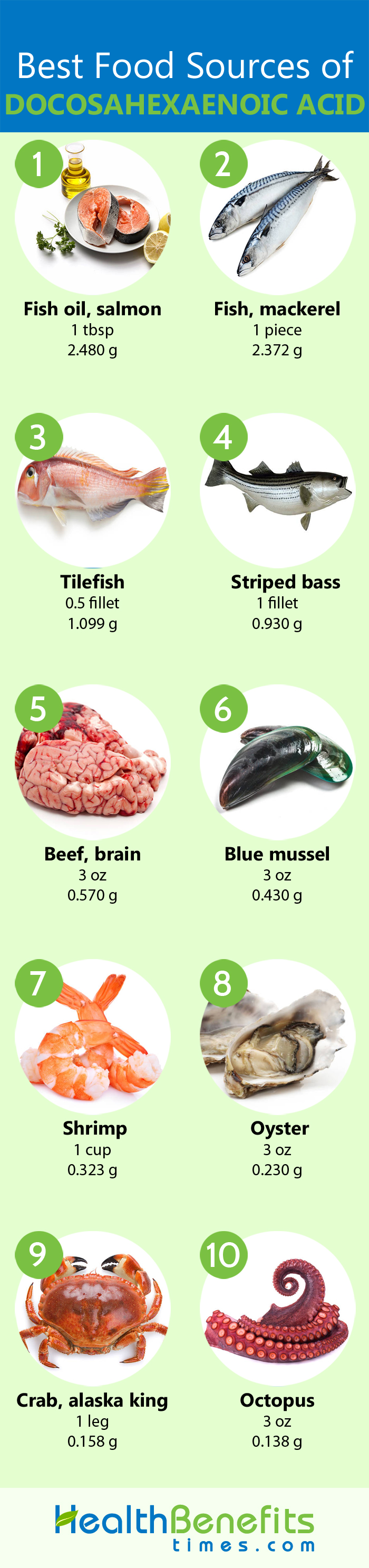
Food Sources
| Food name | Weight (g) | Docosahexaenoic acid (g) |
| Salmon oil | 13.6 | 2.480 |
| Mackerel fish | 80 | 2.372 |
| Sardine oil | 13.6 | 1.449 |
| Tilefish | 150 | 1.099 |
| Striped bass fish | 124 | 0.930 |
| Sablefish | 85 | 0.782 |
| Swordfish | 85 | 0.656 |
| Herring oil | 13.6 | 0.572 |
| Beef brain | 85 | 0.570 |
| Cod liver oil | 4.5 | 0.494 |
| Pompano fish | 88 | 0.444 |
| Blue mussel | 85 | 0.430 |
| Shrimp | 128 | 0.323 |
| Fish broth | 244 | 0.246 |
| Oyster | 85 | 0.230 |
| Cisco fish | 28.35 | 0.174 |
| Crab | 134 | 0.158 |
| Jellyfish | 58 | 0.145 |
| Octopus | 85 | 0.138 |
| Striped mullet | 93 | 0.138 |
Health Benefits of is Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
- Development of Brain
DHA is crucial for brain function and brain tissue growth especially at the time of infancy and development. It needs to assemble in central nervous system for eyes and brain in order to form normally.
During third trimester of pregnancy, intake of DHA determines baby’s levels with tremendous accumulation occurring in brain during first few months of life. It is found in gray matter of brain and frontal lobes are dependent on DHA during development. These brain parts are accountable for processing information, emotions and memories. It is necessary for sustained attention, problem solving, planning and social, emotional or behavioral development.
In animals, low DHA in developing brain results to low amount of new nerve cells and change nerve function. It also hinders eyesight and learning. In humans, deficiency of DHA in early life is associated with ADHD, learning disabilities, aggressive hostility and various other disorders. Studies have associated low levels of DHA in mother to increased chances of poor visual and neural development in child. Study shows that babies of mothers with intake of 200 mg per day from 24th week of pregnancy till delivery had improvement in vision as well as problem solving.
- Vision health
DHA is a vital membrane component in eye. It activates protein known as rhodopsin, a membrane protein in rods of eye. Rhodopsin supports brain to receive images by changing membrane permeability, thickness and fluidity and other properties inside eye. Deficiency of DHA causes vision problems in children. Generally, baby formulas are fortified with it that helps to prevent vision impairment in babies.
- Heart health
Generally omega-3 fatty acids are associated to lowering chances of heart disease. Low levels are related with increasing chances of heart diseases and death and some studies have shown that omega-3s could reduce risk. Its intake could promote heart diseases including blood triglycerides, blood pressure, cholesterol levels and endothelial function.
- ADHD improvement
ADHD known as Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder is characterized by difficulty concentrating that generally starts in childhood and continues to adulthood. Being main omega-3 fat in brain, DHA promotes blood flow during mental tasks. Research has shown low blood levels of DHA in children and adults with ADHD.
- Combat inflammation
DHA possess anti-inflammatory properties. Increasing intake of DHA balances excess inflammatory omega-6 fats which are typical of Western diet rich in soybean and corn oil. Its anti-inflammatory properties lowers the chances of chronic diseases which are common with age such as gum and heart disease and improve autoimmune conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis that causes joint pain.
- Muscle health
Strenuous exercise triggers muscle soreness and inflammation. DHA with EPA lowers muscle soreness and limitations in range of motion after exercise due to its anti-inflammatory properties. A study conducted on 27 women taking 3000 mg of DHA regularly for a week had 23% less muscle soreness after doing bicep curls in comparison to placebo group.
- Prevent cancer
Chronic inflammation is the major cause for cancer. High intake of omega-3 fats such as DHA is associated to lowering the chances of various cancers including pancreatic, colorectal, and prostate and breast cancer. DHA could lower the chances of cancer with its anti-inflammatory effects. Cell studies have shown that it could inhibit the chances of cell growth. Study shows that DHA could promote efficacy of anticancer drugs and combat cancer cells but further research is still required.
- Promote circulation
DHA assist proper flow of blood and circulation and promotes endothelial function i.e. ability of blood vessels to dilate. DHA lowers diastolic blood pressure and EPA lowers systolic blood pressure. Elevated systolic blood pressure is the contributor to heart disease than diastolic pressure.
- Reproductive health
About 50% of infertility cases are due to factors in reproductive health in men and dietary fat intake has shown to affect sperm health. Low DHA is the most cause low quality sperm and frequently found in men with infertility and subfertility problems. Adequate amounts DHA support both vitality and motility of sperm which impacts fertility.
What Dose of DHA Do You Need?
Though Reference Daily Intake for DHA but it is recommended to consume 200 to 500 mg of DHA per day. It could be obtained from fish, supplements or both. FDA has advised to limit total EPA and EPA intake to 3000 mg daily from all sources and only 2000 mg from supplements. In some studies, doses used are higher and it is claimed that 5000 mg of EPA plus DHA regularly in supplements are found to be safe.
Precautions and Possible Side Effects
- People should consult with a doctor before taking DHA supplements.
- People taking blood thinning drug or with planned surgery should avoid fish oil supplements.
- It may cause other potential side effects such as burping and fishy taste in mouth.
- Highly-purified supplements and freezing capsules could minimize these side effects.
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Docosahexaenoic_acid
