| Rehmannia Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Rehmannia |
| Scientific Name: | Rehmannia glutinosa |
| Origin | Northern and northeastern China, particularly in Hunan province |
| Shapes | Capsule ovoid to narrowly ovoid, 1-1.5 cm long |
| Taste | Sweet, Bitter |
| Health benefits | Cure Cancer, Kidney Function, Diabetes, Bone Loss, Allergies and Asthma, Brain health, Fatigue & Endurance, Women’s health, Skin Health |
| Name | Rehmannia |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Rehmannia glutinosa |
| Native | Northern and northeastern China, particularly in Hunan province |
| Common Names | Chinese foxglove, Chinese rehmanniae Radix, Chinese RR, Di Huang, Gun-Ji-Whang, Japanese Rehmanniae Radix, Shu Di Huang, Sook-Ji-Whang and To-Byun |
| Name in Other Languages | Chinese: Di huang, SHu Di Huang English: Chinese-foxglove, Rehmannia Finnish: Pikkusoilio German: China-Fingerhut, Chinesischer Fingerhut, Klebriger Chinafingerhut Japanese: Akayajiou (アカヤジオウ) Korean: Jihwang Persian: رهمانیا گلاتنوسا Thai: Koṭ̄h k̄hī̂mæw (โกฐขี้แมว) Vietnamese: Địa hoàng |
| Plant Growth Habit | Small, hairy, rhizomatous, rosette-forming, herbaceous perennial plant |
| Growing Climates | Well-drained stony ground along roadsides, in woods, mountain slopes, trail sides, hillside, field ridge and roadside |
| Plant Size | About 0.3 to 0.6 m tall |
| Root | Thick and reddish yellow |
| Stem | Erect, simple or branched from base |
| Leaf | Basal leaves usually rosulate. Stem leaves gradually or abruptly decreasing in size or reduced to bracts upward; leaf blade ovate to narrowly elliptic |
| Flowering season | April to June |
| Flower | Flowers axillary and solitary or in terminal racemes, pedicellate. Bracteoles present or absent. Calyx 5(-7)-lobed. |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Capsule ovoid to narrowly ovoid, 1-1.5 cm long |
| Plant Parts Used | Root (Dried, Fresh or Prepared) |
| Taste | Sweet, Bitter |
| Season | May to July |
| Health Benefits |
|
Plant Description
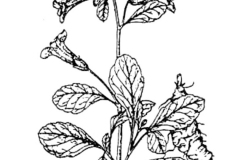
Rehmannia is a small, hairy, rhizomatous, rosette-forming, herbaceous perennial plant that normally grows about 0.3 to 0.6 m tall and is covered with long, soft, gray-white, glandular hairs over the whole plant. The plant is found growing in well-drained stony ground along roadsides, in woods, mountain slopes, trail sides, hillside and field ridge. Root is thick and reddish yellow. The fresh and dried roots and rhizomes have a soft texture, with deep longitudinal wrinkles on the external surface and a darker central cortex. Stem is erect, simple or branched from base. Basal leaves are usually rosulate. Stem leaves gradually or abruptly decreasing in size or reduced to bracts upward. Leaf blade is ovate to narrowly elliptic, 2-13 cm long and 1-6 cm wide, base tapering, margin irregularly crenate or obtusely serrate to toothed.
Flowers
Inflorescences are sometimes scapose. Flowers are axillary and solitary or in terminal racemes, pedicellate. Bracteoles may be present or absent. Calyx is 5(-7)-lobed. Corolla is purple-red or yellow, tubular; tube slightly curved or straight, dorsi-ventrally compressed, with 2 plaits from tube base to throat; limb 2-lipped, 5-lobed. Stamens are 4, didynamous, rarely 5 and 1 smaller than other 4, included; anthers coherent in pairs, locules fertile. Ovary base with a disc, 2-loculed, rarely 1-loculed; ovules numerous. Stigma 2-lamellate. Flowering normally takes place from April to June.
Fruits
Fertile flowers are followed by many seeded, ovoid to narrowly ovoid, 1-1.5 cm long capsules that consist of nearly 300–400 seeds. Fruits start maturing from May– early June. The plant part for medicinal use is the root tuber
History
Rehmannia glutinosa has been considered a panacea in traditional Chinese medicine, primarily in combination with other herbs. Dried Rehmannia rhizome is reputed to “nourish the yin” and remove heat from the blood, and is used as a tonic for the liver.
Documented historical uses include treatment of anemia, cancer, constipation, diabetes, fatigue, bacterial and fungal infections, hypertension, insomnia, tinnitus, inflammatory conditions, burns, impotence and osteoporosis.
Health benefits of Rehmannia
Rehmannia root consists of wonderful amount of Vitamin A, B, C, amino acids, and rehmaglitin, all of which have strong anti-inflammatory and anti fungal properties. This root prevents depletion of glycogen for hypoglycemia. It has a rich, starchy and sweet content that makes it effective as a cloying agent, which makes it good for improving liver function and digestion. Listed below are some of the popular health benefits of rehmannia
1. Cure Cancer
Rehmannia helps to prevents liver and lung cancer cells from growing and even kills them. Rehmannia activate cancer-fighting immune cells. Additionally, it may cause cancer cells to express proteins that slow their growth. Its antioxidants and nutrients reduced the side effects of chemotherapy drugs, while cancer-suppressing components may boost their effect. However, these effects have only been observed in cell studies, which may have no bearing whatever on animal or human bodies. Rehmannia-containing herbal concoctions improved responses to treatment when used in combination with chemotherapy. Rehmannia sugars inhibited the growth of lung and skin tumors.(1), (2), (3), (4), (5), (6), (7), (8), (9)
2. Kidney Function
Several scientific evidences suggest a potential role of Rehmannia in preventing kidney failure in diabetic humans and animals.
Research was done in people with nephrotic syndrome (a type of kidney failure); some people were given Liuwei Dihuang Pills as an add-on to standard treatment. The herbal pills improved kidney function better than the standard treatment alone.(10), (11), (12)
3. Diabetes
Rehmannia, alone or in combination with other herbs, holds promise for diabetes. Its components lowered blood sugar and improved kidney function in diabetic person. Aside from its effects on glucose control, it may also reduce diabetic complications.(13), (14), (15), (16)
4. Bone Loss
Rehmannia, together with other herbs, may prevent bone loss. An analysis of over 100 studies including Rehmannia found that herbal formulations were normally effective, although many of the studies had limitations. Rehmannia, alone or in combination with other herbs, also helped prevent bone loss in menopausal rats and mice.(17), (18), (19), (20)
5. Allergies and Asthma
Despite a long history of use as a remedy for allergies and asthma, there are few studies directly examining how Rehmannia affects these conditions. In rats with allergies, its extracts decreased inflammatory symptoms. Likewise, an extract of this herb lowered inflammation and skin lesions in mice with eczema. (21), (22), (23)
6. Brain health
Rats with dementia given a Rehmannia extract performed better on memory and learning tests. Catalpol also protected brain cells in dishes and helped them survive the effects of bacterial toxins. Its brain-protective effects are perhaps closely linked to its ability to lower the stress response, neutralize free radicals, and affect important brain regions like the hippocampus.(24), (25)
7. Fatigue & Endurance
Rehmannia is often described as an invigorator or a tonic – essentially, a substance to wake you up and make you feel more energized. In research higher doses of Rehmannia sugar extracts improved swimming endurance in mice. This point it’s probable to combat exhaustion and improve exercise endurance. Tonics like Rehmannia may help the body adapt to stress and increased physical demands. However, research on these effects is essential.(26), (27)
8. Women’s health
Rehmannia glutinosa has also been used traditionally to treat the various symptoms related to a woman’s menstrual cycle. According to traditional use, the herb can help relieve many of the symptoms linked to menstruation including pain and fatigue.
9. Skin Health
Rehmannia glutinosa is often applied topically to deal with dry and itchy skin and common inflammatory conditions like eczema. According to research, the herb has excellent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties that make it an ideal treatment for various skin disorders.
Traditional uses and benefits of Rehmannia
- This plant is commonly used in Chinese herbalism, where it is one of the most popular tonic herbs and is considered to be one of the 50 fundamental herbs.
- Root is the main part used and it can be prepared in four different ways – charcoaled, prepared when it is called Shu Di Huang and fresh or dried when it is called Sheng Di Huang.
- Roots are antibacterial, antiseptic, cardiac, diuretic, febrifuge, hemostatic, hypoglycemic and tonic.
- They are used in the treatment of a wide range of ailments, including anemia, cancer, bleeding, constipation, coughs, fever and premature ejaculation.
- Charcoaled root is used to stop bleeding and tonify the spleen and stomach.
- Fresh root is used to treat thirst, the rash of infectious diseases and bleeding due to pathological heat.
- Dried root is used to treat bleeding due to blood deficiency and to nourish the vital essence.
- Prepared root is used to treat dizziness and palpitations due to anemia or blood deficiency, chronic tidal fever, night sweats, dry mouth, lumbago and nocturnal emissions.
- Root is an ingredient of ‘Four Things Soup’, the most widely used woman’s tonic in China.
- Leaves are bruised and used in the treatment of scaly eczema or psoriasis.
- Rehmannia has traditionally been used as an emmenogogue.
- Cured root is used as an immuno-suppressive agent in rheumatoid arthritis.
- It is also used to help women in pain due to cramps during Menstruation.
- It increases the life expectancy of a person and delays the process of aging.
Ayurvedic Health benefits of Rehmannia
- Endometriosis: Make a decoction of dried Rehmannia root and drink it 2 times in a day.
- Strangury: Make a decoction of Rehmannia root, Licorice, Virginia Snakeroot. Have it two times a day.
- Night Sweat: Take equal quantity of Rehmannia and Anemarrhena. Grind them together. Have 1/4 teaspoon with lukewarm water thrice a day.
- Night Sweat: Take equal quantity of Rehmannia, Cornus Florida, White Peony, Yam Rhizome, Hoelen, Water Plantain, Anemarrhena and Phellodendron Amurense. Powder all ingredients together. Have one teaspoon with milk at night.
- Reproductive Problems of Males: Ginseng Korean, Dong Quai, Dodder, Cinnamon, Chinese Licorice, Rehmannia, Atractylodes Macrocephala, Black Musli, Astragalus, Hoelen, Psoralea, Dipsacus Fullonum, Morinda Officinalis, Cynomorium Songaricum, Horny Goat Weed, Mondo Grass, Chinese Raspberry, Achyranthes Aspera, Fenugreek, Cistanche Deserticola, Goji Berry and Paeonia Suffruticosa in conjunction are beneficial for Reproductive Problems of Males and act as a powerful Kidney tonic. or You may buy the formula, containing the above mentioned Herbs. Capsule form is readily available. Consume 2 capsules per day.
- Liver and Kidney Tonic: Chinese Knotweed, Dong Quai, Polygonatum, Rehmannia, Ligusticum Wallichii, Angelica Dahurica, Allspice, Clove and Citron in conjunction are beneficial for Liver and Kidney nourishment. OR You may buy the formula, containing the above mentioned Herbs. Capsule form is readily available. Consume 1 capsule per day.
- Sexual Health: Morinda Officinalis, Dong Quai, Eucommia, Aconitum Carmichaelii, Goji Berry, Garlic Chives, Ginseng Korean, Cinnamon, Yam Rhizome, Cornus Officinalis, Cnidium, Rehmannia, Cynomorium Songaricum, Cuscuta Chinensis and Horny Goat Weed in conjunction are beneficial for male and female Sexual energy. You may buy the formula, containing the above mentioned Herbs. Capsule form is readily available. Consume 1 capsule 3 times a day for one month.
- Reproductive Problems of Males: Ginseng Korean, Astragalus, Dong Quai, Rehmannia, Cuscuta Chinensis, Goji Berry, Fennel, Zanthoxylum Piperitum, Morinda Officinalis, Cornus Officinalis, Polyporus Umbellatus, Psoralea, Achyranthes Aspera, Yam Rhizome, Horny Goat Weed, Eucommia, Cinnamon, Paeonia Suffruticosa, Raspberry, Chinese Knotweed, Anemarrhena, Atractylodes Macrocephala, Water Plantain, Senega, White Peony, Anemone Chinensis and Honey in conjunction are beneficial for Reproductive Problems of Males and act as a powerful kidney tonic. You may buy the formula, containing the above mentioned Herbs. Capsule form is readily available. Consume 1 capsule 3 times a day.
Precautions
- Mild effects possible when taken for the first time including: loose stools, abdominal pain, dizziness and palpitations.
- It can be used only as part of an herbal formula.
- Minor and transient adverse reactions have been reported and include GI reactions (e.g., diarrhea, abdominal pain), edema, heart palpitations, fatigue, and vertigo.
- Use with caution in individuals with a history of bleeding, hemostatic disorders, or drug-related hemostatic problems.
- Use with caution in individuals taking anticoagulant medications, including warfarin, aspirin, aspirin-containing products, NSAIDs, or antiplatelet agents (e.g., ticlopidine, clopidogrel, dipyridamole).
- Discontinue use prior to dental or surgical procedures (generally at least 14 days before).
- Use with caution if taking anti-hypertensive medications.
- Use with caution in individuals with diabetes or those predisposed to hypoglycemia.
- Blood sugar should be closely monitored, and the dosage of hypoglycemic medications may require adjustment.
- Avoid use during Pregnancy and Breastfeeding.
- Rehmannia may affect blood sugar levels. It is recommended that you consult your healthcare practitioner if you have diabetes before consuming this herb.
- Not recommended for people who have liver disease or pre-existing digestive or immune issues.
- Young children should not use rehmannia glutinosa.
References:
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Rehmannia+glutinosa
http://www.missouribotanicalgarden.org/PlantFinder/PlantFinderDetails.aspx?taxonid=299085&isprofile=0&s_cid=queue-18
https://www.healthline.com/health/rehmannia-traditional-chinese-medicine#1
https://www.drugs.com/npp/chinese-foxglove.html
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rehmannia_glutinosa
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?30911
http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=2&taxon_id=200021237
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl/record/kew-2527243
https://somepomed.org/articulos/contents/mobipreview.htm?26/30/27116
http://temperate.theferns.info/plant/Rehmannia+glutinosa
http://www.naturalmedicinalherbs.net/herbs/r/rehmannia-glutinosa=chinese-foxglove.php
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/110300